Overton window
Range of ideas tolerated in public discourse From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Overton window is the range of subjects and arguments politically acceptable to the mainstream population at a given time.[1] It is also known as the window of discourse.[2] The key to the concept is that the window changes over time; it can shift, or shrink or expand.[3] It exemplifies "the slow evolution of societal values and norms".[3]
The term is named after the American policy analyst and former senior vice president at Mackinac Center for Public Policy, Joseph Overton, who proposed that the political viability of an idea depends mainly on whether it falls within an acceptability range, rather than on the individual preferences of politicians using the term or concept.[4][3] According to Overton, the window frames the range of policies that a politician may recommend without appearing too extreme to gain or keep public office given the climate of public opinion at that particular time.[5]
Summary
Summarize
Perspective
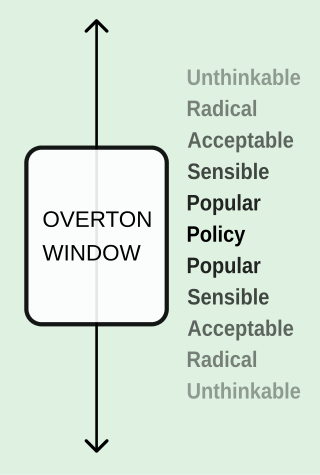
In the early 1990s, Overton described a spectrum from "more free" to "less free" with regard to governmental intervention, that was oriented vertically on an axis (to avoid comparison with the left-right political spectrum).[6] As the spectrum moves or expands, an idea at a given location on the scale may become more or less politically acceptable. After Overton's death, his Mackinac Center for Public Policy colleague, Joseph Lehman, further developed the idea and named it after Overton.[7]
The political commentator Joshua Treviño has postulated that the six degrees of acceptance of public ideas are roughly:[8]
- unthinkable
- radical
- acceptable
- sensible
- popular
- policy
The Overton window is an approach to identifying the ideas that define the spectrum of acceptability of governmental policies. The premise of the concept Overton defined was that politicians typically act freely only within a window seen as acceptable. Shifting the Overton window would involve proponents of policies outside the window persuading the public to expand the window while proponents of current policies, or similar ones within the window, attempt to convince people that policies outside the status quo should be deemed unacceptable. According to Lehman, who coined the term:
The most common misconception is that lawmakers themselves are in the business of shifting the Overton window. That is absolutely false. Lawmakers are actually in the business of detecting where the window is, and then moving to be in accordance with it.[7]
According to Lehman, the concept is just a description of how ideas work, not about advocacy of extreme policy proposals. In an interview with The New York Times, he said:
It just explains how ideas come in and out of fashion, the same way that gravity explains why something falls to the earth. I can use gravity to drop an anvil on your head, but that would be wrong. I could also use gravity to throw you a life preserver; that would be good.[5]
Use of the shifting scale concept has been adopted as relevant in broader areas and one may find references to an Overton window applied regarding shifting acceptability in fields without political policy implications.[9]
See also
- Argument to moderation – Informal fallacy that the truth is always a compromise, even if such a position is unfeasible
- Comfort zone – Psychological state
- Creeping normality – Process by which a change can be accepted through happening slowly
- Door-in-the-face technique – Starting with an unreasonable offer to make the next one more appealing
- Hallin's spheres – Theory of media objectivity
- Moral relativism – Philosophical positions about the differences in moral judgments across peoples and cultures
- Normalization – Social processes through which ideas and actions come to be seen as normal
- Opinion corridor – Theory of legitimate public discourse
- Paradox of tolerance – Logical paradox in decision-making theory
- Ratchet effect – Restrained ability of human process reversal
- Sanewashing – Downplaying the radical aspects of a person or idea
- Single-issue politics – Political campaigning or support based on one essential policy goal
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
