Cervical sinus
Embryonic structure From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The cervical sinus is a structure formed during embryonic development. It is a deep depression found on each side of the neck. It is formed as the second pharyngeal arch (hyoid arch) grows faster than the other pharyngeal arches, so they become covered. The first pharyngeal arch (mandibular arch) also grows slightly faster. It may fail to obliterate, forming a branchial cleft cyst or fistula, which is prone to infection.
| Cervical sinus | |
|---|---|
 Scheme of the pharyngeal arches
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sinus cervicalis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
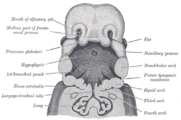
The cervical sinus is bounded in front by the second pharyngeal arch (hyoid arch), and behind by the thoracic wall. The second pharyngeal arch (hyoid arch) grows faster than the other pharyngeal arches, so they become covered. It is ultimately obliterated by the fusion of its walls by the 7th week of gestation.
Clinical significance
Sometimes, the cervical sinus can fail to obliterate and thus remains as a branchial cleft cyst.[citation needed] The second pharyngeal arch may also not grow over the lower pharyngeal arches.[1] This may be found anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.[1] It can also communicate with the skin as an external cervical fistula or with the pharynx as an internal cervical fistula.[citation needed] It is prone to infection. Medical ultrasound may be used to diagnose them.[1]
Additional images
- The head and neck of a human embryo 32 days old, seen from the ventral surface
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.