Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras
LGBT pride event From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
LGBT pride event From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras or Sydney Mardi Gras is an event in Sydney, New South Wales attended by hundreds of thousands of people from around Australia and overseas. One of the largest LGBT festivals in the world, Mardi Gras is the largest Pride event in Oceania.[lower-alpha 1] It includes a variety of events such as the Sydney Mardi Gras Parade and Party, Bondi Beach Drag Races, Harbour Party, the academic discussion panel Queer Thinking, Mardi Gras Film Festival, as well as Fair Day, which attracts 70,000 people to Victoria Park, Sydney.
| Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras | |
|---|---|
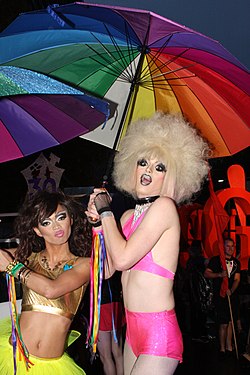 Participants in 2012 | |
| Genre | LGBTQ pride parade and festival |
| Begins | Second Thursday in February |
| Ends | First Saturday in March |
| Frequency | Annually |
| Location(s) | Sydney, New South Wales, Australia |
| Years active | 46 |
| Inaugurated | 24 June 1978 |
| Most recent | 2 March 2024 |
| Participants | 16,500 (Parade 2019)[1] 13,626 (Party 2019)[1] |
| Attendance | 500,000 (Parade 2019)[1] 80,000 (Fair Day 2019)[1] |
| Website | www |
The Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras is one of Australia's biggest tourist drawcards,[14] with the parade and dance party attracting many international and domestic tourists. It is New South Wales' second-largest annual event in terms of economic impact,[15] generating an annual income of about A$30 million for the state.
The event grew from gay rights parades held annually since 1978, when numerous participants had been arrested by New South Wales Police Force.[16] The Mardi Gras Parade maintains a political flavour, with many marching groups and floats promoting LGBTQIA+ rights issues or themes.[17] Reflecting changes since the first Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras, participants in the Mardi Gras Parade now include groups of uniformed Australian Defence Force personnel, police officers from New South Wales Police Force, as well as interstate and federal police officers, firefighters and other emergency services personnel from the Australian LGBTQIA+ communities. Marriage equality was a dominant theme in the 2011 Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras Parade with at least 15 floats lobbying for same-sex marriage.[18]
In 2019 Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras submitted a bid to host WorldPride 2023 competing against Montreal, Canada and Houston, Texas. InterPride chose Sydney, Australia to host WorldPride 2023 at their Athens October 2019 Annual General Meeting of three hundred delegate organizations, the first time WorldPride was held in the Southern Hemisphere or Asia Pacific region.[19][20][21]
The Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras or Sydney Mardi Gras is a celebration of LGBTQIA+ history and culture.[22]
The term Mardi Gras derives from the celebration on Mardi (French for "Tuesday") when Gras (French for "fat") is eaten prior to the Christian abstinence period of Lent preceding Easter.[23]
On 24 June 1978 at 10 pm as a night-time celebration following a morning protest march and commemoration of the Stonewall riots[24] organised by the Gay Solidarity Group more than 500 people gathered on Oxford Street, in a planned street "festival" calling for an end to discrimination against homosexuals in employment and housing, an end to police harassment and the repeal of all anti-homosexual laws.[25] The figure rose to around 2,000 as revellers out for the Saturday night at Oxford Street bars and clubs responded to the call "Out of the bars and into the streets!".[26] Although the organisers had obtained permission, this was revoked, and the parade was broken up by the police. After the parade was dispersing in Kings Cross, 53 of the participants were arrested.[27] Although most charges were eventually dropped, The Sydney Morning Herald published the names of those arrested in full, leading to many people being outed to their friends and places of employment, and many of those arrested lost their jobs as homosexuality was a crime in New South Wales (NSW) until 1984.[28] Only two people who were arrested were fined.[29] The rest were released without bail and the charges dismissed. The police response to a legal, local minority protest transformed it into a nationally significant event which stimulated gay rights and law reform campaigns.[26] A documentary, Witches and Faggots, Dykes and Poofters, produced by Digby Duncan in 1980 tells the story of the first Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras.[30][31]
The second Mardi Gras Parade occurred in 1979 despite opposition by gay media, businesses and groups. The 1979 parade, in recognition of the Stonewall Riots and commemorating the riot of the previous year, was attended by 3,000 people. In that same year, the Labor Government of New South Wales, led by Neville Wran, repealed the Summary Offences Act 1988 (NSW) under which the arrests in 1978 were made.[29] The second Mardi Gras had the theme of Power in the Darkness.[29] While there was a large police presence, there were no arrests made.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

In 1980, after the third successful Mardi Gras parade, at community consultations, decisions were made to move the parade to the summer.[25] In 1981, the parade was shifted to February, with the name changed to the "Sydney Gay Mardi Gras".[27] An increasingly large number of people not only participated in the now summertime event, but a crowd of 5,000 came to watch it.[34] 1981's event saw a split develop between lesbian and gays over the inclusion of floats representing businesses. For most of the decade many lesbians excluded themselves from the event.[29] A large post-parade party was held in 1982, which 4,000 people attended. This would continue to become an integral part of the Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras. 1983 saw 44 floats participate with 20,000 onlookers.[29] Footage of the 1984 event appeared in the music video for the Cold Chisel song "Saturday Night". In 1987, an estimated 100,000 people came to watch the parade.[35] The mid-1980s saw considerable pressure placed to the Mardi Gras Committee following media controversy regarding AIDS. Despite calls for the parade and the party to be banned, the 1985 parade went ahead with the theme Fighting for Our Lives. In 1988 the parade was renamed the "Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras" at an Extraordinary General Meeting.[25]
1991 saw the eighth annual Sydney Gay and Lesbian Film festival, a Mardi Gras event, included in a national film festival for the first time. In this year the parade had become the largest ever held in Australia.[35] In 1992, the festival lasted for four weeks, making it the largest gay and lesbian festival in the world.[35] Also in 1992, Fiona Cunningham-Reid filmed a documentary about the history of the Mardi Gras called "Feed Them to the Cannibals!".[36][37] By 1993, the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras Parade had become the largest night time outdoor parade in the world.[35] Mardi Gras' Economic Impact Study found that the total Mardi Gras impact into the Australian economy was around A$38 million.[38] In February 1993 an Umbrella Event of the festival was the play "Nothing Personal" designed by Arthur Dicks. In 1994, Mardi Gras Festival adopted the theme We are Family, a nod to it being International Year of the Family. That year there were 137 floats in the parade with 600,000 spectators.[29] For the first time, the parade was filmed by the ABC TV and shown on Sunday 6 March at 8.30 pm. It won its time slot and earned ABC TV its highest ratings in history.[25] The 1997 parade was covered by Libbi Gorr's current affairs show McFeast on ABC TV.[39]
In 1988, Aboriginal Australian dancers Malcolm Cole (1949-1995) and Rodney Junga-Williams (1962-2011), in collaboration with artist Panos Couros, enacted the story of the First Fleet, with Cole as Captain Cook, and Junga-Williams as Joseph Banks – the first ever Aboriginal float entry in the parade. A boatful of black sailors was pulled by a white man,[40] with this leading float commemorating 218 years after Cook's landing and claim on the land.[41] Cole died of HIV/AIDS, and in 2024 his twin brother Robert recreated his costume in order to march again in the parade to commemorate his life.[42]
Criticism of the Sydney Mardi Gras was perhaps at its strongest during the early years of the AIDS crisis, and flared again when in 1994 the national broadcaster ABC telecast the parade for the first time.[27]
In 1996 there was criticism over the inclusion of bisexuals and heterosexuals as members of the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras. It was claimed that the subsequent requirement for those people to correctly answer specific questions, created two classes of membership – namely (1) gays, lesbians and transgender people and (2) bisexuals and heterosexuals.[43]
In 1997 a small group of people who were part of the 1978 events contributed to planning the commemoration of the 20th anniversary of the Sydney Mardi Gras parade in 1998. This group became known as the 78ers and has led each year's Mardi Gras parade since 1998.[44]

The 2001 Parade was broadcast on Network Ten and had a theme of gay and lesbian parenting.[39] The 2002 event saw a loss of A$400,000.[47] In August the organising company was bankrupt.[48] In 2003, the festival organisers responded to claims that the event was becoming too commercialised by implementing a scaled-down, grassroots approach.[49] The 2009 performance figures indicated about 9,500 participants and 134 floats were part of the parade, making it the largest ever.[50] Up to 300,000 spectators from Australia and overseas turned out in 2011 for the celebrations.[51]
Mardi Gras, at different times, has attracted criticism from its own members, LGBTQIA+ communities, and a variety of religious and political groups. Some argue Mardi Gras is inherently subversive to traditional Christian, Islamic and Jewish values.[29] Each year the event is held, Fred Nile, a former member of the New South Wales Legislative Council and a former minister of the Uniting Church in Australia, leads a prayer for rain on the event.[52]
In January 2008 Robert Forsyth, the Anglican bishop of South Sydney, condemned Corpus Christi for opening the Mardi Gras because it depicted Judas seducing a gay Jesus as well as Jesus' administration of gay marriage between two apostles. Director Leigh Rowney accepted that it would generate discussion on Homosexuality and Christianity and stated: "I wanted this play in the hands of a Christian person like myself to give it dignity but still open it up to answering questions about Christianity as a faith system." Playwright Terrence McNally, a gay man, received death threats when it was played in the United States.[53]

In early 2011, members of the organisation unanimously voted to include intersex formally into the organisation at the Annual General Meeting and adopt the formal use of the LGBTQIA+ acronym. To allow for greater inclusion of the LGBTQIA+ community it represents (including those identifying as bisexual, transgender, queer, intersex and asexual), on 17 November 2011 the festival and event organisers changed the event name to "Sydney Mardi Gras". On the same date the organisation reverted to its former name, "Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras" (from "New Mardi Gras"),[55] as more than 9,100 participants joined in the 2012 Parade, on 134 floats.[56]
In 2011 Mardi Gras came under fire from LGBTQIA+ communities for removing the words "Gay and Lesbian" from the festival's name.[57] The organisation's board confessed that they did not adequately consult the community in such an important decision. The organisation was also criticised for focusing on the requests of corporate sponsors, and allowing their floats rather than maintaining its original sense of identity.[58] This followed the 2010 season in which the Mardi Gras Parade and Party were held on separate dates for the first time in history.
During the rebranding in 2011, Mardi Gras Chairman Peter Urmson said "I think that whilst we are first and foremost a GLBTQI community organisation, we also are very open to all of our friends that do not necessarily identify within that alphabet soup."[59] Many community members were offended by the change, including former Mardi Gras president Richard Cobden, who said that the group did not have the authority to make such a change, adding "For 20-plus years we have been able to force the mainstream media to call it the 'Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras.' They had to say the words. For a long time they did not want to but we made them. That has been thrown away".[60]
The name of the festival was subsequently restored as the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras.[when?]
In 2013, the New South Wales Police were accused of police brutality after a video shot by a bystander and uploaded to YouTube showed a handcuffed man thrown to the ground twice by an officer.[61][62] The man repeatedly kicked police officers before being handcuffed.[63] By 2014, all charges against the bystander were withdrawn by police and the officer concerned was facing disciplinary proceedings.[64] Disciplinary proceedings against the officer were withdrawn.[65]
On a number of occasions, there have been controversies with, and bans of, the UFO-related Raelians participation in the parade. A Raelian spokesman said the bans were unfair as the Raelians support non-discrimination and have gay and lesbian members.[66][67][68][69]
In 2012 Mardi Gras organisers faced the issue of having a Sydney Polyamorists float in the parade, whilst also promoting same-sex marriage for couples. Particularly, as the 2012 Mardi Gras theme was "universal and infinite love", some polyamorists felt discriminated against.[70] The issue was resolved[71] with a polyamory float, based on the theme, "Queer Polyamory".[72] In the 2014 Mardi Gras there was another float, "Polyamory Sydney 'Birds of a Feather, love together' – the infinite love Nest".[73]
In 2015, some members of the LGBTIQ community argued that the Mardi Gras perpetuates gay stereotypes and excludes other members of the LGBTIQ community.[74]
In 2020, the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras was held just prior to the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia. NSW Health advised there was no evidence of community transmission of the virus at that time.[75] British singer Dua Lipa debuted her single Physical at the event.[76]
In 2021, as a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic the parade, held on 6 March 2021, was relocated to the nearby Sydney Cricket Ground as a paid, ticketed event with 36,000 spectators and was televised live on the Special Broadcasting Service.[77][78]
In 2023, independent senator for Victoria Lidia Thorpe disrupted the parade in an attempt to raise awareness about intractable social issues such as Indigenous rates of incarceration and the role of police in that process.[79]
In 2024, after the alleged murder of Jesse Baird and his partner Luke Davies around 20 February 2024 by serving NSW Police officer Beau Lamarre, the Mardi Gras board decided to ban members of the force from participating in Mardi Gras. Owing to sensitivities in the LGBTQIA+ community and recollections of past poor treatment by NSW Police. However this decision was reversed on 28 February 2024, and it was agreed by both the board and Police Commissioner Karen Webb that the Force could participate, but not in uniform. They would march as a group, without a float.[80][81]
Additionally in 2024, Malcolm Cole's twin brother Robert recreated his 1988 Captain Cook costume, in order to wear it in the parade to commemorate Malcolm's life.[42]
The Australian Queer Archives, City of Sydney Archives, Pride History Group,[citation needed] and the State Library of New South Wales hold an extensive collections of material related to the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras, including oral history interviews, organisational records, personal papers, posters, clippings, and photographs.[82]
| External media | |
|---|---|
| Images | |
| Video | |

The Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras festival culminates in the renowned Sydney Mardi Gras Parade, an LGBTQIA+ rights protest and celebration of sexuality. The parade features more than 12,500 entrants in colourful costumes and elaborate floats, who represent a community group, topical theme or political message. Parade entrants include members of Parents, Families and Friends of Lesbians and Gays, the Australian Defence Force, Amnesty International Australia, Australian Marriage Equality, City of Sydney, Fire & Rescue New South Wales, Taronga Conservation Society and DNA among many others.
Each parade starts with approximately 200 Dykes on Bikes riding up Oxford Street.[84] It is often accompanied by fireworks displays, which are launched from the rooftops of buildings along the parade route. Approximately 300,000 spectators watch the Parade as it snakes 1.7 kilometres (1.1 mi) from the Sydney central business district to Darlinghurst.[18][85]
The parade travels along Oxford Street before turning into Flinders Street and finally into the bus lane that runs parallel to Anzac Parade – to the parade end. These roads and others including some around Hyde Park, are closed to traffic for the duration of the parade and for a few hours after as clean-up operations proceed.
Each year, a Chief of Parade (Grand Marshal), is chosen by the organisation New Mardi Gras as someone who represents the values and spirit of Mardi Gras. This honourable title has previously been awarded to:
The Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras Parade is extensively covered by the media. In 2011, it was broadcast on radio by Joy 94.9 FM Melbourne and 2SER 107.3 FM Sydney. The Parade was also shown live on Foxtel's Arena in its entirety. The Arena broadcast was presented by hosts Louie Spence of Pineapple Dance Studios, Charlotte Dawson, Ruby Rose and Matthew Mitcham. The Parade was also broadcast on radio live by various community radio stations, via the CBAA's Community Radio Network satellite. In 2012, Optus, a corporate sponsor, broadcast a delayed and edited highlights of the parade via www.mardigrastv.org.au. In 2014, SBS TV broadcast delayed and edited coverage of the parade highlights, hosted by Tom Ballard, Patrick Abboud and Heather Peace.[89]
Despite its name, Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras is not held on Mardi Gras (Shrove Tuesday) or indeed, on a Tuesday at all.[90] In recent years, the Mardi Gras Parade has been on the first Saturday of March, with a festival of events going for approximately three weeks preceding it.
The parade running order for 4 March 2017.[91]


The post parade party is one of the largest ongoing party events in the country.[citation needed] Mardi Gras Party attendances at Sydney's Hordern Pavilion / Royal Hall of Industries peaked in 1998 with 27,000 tickets sold.[94] In the years since 17,000 to 20,000 tickets are consistently sold, an increase over the first Parade Ball held in 1980 at the Paddington Town Hall, a BYO event which attracted 700 guests.[95] Although, by the late first decade of the 21st century, ticket sales has begun to fall, with the 2012 post parade party selling out at 15,300 tickets;[56] and ticket sales a little lower again in 2013.[89]
The 2010 party was not held on the night of the parade and was later described by the organisers as human error during scheduling.
Several well known local and international artists have performed at the Party and include:[96]
By 1987 the festival included 35 events.[41] The 1998 festival was estimated to contribute $99 million to the Sydney economy.[48]
Multi-disc Mardi Gras compilation albums were released in 1995,[35] 1997, 2002 and 2003.
The festival's live entertainment includes cabaret, comedy, music and theatre. The Mardi Gras Film Festival showcases international and local gay and lesbian films. There are many literature and arts events, forum and conferences to attend between the many social activities. Individual and team sports have always been a big part of the festival.

In 1979 an 'Alternative Lifestyle Fair' as part of a week of activities around International Gay Solidarity Day. During the early 1980s the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Business Association held an annual Fair Day, which was brought into the Sydney Gay Mardi Gras program in 1985. From 1985 to 1988 the Business Association continued to run the Fair, which was subsequently run by the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras from 1989. The event is the kick off event for the official Mardi Gras season in Victoria Park, Sydney for Sydney's wider LGBTQIA+ communities and their friends and family. Up to 70,000 people routinely turn out to sit on the grass, browse the stalls and catch up with old friends or make some new ones. Fair Day 2011 saw record numbers of attendees. Entertainment came from the Foxtel Main Stage and included a set from Zoe Badwi and Garçon Garçon, and one of the biggest ever "Mr and Mrs Fair Day" competitions.[103] Approximately 250 volunteers assisted with 220 stalls made up of many LGBTQIA+community groups.[103]
In 2017, Mardi Gras Fair Day was held at Camperdown Memorial Rest Park on Sunday 19 February.[104]
| Hall of Fame winners | |
|---|---|
| 1992 | Brian McGahen, Bruce Belcher, David Wilkins, Kimberly O'Sullivan, Lance Gowland, Peter Tully, Ron Muncaster |
| 1993 | Colin Fawcett, Leggs Galore, Robyn Laverack, and Cath Phillips |
| 1994 | Barry Cecchini, Peter Macdonnell, and Bruce Pollack |
| 1995 | Ron Austin, Murray McLachlan, and Bill Whittaker |
| 1996 | Corby Beard, Brent Beadle, Richard Cobden |
| 1997 | Kathy Pavlich and Susan Harben |
| 1998 | Margaret McMann and Stephen Alkins |
| 1999 | Gillian Minervini, Phillipa Playford, Tony Crewes, Rodney Thorpe |
| 2000 | Bill Morley, George Petersen, David McDiarmid. John Marsden |
| 2001 | Brian Hobday, Gary Leeson, Ron Smith |
| 2002 | Dr Richard Liddy, Jade-Snow Kemety, Katrina Marton, Doris Fish, Richard Wherret |
| Source: Hall of Fame & Lifetime Achievement Award Winners[105] | |
The Mardi Gras Awards are presented to organisations and individuals who made an outstanding contribution to Mardi Gras and the gay and lesbian community.[32]
InterPride, at their October 2019 Annual General Meeting of three hundred delegate organizations, held in Athens, Greece chose Sydney, Australia to host WorldPride 2023, the first time WorldPride will be held in the Southern Hemisphere or Asia Pacific region. Sydney received 60% of the vote ahead of the other bid contenders Montreal, Canada (36%) and Houston, Texas (3%).[19][20][21]
WorldPride 2023 coincided with the 50th Anniversary of the first Australian Gay Pride Week, 45th Anniversary of the first Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras and 5th Anniversary of Marriage Equality in Australia. According to the bid document the stated objective of WorldPride Sydney 2023 is to celebrate the diversity of culture and identity in the Asia Pacific region, while shining a light on widespread human rights abuses.[106]
WorldPride Sydney 2023 was held between 16 February and 4 March during Australia's summer and consisted of a 17-day combined 45th Anniversary Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras/WorldPride 2023 Festival.[106] The centrepiece was a three-day LGBTQIA+ Human Rights and Health Conference focusing on LGBTQIA+ people's experiences of violence, torture, abuse, discrimination and persecution in the Asia Pacific region and more broadly. Other stated signature events included:
• Aboriginal Smoking Ceremony and Welcome to Country
• WorldPride Opening Ceremony
• 45th Anniversary Mardi Gras Parade
• 45th Anniversary Mardi Gras Party
• Interpride Reception
• Bondi Beach Party
• Mardi Gras International Arts Festival
• 30th Anniversary Queer Screen Mardi Gras Film Festival
• WorldPride First Nations Gala Concert
• Sissy Ball Grand Final
• WorldPride March
• WorldPride Closing Ceremony


Political support has come from a number of local and federal politicians such as former Australian Democrats Senator Natasha Stott Despoja[108] and current Labor Senator Penny Wong,[109] Members of the House of Representatives Tanya Plibersek[110] and current Prime Minister Anthony Albanese,[111] former Leader of the Opposition and Labor Party Bill Shorten[110] Former Premier Barry O'Farrell[112] as well as the present Lord Mayor of Sydney, Clover Moore.[113] In 2023 Albanese became the first Prime Minister to march in Mardi Gras while in office.[111] In 2024 Chris Minns became the first Premier of New South Wales to march in Mardi Gras.[114]
As Prime Minister, Malcolm Turnbull attended the 2016 Mardi Gras but did not march. There was a movement by some Mardi Gras members to disinvite him in 2017 due to "lack of action" on same-sex marriage and his cuts to the Safe Schools program[115] however the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras board subsequently rejected the move.[116]
Hundreds of thousands of Australians and international guests come out in support of the Parade, with many lining up for a viewing spot from early in the afternoon. By the 7.45 pm Parade kick-off, crowds are usually ten-people deep.[117] Though it has rained on several Mardi Gras parades (notably with heavy downpours prior to, and drizzle during, the parade in 1995, and heavy rainfall during the parade in 2004), this has never stopped the parade.
The Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras is regarded internationally as one of the world's biggest and best LGBTQI marches and festivals, and has been described as an "absolute once-in-a-lifetime must for every travelling gay man".[118] Mardi Gras is featured in the programmes of tour operators which target the gay market.[48]
In the 2000s the Mardi Gras organisation struck financial trouble, and collapsed. This was attributed at the time to poor financial management and a downturn in international tourism following the attack on the World Trade Center in New York City, while another explanation was given as Australia's ongoing public liability crisis, which has seen massive insurance premiums impose a significant burden on community and public events, if not preventing them. As a consequence of the impending collapse of the organisation, there was a groundswell of concern and support within Sydney's LGBTQI communities for the continuation of the work and events of Mardi Gras. A series of crisis meetings culminated in the creation of a reformed organisation "New Mardi Gras" being formed to continue the Parade, the Festival & the Party.[119]
In 2008, it was announced that the Government of New South Wales would provide funding for Mardi Gras as it had become part of the state's Master Events Calendar.[120] Limited funds have also been sourced from the Sleaze Ball party held in Sydney towards the end of the year. Mardi Gras still receives significant public support and the event now receives some limited government funding.
In 2013, a temporary rainbow crossing was created by City of Sydney Council as part of the 35th anniversary celebrations.[121] The rainbow crossing proved popular with tourists and when it was removed as part of a condition with Roads & Maritime Services when the rainbow crossing was built, DIY rainbow crossings, emerged and was picked up by the local and international media.[122] In 2018 the rainbow crossing was reinstated.[123]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.