Directed ortho metalation
Chemical reaction From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
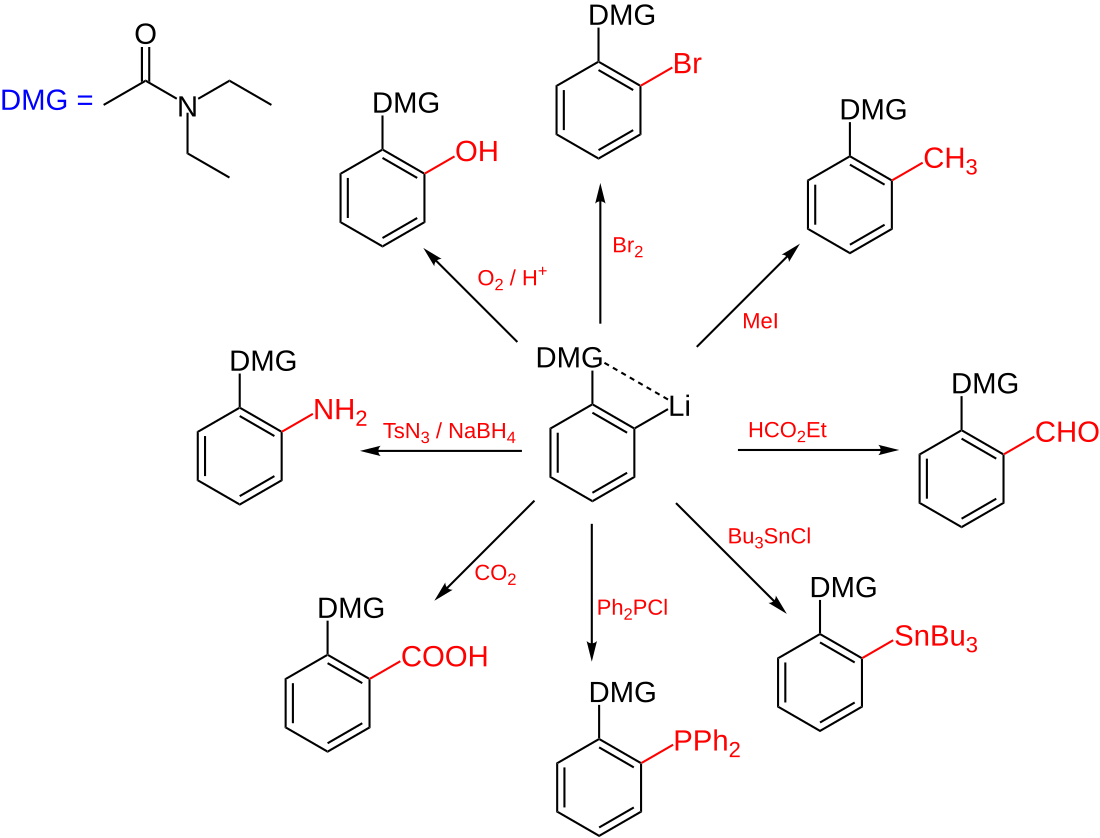
Directed ortho metalation (DoM) is an adaptation of electrophilic aromatic substitution in which electrophiles attach themselves exclusively to the ortho- position of a direct metalation group or DMG through the intermediary of an aryllithium compound.[1] The DMG interacts with lithium through a hetero atom. Examples of DMG's are the methoxy group, a tertiary amine group and an amide group. The compound can be produced by directed lithiation of anisole.[2]

The general principle is outlined in scheme 1. An aromatic ring system with a DMG group 1 interacts with an alkyllithium such as n-butyllithium in its specific aggregation state (hence (R-Li)n) to intermediate 2 since the hetero atom on the DMG is a Lewis base and lithium the Lewis acid. The very basic alkyllithium then deprotonates the ring in the nearest ortho- position forming the aryllithium 3 all the while maintaining the acid-base interaction. An electrophile reacts in the next phase in an electrophilic aromatic substitution with a strong preference for the lithium ipso position replacing the lithium atom.
Ordinary electrophilic substitutions with an activating group show preference for both the ortho and para position, this reaction demonstrates increased regioselectivity because the ortho position alone is targeted.

This reaction type was reported independently by Henry Gilman and Georg Wittig around 1940.[3][4]
Examples
DOM has traditionally been applied to tertiary anilines and benzyl amines.[5][6]
The method has also been applied to the synthesis of enantiopure benzyl amines[7] in scheme 3,[8] which involves ortho-lithiation of tert-butyl phenyl sulfoxide. On approach to the lithium intermediate, the bulky tosyl group on the imine electrophile is responsible for the asymmetric induction taking place.

In another application[9] DOM is applied in placing a bulky tert-butyl group in an ortho position (scheme 4). The lithiation is a nucleophilic aromatic substitution and the subsequent reaction to the sulfoxide an electrophilic aromatic substitution. In the final step tert-butyllithium acts as a nucleophile in another nucleophilic aromatic substitution through an anionic intermediate.

DoM has also been applied combined with a Suzuki reaction in a one-pot synthesis:[10][11]

Thiophenol derivatives
DOM has also been used with thiophenols to prepare compounds that are useful as hindered ligands.[12]
Related reaction
Directed metallation is not limited to lithium intermediates or even to an ortho preference. In one study [13] it is found that the reaction product of N,N-dimethylaniline with a complex of TMEDA, sodium salt of TMP and di-tert-butylzinc is a meta zincated complex as a stable crystalline compound. This complex reacts with electrophilic iodine to N,N-dimethyl-3-iodoaniline:[14]

References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.