Raymond Damadian
American physician and inventor (1936–2022) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Raymond Vahan Damadian (March 16, 1936 – August 3, 2022) was an American physician, medical researcher, and inventor of the first nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) scanning machine.[1][2][3][4]
Raymond Damadian | |
|---|---|
| Born | Raymond Vahan Damadian March 16, 1936 New York City, New York, U.S. |
| Died | August 3, 2022 (aged 86) Woodbury, New York, U.S. |
| Alma mater | |
| Known for | Inventor of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) |
Damadian's research into sodium and potassium in living cells led him to his first experiments with nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which caused him to first propose the MR body scanner in 1969. Damadian discovered that tumors and normal tissue can be distinguished in vivo by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) because of their prolonged relaxation times, both T1 (spin-lattice relaxation) or T2 (spin-spin relaxation). Damadian was the first to perform a full-body scan of a human being in 1977 to diagnose cancer. Damadian invented an apparatus and method to use NMR safely and accurately to scan the human body, a method now well known as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).[5]
Damadian received several prizes. In 2001, the Lemelson-MIT Prize Program bestowed its $100,000 Lifetime Achievement Award on Damadian as "the man who invented the MRI scanner."[6] He went on to collaborate with Wilson Greatbach, one early developer of the implantable pacemaker, to develop an MRI-compatible pacemaker. The Franklin Institute in Philadelphia gave its recognition of Damadian's work on MRI with the Bower Award in Business Leadership.[7] He was also named Knights of Vartan 2003 "Man of the Year".[8] He received a National Medal of Technology in 1988 and was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 1989.[9]
Biography
Summarize
Perspective
Early life
Raymond Vahan Damadian (Armenian: Ռայմոնտ Վահան Տամատեան) was born in New York City, to an Armenian family.[10][11][12] His father Vahan was a photoengraver who had immigrated from what is now Turkey, while his mother Odette (née Yazedjian) was an accountant.[13][12][14] He earned his bachelor's degree in mathematics from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1956, and an M.D. degree from the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City in 1960. He studied the violin at Juilliard for 8 years,[15] and played in Junior Davis Cup tennis competitions.[16][17]
He met his future wife, Donna Terry, while he had a job as a tennis coach. She invited him to the 1957 Billy Graham crusade at Madison Square Garden, and he responded to the altar call. Raymond and Donna married a year after he finished medical school,[16] and they had three children. Raymond said that he first became interested in detecting cancer when, as a boy of 10, he saw his maternal grandmother, with whom he was very close, die painfully of breast cancer.[18]
Magnetic resonance imaging
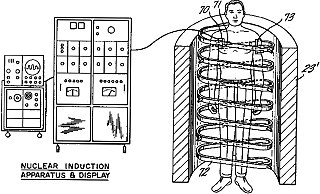
Damadian's early work on NMR concerned investigating potassium ions inside cells.[19] He found that the potassium relaxation times were much shorter compared with aqueous solutions of potassium ions. This suggested that potassium was not free but complexed to 'fixed-charge' counter-ions, as he had previously determined.[20]
He and other researchers independently investigated the signals of 1H NMR in cells, and found that the relaxation times were much shorter than in distilled water. This was consistent with ordering of a large part of the water by adsorption onto macromolecular surfaces. Damadian predicted that cancerous cells would have longer relaxation times, both because of the disordering of malignant cells and because of their elevated potassium levels, since the potassium ions would be 'structure-breaking' to the ordered water fraction.[citation needed]
In a 1971 paper in the journal Science,[21] SUNY Downstate Medical Center professor Damadian reported that tumors can be detected in vivo by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) because of much longer relaxation times than normal tissue. He suggested that these differences could be used to detect cancer, even in the early stages where it would be most treatable, though later research would find that these differences, while real, are too variable for diagnostic purposes. However, Damadian in his seminal paper claimed only that his method was a detection tool, making no claim about being a diagnostic tool, but intended that it would provide a non-invasive way of detecting cancers and monitoring the effectiveness of their therapy.[citation needed]
In 1974, he received the first patent in the field of MRI when he patented the concept of NMR[22] for detecting cancer after filing an application in 1972. As the National Science Foundation notes, "The patent included the idea of using NMR to 'scan' the human body to locate cancerous tissue."[23] However, it did not describe a method for generating pictures from such a scan or precisely how such a scan might be done.[24] However, Damadian's recognition that NMR relaxation time can be used to distinguish different tissue types and malignant tissue is what gives MRI its contrast to tissue types.
In the 1950s, Herman Carr reported [25] creating a one-dimensional magnetic resonance (MR) image. Prompted by Damadian's report on the potential medical uses of NMR, Paul Lauterbur expanded on Carr's technique and developed a way to generate the first MRI images, in 2D and 3D, using gradients. Peter Mansfield from the University of Nottingham then developed a mathematical technique that would allow scans to take seconds rather than hours and produce clearer images than Lauterbur had. While Lauterbur and Mansfield focused on animals and human limbs, Damadian built the first full-body MRI machine[26] and produced the first full magnetic resonance imaging ("MRI") scan of the human body, albeit using a "focused field" technique that differs considerably from modern imaging.
According to a Wall Street Journal article,[27] Damadian's initial methods were flawed for practical use,[26] relying on a point-by-point scan of the entire body and using relaxation rates, which turned out to not be an effective indicator of cancerous tissue. However, the same article pointed out, "Nevertheless, his observation of T1 and T2 differences in cancerous tissue was a Eureka moment for Paul Lauterbur." Furthermore, Damadian's seminal paper[21] documented in its Table 2 that T1 relaxation times were different, beyond experimental uncertainty, across all his samples over different healthy tissues: rectus muscle, liver, stomach, small intestine, kidney, and brain. This showed the way to accurate imaging of the body's soft tissues for the first time; X-ray imaging was severely deficient for soft tissue analysis because the difference in absorption was so small (<4%). So when in the court case Fonar v. General Electric, GE's attorneys made the same claim that relaxations times were also prolonged in non-cancerous tissue, so were not a good diagnostic, Fonar's attorneys responded that it was unfair to punish Damadian because his methods detected even more features than he had intended. Indeed, even today, 90% of MRI scans on patients produce images that are relaxation dependent, either T1- or T2-dependent images.
First human MRI body scan
On July 3, 1977, the first MRI body exam was performed on a human being[28] (the first human scan was performed by Peter Mansfield's team in Nottingham a year earlier, on fellow author Andrew Maudsley's finger). It took almost five hours to produce one image: a 106-voxel point-by-point scan of Larry Minkoff's thorax. The images were rudimentary by modern standards. Damadian, along with colleagues Larry Minkoff and Michael Goldsmith took seven years to reach this point. They named their original machine "Indomitable" to capture the spirit of their struggle to do what many said could not be done, though no systems would ever use Damadian's method. His technique of imaging was never made into a practically usable method and has therefore never been used in MR imaging as we know it today.
His patent followed on the heels of rumors already floating throughout the scientific community of Lauterbur's proposed idea of using NMR in vivo (still in the human body, an imaging device). However, in 1969, Damadian had previously proposed NMR as a method for external scanning of internal cancers in the body, i.e. in vivo:
- I am very much interested in the potential of NMR spectroscopy for early non-destructive detection of internal malignancies. … I will make every effort myself, and through collaborators, to establish that all tumors can be recognized by their potassium relaxation times or H2O-proton spectra and proceed with the development of instrumentation and probes that can be used to scan the human body externally for early signs of malignancy. Detection of internal tumors during the earliest states of their genesis should bring us very close to the total eradication of the disease.[29]
Though it would later turn out to be irreproducible, in his 1971 Science paper, Damadian showed different NMR signals for tumors and different tissue types:[21]
- In principle, nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] techniques combine many of the desirable features of an external probe for the detection of internal cancer.
This was clearly influential, as Lauterbur wrote in 1986:
- … the attention of the medical community was first attracted by the report of Damadian[21] that some animal tumors have remarkably long water proton relaxation times.
- … even long normal tissues differed markedly among themselves in NMR relaxation times, and I wondered whether there might be some way to noninvasively map out such quantities within the body.[30]
Thus it was the discovery of strongly variant relaxation times that led to Lauterbur's quest to represent these relaxation time differences graphically. Without these differences, unknown until Damadian's work, there would be nothing to make an image with. Hence a book on MRI history, which included chapters on both Damadian and Lauterbur, Chapter 8 entitled, "Raymond V. Damadian: Originator of the Concept of Whole-Body NMR Scanning (MRI) and Discoverer of the NMR Tissue Relaxation Differences That Made It Possible."[31] The book pointed out the importance of both men:
- Because of the contributions of Dr. Raymond Damadian and Dr. Paul Lauterbur, magnetic resonance imaging has become the most powerful and reliable diagnostic tool in medicine....
- Millions of people the world over enjoy a higher quality of life and many lives have been saved, thanks to the contributions of Damadian and Lauterbur.
- NMR scanning resulted from two essential steps. They were taken by the two great MRI pioneers of this volume, Dr. Raymond Damadian and Dr. Paul Lauterbur. Dr. Damadian provided the first step, the discovery of tissue NMR signal differences from which the image is made and the first concept of an NMR body scanner that would utilize these signal differences to detect disease in the human body. Dr. Lauterbur provided the next step of visualizing these signal differences as an image and supplied the first method for acquiring these signals at practical speeds. It does not seem likely that MRI could have come to pass without the key steps contributed by both scientists.
- Without Damadian's discovery, it could not be known that serious diseases like cancer could be detected by an NMR scanner or that tissue NMR signals possessed sufficient contrast to create medically useful images. Without Lauterbur's contribution, development of a practical method for visualizing these signal differences as an image might have occurred much less efficiently. Moreover, the incredible amount of courage and pugnacity shown by Damadian, working alone with only two students, without any consistent granting, thus leading him to do most of the development of his system as a self-made man learning when required, electronics, machining, welding and many other technologies in order to build his first prototype, is exemplary for any researcher. This have to be compared with the working conditions of Lauterbur or Mansfield, both working with comfortable fundings in spacious laboratories with many colleagues and students. At least from the point of view of the merit, the work of Damadian, indeed, is considerable. …
- Recognizing their achievements, the President of the United States awarded the nation's highest honor in technology, the National Medal of Technology, jointly to Dr. Damadian and Dr. Lauterbur for the development of MRI. In presenting the award on July 15, 1988, President Ronald Reagan cited both scientists 'for their independent contributions in conceiving and developing the application of magnetic resonance technology to medical uses including whole-body scanning and diagnostic imaging.[31]
Damadian's machine is now in the Smithsonian Institution. As late as 1982, there were a handful of MRI scanners in the entire United States; today there are thousands.
Fonar Corporation
In 1978, Damadian formed his own company, Fonar[32] (which stood for "Field Focused Nuclear Magnetic Resonance"), for the production of MRI scanners, and in 1980, he produced the first commercial one. Damadian's "focused field" technology proved significantly less efficient and slower than Lauterbur's gradient approach. His scanner, named "Indomitable," failed to sell. Fonar eventually abandoned Damadian's technique in favor of the methods adopted by Lauterbur and Mansfield.[33] Damadian and Fonar enforced the royalties on patents held by Damadian.[34] They settled with many large companies, but a case against General Electric went to the Federal Circuit, which upheld a $129 million ruling against GE for violation of Damadian's patents.[35] Damadian said that the judgment money was all put back into Fonar for research and development purposes.
Damadian was the company's largest shareholder, with 8% of stock worth $6.5 million.[15] Despite owning only 8% of the stock, he maintained almost 100% control of the company through a separate class of shares (Class C) that only Damadian controlled 2007.[36] Damadian later collaborated with Wilson Greatbatch, one early developer of the implantable pacemaker, to develop an MRI-compatible pacemaker. He invented a stand-up MRI system and has 15 MRI scanning centers across the United States. There are a number of independent MRI centers that use this technology both in the U.S. and around the world. The company conceived and built the world's first Upright Multi-Positional MRI, which was recognized as The "Invention of the Year" in 2007 by the Intellectual Properties Owners Association Education Foundation.[37]
Creationism
Damadian was a lifelong Christian.[38] In the February 4, 2014, Bill Nye–Ken Ham debate, Damadian was one of the scientists who recorded themselves on video professing a belief in young Earth creationism for Answers in Genesis president Ken Ham to cite.[39][40]
Death
Damadian died on August 3, 2022, at the age of 86 from cardiac arrest.[41]
Awards and honors
Summarize
Perspective
Damadian received a National Medal of Technology in 1988 and was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame[26] in 1989. His original MRI full-body scanner was given to the Smithsonian Institution in the 1980s and is now on loan and on display at the National Inventors Hall of Fame in Ohio.[42] In 2001, the Lemelson-MIT Prize Program bestowed its $100,000 Lifetime Achievement Award on Damadian as "the man who invented the MRI scanner."[6]
The Franklin Institute in Philadelphia gave its recognition of Damadian's work on MRI with the Bower Award in Business Leadership. He was named the Knights of Vartan 2003 "Man of the Year." In September 2003, he was honored with the Innovation Award in Bioscience from The Economist.[42]
Nobel Prize controversy
In 2003, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Paul Lauterbur and Sir Peter Mansfield for their discoveries related to MRI. Although Nobel rules allow for the award to be shared by up to three recipients, Damadian was not given the prize. The controversy over who played what part in the development of the MRI had gone on for years prior to the Nobel announcement, and many in the scientific community felt that the Nobel had not been awarded for the MRI for so long due to debate over Damadian's role in its development.[27]
Damadian said that credit should go to "me, and then Lauterbur," and Lauterbur felt that only he should get credit. In 1997 the National Academy of Sciences commissioned a timeline of MRI milestones, and four of the 12 in an initial draft were attributed to Damadian. At the final publication in 2001, longer than any other publication in the series had ever been taken, none of the milestones was attributed to Damadian. The text said that Damadian's methods had "not proved clinically reliable in detecting or diagnosing cancer."[27] After Damadian's lawyers sent the NAS a threatening letter, the text on the NAS website was revised, but not to Damadian's satisfaction. Damadian said in 2002, "If I had not been born, would MRI have existed? I don't think so. If Lauterbur had not been born? I would have gotten there. Eventually."[27]
The New York Times wrote:
The issue has been the subject of a dispute between Dr. Damadian and Dr. Lauterbur and has been known for years in academic circles, with some fearing that the Nobel committee would steer clear of magnetic resonance imaging altogether because of the Swedes' supposed distaste for controversial discoveries. Dr. Lauterbur, 74, is not in good health, and the committee may have decided that its prize, which cannot be given posthumously, needed to be awarded for the discovery now or never.".[35]
After the announcement of Lauterbur and Mansfield's Nobels, between October and November 2003, an ad hoc group called "The Friends of Raymond Damadian" (formed by Damadian's company FONAR[43]) took out full-page advertisements in The New York Times twice, The Washington Post, The Los Angeles Times, and one of the largest newspapers in Sweden, Dagens Nyheter protesting his exclusion with the headline "The Shameful Wrong That Must Be Righted"[44] in an attempt to get the Nobel Committee to change its mind and grant him a share of the Prize.[15][45]
Damadian suggested that Lauterbur and Mansfield should have rejected the Nobel Prize unless Damadian was given joint recognition. Supporting Damadian were various MRI experts including John Throck Watson, Eugene Feigelson, V. Adrian Parsegian, David Stark, and James Mattson.[citation needed] New York Times columnist Horace Freeland Judson criticised this behavior, noting that there is "no Nobel Prize for whining" and that many deserving candidates who may have had better claims than Damadian, such as Lise Meitner, Oswald Avery, and Jocelyn Bell, had been previously denied a share of the Nobel.[46] However, he had to admit that Erwin Chargaff, whose two rules were instrumental in the discovery of DNA's structure, was very vocal about his omission, and Fred Hoyle was irate about Jocelyn Bell's exclusion.[citation needed]
Others pointed out that while Damadian had hypothesized that NMR relaxation times might be used to detect cancer, he did not develop (nor did he suggest) the current way of creating images.[24] Since the Nobel Prize was awarded to Lauterbur and Mansfield for the development of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Damadian's exclusion makes more sense. Some felt that research scientists sided with Lauterbur because he was one of their own, while Damadian was a physician who had profited greatly from his early patents.[27] Charles Springer, an expert in MRI at Oregon Health and Science University, said that if a poll was taken of the academic community, most would agree with the Nobel Committee's conclusions.[35] And Mansfield wrote in his autobiography that "the person who really missed out" on winning the prize was Erwin Hahn for his contribution to the principles of spin echoes.[47]
Chemist George Kauffman argued that Damadian deserved the Nobel:
Undoubtedly, both Damadian and Lauterbur made major contributions to MRI imaging and scanning. Without Damadian's relaxation discoveries that showed sharp discrimination between tissues and particularly a serious disease like cancer, there would have been no reason to entertain or even consider a method for displaying the relaxation differences so that they could be visualized as an image. Furthermore, except for the relaxation differences discovered by Damadian, there would be no reason to expect that such an image would show anything, i.e., that any tissue NMR contrast existed with which to make an image.
Science and technology are two distinctly different enterprises. Science is the branch of knowledge dedicated to compiling factual information and understanding natural phenomena. It precedes technology, and technology cannot advance without it. Without science's new knowledge of natural phenomena, technology's new methods for exploiting and taking advantage of nature's secrets cannot be created. The new scientific information is necessarily the first step.
Moreover, there is no doubt that Damadian's seminal discovery preceded Lauterbur's developments.[48]
Philosopher Michael Ruse writing for the Metanexus Institute suggested that Damadian might have been denied a Nobel prize because of his creationist views, saying:
I cringe at the thought that Raymond Damadian was refused his just honor because of his religious beliefs. Having silly ideas in one field is no good reason to deny merit for great ideas in another field. Apart from the fact that this time the Creation Scientists will think that there is good reason to think that they are the objects of unfair treatment at the hands of the scientific community.[49]
Damadian himself said, "Before this happened, nobody ever said to me 'They will not give you the Nobel Prize for Medicine because you are a creation scientist'. If people were actively campaigning against me because of that, I never knew it."[26]
In his 2015 memoir Gifted Mind, Damadian suggested the Nobel committee may have rejected him because of his religious beliefs.[50]
Bibliography
- Gifted Mind: The Dr. Raymond Damadian Story, Inventor of the MRI. Master Books. 2015. ISBN 978-0890518038. (with Jeff Kinley)
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.