Orotidine 5'-monophosphate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
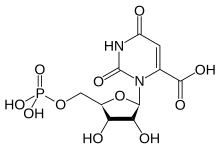
Orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP), also known as orotidylic acid, is a pyrimidine nucleotide[1] which is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of uridine monophosphate.[2] OMP is formed from orotate and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme orotate phosphoribosyltransferase.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,6-Dioxo-3-(5-O-phosphono-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-{(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-6-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl}-2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Orotidylic acid, OMP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Orotidine+5'-monophosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N2O11P | |
| Molar mass | 368.191 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In humans, the enzyme UMP synthase converts OMP into uridine 5'- monophosphate.[2] If UMP synthase is defective, orotic aciduria can result.[2]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
