Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Crest factor
Peak divided by the Root mean square (RMS) of the waveform From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
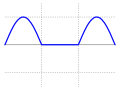
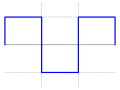
Crest factor is a parameter of a waveform, such as alternating current or sound, showing the ratio of peak values to the effective value. In other words, crest factor indicates how extreme the peaks are in a waveform. Crest factor 1 indicates no peaks, such as direct current or a square wave. Higher crest factors indicate peaks, for example sound waves tend to have high crest factors.
Crest factor is the peak amplitude of the waveform divided by the RMS value of the waveform.
The peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) is the peak amplitude squared (giving the peak power) divided by the RMS value squared (giving the average power).[1] It is the square of the crest factor.
When expressed in decibels, crest factor and PAPR are equivalent, due to the way decibels are calculated for power ratios vs amplitude ratios.
Crest factor and PAPR are therefore dimensionless quantities. While the crest factor is defined as a positive real number, in commercial products it is also commonly stated as the ratio of two whole numbers, e.g., 2:1. The PAPR is most used in signal processing applications. As it is a power ratio, it is normally expressed in decibels (dB). The crest factor of the test signal is a fairly important issue in loudspeaker testing standards; in this context it is usually expressed in dB.[2][3][4]
The minimum possible crest factor is 1, 1:1 or 0 dB.
Remove ads
Examples
Summarize
Perspective
This table provides values for some normalized waveforms. All peak magnitudes have been normalized to 1.
Notes:
- Crest factors specified for QPSK, QAM, WCDMA are typical factors needed for reliable communication, not the theoretical crest factors which can be larger.
Remove ads
Crest factor reduction
Summarize
Perspective
Many modulation techniques have been specifically designed to have constant envelope modulation, i.e., the minimum possible crest factor of 1:1.
In general, modulation techniques that have smaller crest factors usually transmit more bits per second than modulation techniques that have higher crest factors. This is because:
- any given linear amplifier has some "peak output power"—some maximum possible instantaneous peak amplitude it can support and still stay in the linear range;
- the average power of the signal is the peak output power divided by the crest factor;
- the number of bits per second transmitted (on average) is proportional to the average power transmitted (Shannon–Hartley theorem).
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a very promising modulation technique; perhaps its biggest problem is its high crest factor.[14][15] Many crest factor reduction techniques (CFR) have been proposed for OFDM.[16][17][18] The reduction in crest factor results in a system that can either transmit more bits per second with the same hardware, or transmit the same bits per second with lower-power hardware (and therefore lower electricity costs[19] and less expensive hardware), or both. Over the years, numerous model-driven approaches have been proposed to reduce the PAPR in communication systems. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in exploring data-driven models for PAPR reduction as part of ongoing research in end-to-end communication networks. These data-driven models offer innovative solutions and new avenues of exploration to address the challenges posed by high PAPR effectively. By leveraging data-driven techniques, researchers aim to enhance the performance and efficiency of communication networks by optimizing power utilization. [20]
This article appears to contain a large number of buzzwords. (August 2023) |
Crest factor reduction methods
Various methods for crest factor reduction exist, such as peak windowing, noise shaping, pulse injection and peak cancellation.
Remove ads
Applications
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
 ,
,  ...
...