Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Humoral immune deficiency
Medical condition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Humoral immune deficiencies are conditions which cause impairment of humoral immunity, which can lead to immunodeficiency. It can be mediated by insufficient number or function of B cells, the plasma cells they differentiate into, or the antibody secreted by the plasma cells.[7] The most common such immunodeficiency is inherited selective IgA deficiency, occurring between 1 in 100 and 1 in 1000 persons, depending on population. They are associated with increased vulnerability to infection, but can be difficult to detect (or asymptomatic) in the absence of infection.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Signs and symptoms
Signs/symptoms of humoral immune deficiency depend on the cause, but generally include signs of infection such as:[1]
Causes
Summarize
Perspective
Cause of this deficiency is divided into primary and secondary:
- Primary the International Union of Immunological Societies classifies primary immune deficiencies of the humoral system as follows:[3][2]
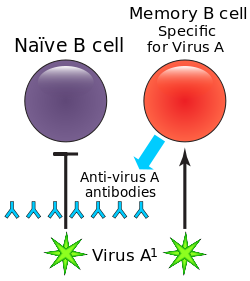
- Absent B cells with a resultant severe reduction of all types of antibody: X-linked agammaglobulinemia (btk deficiency, or Bruton's agammaglobulinemia), μ-Heavy chain deficiency, l 5 deficiency, Igα deficiency, BLNK deficiency, thymoma with immunodeficiency
- B cells low but present, but with reduction in 2 or more isotypes (usually IgG & IgA, sometimes IgM): common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), ICOS deficiency, CD19 deficiency, TACI (TNFRSF13B) deficiency, BAFF receptor deficiency.
- Normal numbers of B cells with decreased IgG and IgA and increased IgM: Hyper-IgM syndromes
- Normal numbers of B cells with isotype or light chain deficiencies: heavy chain deletions, kappa chain deficiency, isolated IgG subclass deficiency, IgA with IgG subsclass deficiency, selective immunoglobulin A deficiency
- Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy (THI)
- Secondary secondary (or acquired) forms of humoral immune deficiency are mainly due to hematopoietic malignancies and infections that disrupt the immune system:[4]
Remove ads
Diagnosis
In terms of diagnosis of humoral immune deficiency depends upon the following:[5][6]
- Measure serum immunoglobulin levels
- B cell count
- Family medical history
Treatment
Treatment for B cell deficiency (humoral immune deficiency) depends on the cause, however generally the following applies:[5]
- Treatment of infection (antibiotics)
- Surveillance for malignancies
- Immunoglobulin replacement therapy
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads