Loading AI tools
Extinct languate of Venezuela From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
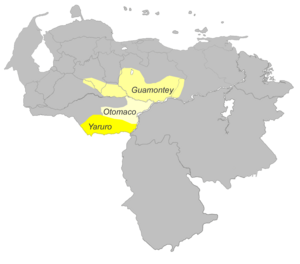
Otomaco and Taparita are two long-extinct languages of the Venezuelan Llanos.[1][2]
| Otomakoan | |
|---|---|
| Otomaco–Taparita | |
| Geographic distribution | Venezuelan Llanos |
| Linguistic classification | Macro-Otomakoan ?
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | otom1276 |
 | |
In addition to Otomaco and Taparita, Loukotka (1968) also lists Maiba (Amaygua), an unattested extinct language that was once spoken in Apure State, Venezuela between the Cunaviche River and Capanaparo River.[3]
Loukotka (1968) lists the following basic vocabulary items for Otomac and Taparita.[3]
| gloss | Otomac | Taparita |
|---|---|---|
| one | engá | enda |
| two | dé | deñiaro |
| three | yakia | deni |
| head | dapad | dupea |
| eye | inbad | indó |
| tooth | miʔi | mina |
| man | andua | mayná |
| water | ya | ia |
| fire | núa | muita |
| sun | nua | mingua |
| maize | onona | |
| jaguar | maéma | |
| house | augua | ñaña |
Additional vocabulary for Otomaco and Taparita are documented in Rosenblat (1936).[2]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.