Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
CD14
Mammalian protein found in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14) is a human protein made mostly by macrophages as part of the innate immune system.[5][6] It helps to detect bacteria in the body by binding lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP).
CD14 exists in two forms, one anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) tail (mCD14), the other a soluble form (sCD14). Soluble CD14 either appears after shedding of mCD14 (48 kDa) or is directly secreted from intracellular vesicles (56 kDa).[7]
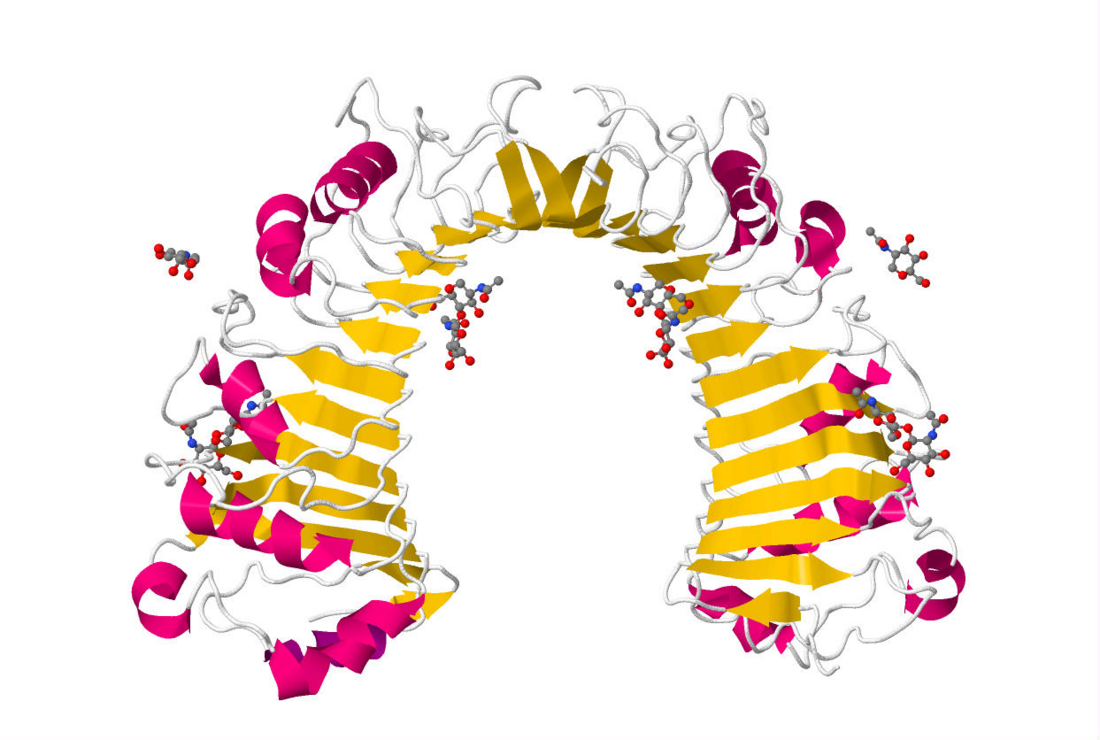
The x-ray crystal structure of human CD14 reveals a monomeric, bent solenoid structure containing a hydrophobic amino-terminal pocket.[8]
CD14 was the first described pattern recognition receptor.
Remove ads
Function
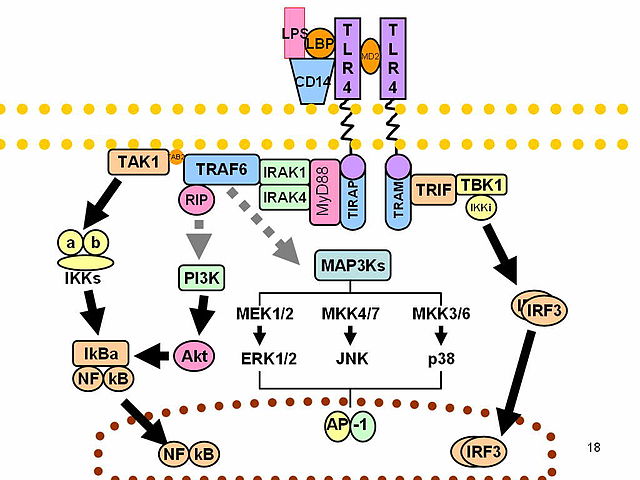
CD14 acts as a co-receptor (along with the Toll-like receptor TLR 4 and MD-2) for the detection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS).[9][10] CD14 can bind LPS only in the presence of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP). Although LPS is considered its main ligand, CD14 also recognizes other pathogen-associated molecular patterns such as lipoteichoic acid.[11] Cluster of differentiation CD14 is a receptor for a very wide range of microbial products including lipopolysaccharide (released from Gram-negative bacteria), peptidoglycans, and lipoteichoic acid (constituents of Gram-positive bacteria).[12]
Remove ads
Tissue distribution
CD14 is expressed mainly by macrophages and (at 10-times lesser extent) by neutrophils. It is also expressed by dendritic cells. The soluble form of the receptor (sCD14) is secreted by the liver and monocytes and is sufficient in low concentrations to confer LPS-responsiveness to cells not expressing CD14. mCD14 and sCD14 are also present on enterocytes.[13] sCD14 is also present in human milk, where it is believed to regulate microbial growth in the infant gut.
Remove ads
Differentiation
CD14+ monocytes can differentiate into a host of different cells, including dendritic cells, a differentiation pathway encouraged by cytokines, including GM-CSF and IL-4.
Interactions
CD14 has been shown to interact with lipopolysaccharide-binding protein.[14][15]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads