Barilium
Extinct genus of dinosaurs From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Barilium is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur which was first described as a species of Iguanodon (I. dawsoni) by Richard Lydekker in 1888, the specific epithet honouring the discoverer Charles Dawson, who collected the holotype during the 1880s.[1]
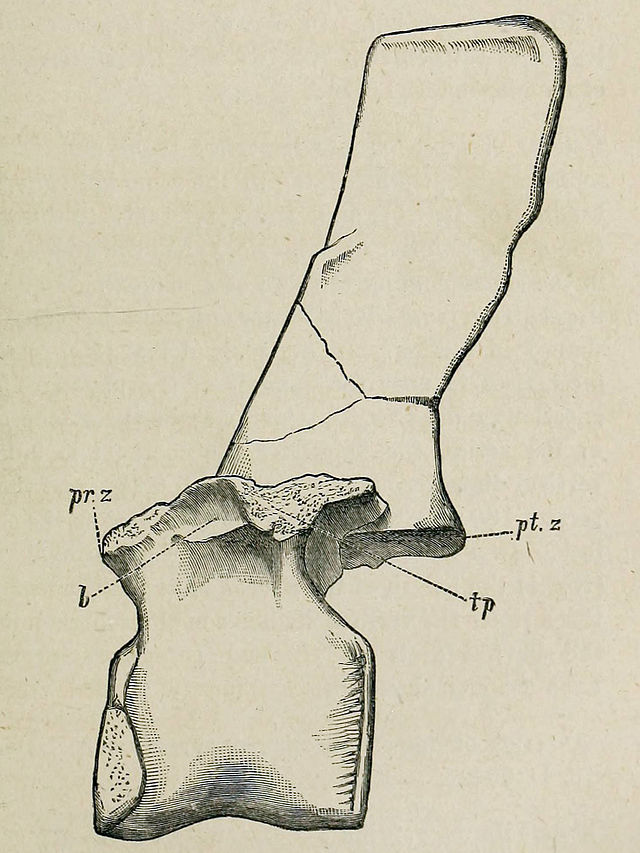
| Barilium Temporal range: Early Cretaceous, | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Pelvis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | †Ornithischia |
| Clade: | †Ornithopoda |
| Clade: | †Styracosterna |
| Genus: | †Barilium Norman, 2010 |
| Species: | †B. dawsoni |
| Binomial name | |
| †Barilium dawsoni (Lydekker, 1888 [originally Iguanodon]) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
In 2010 it was reclassified as a separate genus by David Norman. The generic name Barilium is derived from Greek barys, "heavy", and Latin ilium.[2] Later in 2010, Kenneth Carpenter and Yusuke Ishida independently assigned it to the new genus Torilion,[3] which is thus a junior objective synonym of Barilium. It is known from two partial skeletons found near St Leonards-on-Sea in East Sussex, England,[4] from the middle Valanginian-age Lower Cretaceous Wadhurst Clay.[5] Lydekker based the species on the syntype series BMNH R798, 798a, 803-805, 806, 798b, 802, 802a and 799-801. Norman chose NHMUK R 798 and R802, a dorsal vertebra and a left ilium, as the lectotype.
A contemporary of Hypselospinus (also once thought to be a species of Iguanodon), Barilium was a robust iguanodontian estimated at 8 metres (26 feet) long.[6]
Barilium is separated from Hypselospinus on the basis of vertebral and pelvic characters, size, and build.[6] For example, Barilium was more robust than Hypselospinus, with large Camptosaurus-like vertebrae featuring short neural spines, whereas Hypselospinus is known for its "long, narrow, and steeply inclined neural spines".[7]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
