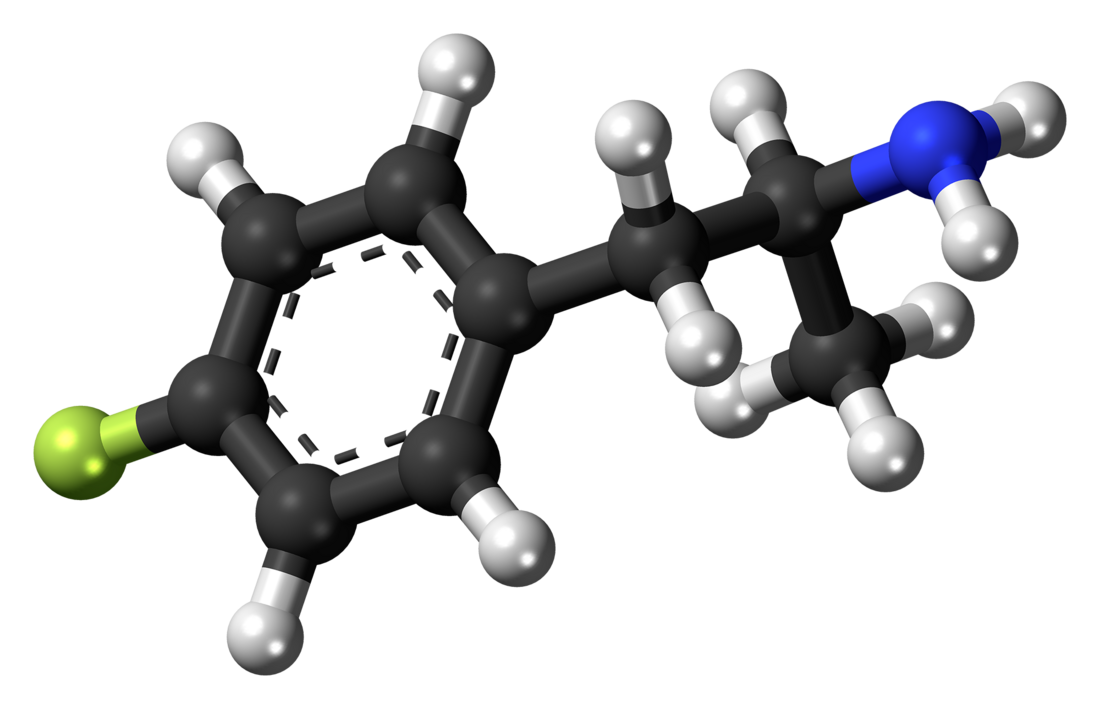
4-Fluoroamphetamine
Psychoactive research chemical From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
4-Fluoroamphetamine (4-FA; 4-FMP; PAL-303; "Flux"), also known as para-fluoroamphetamine (PFA) is a psychoactive research chemical of the phenethylamine and substituted amphetamine chemical classes. It produces stimulant and entactogenic effects. As a recreational drug, 4-FA is sometimes sold along with related compounds such as 2-fluoroamphetamine and 4-fluoromethamphetamine.[2][3]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H12FN |
| Molar mass | 153.200 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Usage

4-FA is popular in the Netherlands where it is predominantly used for its specific effects (77% of users) rather than its legal status (18%).[4] 4-FA has become illegal since May 2017.[5]
Effects
The subjective effects of 4-fluoroamphetamine include euphoria which some find similar to the effects of MDMA and amphetamine,[4] increased energy (stimulation), mood elevation, feelings of warmth and empathy, excessive talking, bruxism, and suppressed appetite (anorexic). The general course of effects involves primarily empathogenic effects for the first few hours, which fades out as increased stimulation develops over the next several hours. [medical citation needed]
The dopamine reuptake inhibition produced by 4-FA is stronger than that of either 4-CA or 4-IA.[6] 4-FA also produces less hyperthermia than similar compounds such as PMA, 4-MTA and 4-methylamphetamine.[medical citation needed]
Common acute side effects are nausea, headaches, increased heart rate and insomnia.[medical citation needed]
Chemistry
4-FA reacts with reagent testing to give a semi-unique array of colors which can be used to aid its identification.
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
4-Fluoroamphetamine is a releasing agent and reuptake inhibitor of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.[9] The respective EC50 values are 2.0 x 10−7 M, 7.3 x 10−7 M, and 0.37 x 10−7 M, while the IC50 values are 7.7 x 10−7 M, 68 x 10−7 M, and 4.2 x 10−7 M.[3]
4-Fluoroamphetamine has been found to be a weak monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) inhibitor, with an IC50 of 16,000 nM.[10] For comparison, the IC50 of amphetamine for MAO-A inhibition was 11,000 nM.[10]
Regarding the metabolic fate of 4-FA, the C-F bond at the 4-position on the phenyl ring likely resists deactivation in the liver by cytochrome P450 oxidase.[11][12]
Neurotoxicity
4-FA does not cause long-lasting depletion of brain serotonin, unlike its analogs 4-CA and 4-BA.[13] This is thought to "reflect the inability of the fluoro-compound to be metabolized in the same way as the other haloamphetamines."[14]
Neurotoxicity does not increase down the series of para-halogenated amphetamine derivatives, even though serotonin releasing potency does follow this trend. For example, 4-iodoamphetamine is less toxic than is 4-chloroamphetamine.[6][15] Hence, this property is not related to serotonin releasing potency as such, since PAL-287 was reported to be not at all neurotoxic even though it is a powerful 5-HT releasing agent.[16] It is unclear where 4-methylamphetamine fits in on the neurotoxicity scale. The extensive serotonergic neurotoxicity of 4-chloroamphetamine (and its brominated derivative), and the increased serotonergic toxicity of 4-methylamphetamine[17] suggest that para-substitution seems to increase overall serotonergic (neuro)toxicity, compared to amphetamine. Exceptions include 4-MTA, a para-substituted, non-neurotoxic amphetamine.[18][19][20]
Toxicology
The LD50 (mouse; i.p.) of 4-FA is 46 mg/kg.[21]
Fluoroamphetamine (isomer not determined) in a capsule mixed with 25C-NBOMe was associated with three deaths in Melbourne in 2017.[22]
Legal status
As of October 2015, 4-FA is a controlled substance in China.[23] 4-FA is banned in the Czech Republic.[24] As of 25 May 2017 4-FA is a controlled substance in the Netherlands.[25] 4-FA is also controlled in Australia, Belgium, UK, Germany, Israel, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Chile, Brazil, Canada, Croatia, Sweden, New Zealand and France.[citation needed]
Finland
Scheduled in the "government decree on narcotic substances, preparations and plants" and is therefore illegal.[26]
See also
- 2-Fluoroamphetamine (2-FA)
- 3-Fluoroamphetamine (3-FA)
- 3,4-Difluoroamphetamine
- 4-Fluoromethamphetamine (4-FMA)
- 4-Fluoromethcathinone (4-FMC)
- 4'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex
- para-Bromoamphetamine (PBA)
- para-Bromomethamphetamine (PBMA)
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.