Chewa language
Bantu language of Southern and East Africa From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chewa ( /ˈtʃeɪwə/; also known as Nyanja /ˈnjændʒə/) is a Bantu language spoken in Malawi and a recognised minority in Zambia and Mozambique. The noun class prefix chi- is used for languages,[3] so the language is often called Chichewa or Chinyanja. In Malawi, the name was officially changed from Chinyanja to Chichewa in 1968 at the insistence of President Hastings Kamuzu Banda (himself of the Chewa people), and this is still the name most commonly used in Malawi today.[4] In Zambia, the language is generally known as Nyanja or Cinyanja/Chinyanja '(language) of the lake' (referring to Lake Malawi).[5]
| Chewa | |
|---|---|
| Nyanja | |
| Chichewa, Chinyanja | |
| Native to | Malawi |
| Region | Southeast Africa |
| Ethnicity | Chewa |
Native speakers | 7 million (2007)[1] |
| Latin (Chewa alphabet) Mwangwego Chewa Braille | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ny |
| ISO 639-2 | nya |
| ISO 639-3 | nya |
| Glottolog | nyan1308 |
N.30 (N.31, N.121)[2] | |
| Linguasphere | 99-AUS-xaa – xag |
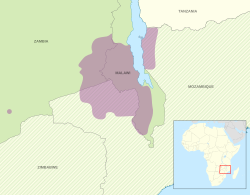 Areas where Chewa is the dominant language (purple). Solid green signifies a nation where Chewa is an official language, striped green signifies a nation where Chewa is a recognized minority language. | |
| Person | Mchewa |
|---|---|
| People | Achewa |
| Language | Chichewa |
Chewa belongs to the same language group (Guthrie Zone N) as Tumbuka, Sena[6] and Nsenga. Throughout the history of Malawi, only Chewa and Tumbuka have at one time been the primary dominant national languages used by government officials and in school curricula. However, the Tumbuka language suffered a lot during the rule of President Hastings Kamuzu Banda, since in 1968 as a result of his one-nation, one-language policy it lost its status as an official language in Malawi. As a result, Tumbuka was removed from the school curriculum, the national radio, and the print media.[7] With the advent of multi-party democracy in 1994, Tumbuka programmes were started again on the radio, but the number of books and other publications in Tumbuka remains low.[8]
Distribution
Chewa in Malawi is spoken in the Central Region where it is dominant as well as in Southern Region due to migration and labour.[9] It is also spoken in Eastern Province of Zambia, as well as in Mozambique, especially in the province of Niassa. It was one of the 55 languages featured on the Voyager spacecraft.[10]
History
Summarize
Perspective
The Chewa were a branch of the Maravi people who lived in the Eastern Province of Zambia and in northern Mozambique as far south as the River Zambezi from the 16th century or earlier.[11][12]
The name "Chewa" (in the form Chévas) was first recorded by António Gamitto, who at the age of 26 in 1831 was appointed as second-in-command of an expedition from Tete to the court of King Kazembe in what became Zambia. His route took him through the country of King Undi west of the Dzalanyama mountains, across a corner of present-day Malawi and on into Zambia.[13] Later he wrote an account including some ethnographic and linguistic notes and vocabularies. According to Gamitto, the Malawi or Maravi people (Maraves) were those ruled by King Undi south of the Chambwe stream (not far south of the present border between Mozambique and Zambia), while the Chewa lived north of the Chambwe.[14]
Another, more extensive, list of 263 words and phrases of the language was made by the German missionary Sigismund Koelle who, working in Sierra Leone in West Africa, interviewed some 160 former slaves and recorded vocabularies in their languages. He published the results in a book called Polyglotta Africana in 1854. Among other slaves was one Mateke, who spoke what he calls "Maravi". Mateke's language is clearly an early form of Nyanja, but in a southern dialect. For example, the modern Chichewa phrase zaka ziwiri 'two years' was dzaka dziŵiri in Mateke's speech, whereas for Johannes Rebmann's informant Salimini, who came from the Lilongwe region, it was bzaka bziŵiri.[15] The same dialect difference survives today in the word dzala or bzala '(to) plant'.[16]
Apart from the few words recorded by Gamitto and Koelle, the first extensive record of the Chewa language was made by Johannes Rebmann in his Dictionary of the Kiniassa Language, published in 1877 but written in 1853–4. Rebmann was a missionary living near Mombasa in Kenya, and he obtained his information from a Malawian slave, known by the Swahili name Salimini, who had been captured in Malawi some ten years earlier.[17] Salimini, who came from a place called Mphande apparently in the Lilongwe region, also noted some differences between his own dialect, which he called Kikamtunda, the "language of the plateau", and the Kimaravi dialect spoken further south; for example, the Maravi gave the name mombo to the tree which he himself called kamphoni.[18]
The first grammar, A Grammar of the Chinyanja language as spoken at Lake Nyasa with Chinyanja–English and English–Chinyanja vocabulary, was written by Alexander Riddel in 1880. Further early grammars and vocabularies include A grammar of Chinyanja, a language spoken in British Central Africa, on and near the shores of Lake Nyasa by George Henry (1891) and M.E. Woodward's A vocabulary of English–Chinyanja and Chinyanja–English: as spoken at Likoma, Lake Nyasa (1895). The whole Bible was translated into the Likoma Island dialect of Nyanja by William Percival Johnson and published as Chikalakala choyera: ndicho Malangano ya Kale ndi Malangano ya Chapano in 1912.[19] Another Bible translation, known as the Buku Lopatulika ndilo Mau a Mulungu, was made in a more standard Central Region dialect about 1900–1922 by missionaries of the Dutch Reformed Mission and Church of Scotland with the help of some Malawians. This has recently (2016) been reissued in a revised and slightly modernised version.[20]
Another early grammar, concentrating on the Kasungu dialect of the language, was Mark Hanna Watkins' A Grammar of Chichewa (1937). This book, the first grammar of any African language to be written by an American, was a work of cooperation between a young black PhD student and young student from Nyasaland studying in Chicago, Hastings Kamuzu Banda, who in 1966 was to become the first President of the Republic of Malawi.[21][22] This grammar is also remarkable in that it was the first to mark the tones of the words. Modern monographs on aspects of Chichewa grammar include Mtenje (1986), Kanerva (1990), Mchombo (2004) and Downing & Mtenje (2017).
In recent years the language has changed considerably, and a dichotomy has grown between the traditional Chichewa of the villages and the language of city-dwellers.[23]
Phonology
Summarize
Perspective
Vowels
Chewa has five short vowel sounds: a, ɛ, i, ɔ, u; these are written a, e, i, o, u. Long vowels are sometimes found, e.g. áákúlu 'big' (class 2), kufúula 'to shout'.[24] When a word comes at the end of a phrase, its penultimate vowel tends to be lengthened,[25] except for non-Chewa names and words, such as Muthárika or ófesi, in which the penultimate vowel always remains short.[citation needed] The added 'u' or 'i' in borrowed words such as láputopu 'laptop' or íntaneti 'internet' tends to be very short.[26]
Vowels are generally lengthened in the penultimate syllable of a prosodic phrase.[27]
Consonants
Chewa consonants can be simple (directly preceding a vowel) or may be followed by w or y:
- b, kh, g, f, m, s etc.
- bw, khw, gw, fw, mw, sw etc.
- bz, tch, j, fy, ny, sh etc.
In the orthography, the place of by is taken by the affricate bz, the place of gy is taken by j, and that of sy by sh.
Voiced and aspirated consonants, as well as [f] and [s], can also be preceded by a homorganic nasal:
- mb, ngw, nj, mv, nz etc.
- mph, nkhw, ntch, mf, ns etc.
It is debated whether these are consonant clusters /NC/, /Cy/ and /Cw/, or whether Chichewa has prenasalized, palatalized and labialized consonants /ᴺC/, /Cʲ/, /Cʷ/. The most straightforward analysis is that they are clusters.[28] The consonant inventory under a cluster analysis is as follows:
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m /m/ |
n /n/ |
ny /ɲ/ |
ng' /ŋ/ |
||||
| Stop | tenuis | p /p/ |
t /t/ |
k /k/ |
||||
| aspirated | ph /pʰ/ |
th /tʰ/ |
kh /kʰ/ |
|||||
| implosive | b /ɓ/ |
d /ɗ/ |
||||||
| voiced | (b) /b/ |
(d) /d/ |
g /ɡ/ |
|||||
| Affricate | tenuis | ts /t͡s/ |
ch /t͡ʃ/ |
|||||
| aspirated | tch /t͡ʃʰ/ |
|||||||
| voiced | dz /d͡z/ |
j /d͡ʒ/ |
||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f /f/ |
s /s/ |
sh /ʃ/ |
(h) /h/ | |||
| voiced | (ŵ) /β/[30] |
v /v/ |
z /z/ |
|||||
| Semivowel | w /w/ |
y /j/ |
||||||
| Liquid | la/ra [l ~ 𝼈] |
|||||||
Consonants in parentheses are marginal or found mainly in loanwords. The lateral is an approximant [l] word-initially and a flap [𝼈] medially.[source that it's reflexive?]
If the more complex syllable onsets are analyzed as single consonants, the inventory is as follows:
| Labial | Alveolar | Velar/Palatal | Glottal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | palatal-ised | labial-ised | plain | palatal-ised | labial-ised | plain | palatal-ised | labial-ised | ||||
| Nasal | m /m/ | my /mʲ/ |
mw /mʷ/ |
n /n/ |
ny /ɲ/ |
ng' /ŋ/ |
ng'w /ŋʷ/ |
|||||
| Stop | tenuis | p /p/ | py /pʲ/ |
pw /pʷ/ |
t /t/ |
ty /tʲ/ |
tw /tʷ/ |
k /k/ |
kw /kʷ/ |
|||
| aspirated | ph /pʰ/ | phw /pʷʰ/ |
th /tʰ/ |
thy /tʲʰ/ |
thw /tʷʰ/ |
kh /kʰ/ |
khw /kʷʰ/ |
|||||
| Pre-nasalized aspirated |
mph /ᵐpʰ/ | mphw /ᵐpʷʰ/ |
nth /ⁿtʰ/ |
nthy /ⁿtʲʰ/ |
nthw /ⁿtʷʰ/ |
nkh /ᵑkʰ/ |
nkhw /ᵑkʷʰ/ |
|||||
| voiced | b /ɓ/ | bw /ɓʷ/ |
d /ɗ/ |
dy /ɗʲ/ |
dw /ɗʷ/ |
g /ɡ/ |
gw /ɡʷ/ |
|||||
| (b) /b/ | (d) /d/ |
|||||||||||
| Pre-nasalized voiced |
mb /ᵐb/ | mbw /ᵐbʷ/ |
nd /ⁿd/ |
ndy /ⁿdʲ/ |
ndw /ⁿdʷ/ |
ng /ᵑɡ/ |
ngw /ᵑɡʷ/ |
|||||
| Affricate | tenuis | ts /t͡s/ |
tsw /t͡sʷ/ |
ch /t͡ʃ/ |
||||||||
| aspirated | ps /pʃʲ/ |
tch /t͡ʃʰ/ |
||||||||||
| Pre-nasalized aspirated |
mps /ᵐpsʲ/ |
ntch /ⁿt͡ʃʰ/ |
||||||||||
| voiced | bz /bʒʲ/ |
dz /d͡z/ |
(dzw) /d͡zʷ/ |
j /d͡ʒ/ |
||||||||
| Pre-nasalized voiced |
mbz /ᵐbzʲ/ |
(ndz) /ⁿd͡z/ |
nj /ⁿd͡ʒ/ |
|||||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f /f/ |
(fy) /fʲ/ |
fw /fʷ/ |
s /s/ |
sh /ʃ/ |
sw /sʷ/ |
(h) /h/ | ||||
| Pre-nasalized | mf /ᶬf/ |
ns /ⁿs/ |
nsw /ⁿsʷ/ |
|||||||||
| voiced | (ŵ) /β/ | v /v/ |
(vy) /vʲ/ |
vw /vʷ/ |
z /z/ |
(zy) /zʲ~ʒ/ |
zw /zʷ/ |
|||||
| Pre-nasalized voiced |
mv /ᶬv/ |
nz /ⁿz/ |
nzw /ⁿzʷ/ |
|||||||||
| Lateral approximant ~ flap | l/r [l ~ 𝼈] |
lw/rw [lʷ ~ 𝼈ʷ] |
||||||||||
| Approximant | w /w/ | y /j/ |
||||||||||
The spelling used here is that introduced in 1973,[31] which is the one generally in use in the Malawi at the present time, replacing the Chinyanja Orthography Rules of 1931.[32]
Notes on the consonants
- In most words, Chewa b and d (when not prenasalised) are pronounced implosively, by sucking slightly.[33] However, there is also a plosive b and d, mostly found in foreign words, such as bála 'bar', yôdúla 'expensive' (from Afrikaans duur) (in contrast to the implosive b and d in native words such as bála 'wound' and yôdúla 'which cuts').[34] A plosive d is also found in kudínda 'to stamp (a document)' and mdidi 'confident step'.
- The affricate sounds bv and pf were formerly commonly heard but are now generally replaced by v and f, e.g. (b)vúto 'problem', (p)fúpa 'bone'. In the Mtanthauziramawu wa Chinyanja dictionary produced by the University of Malawi, the spellings bv and pf are not used in any of the headwords, but bv is used two or three times in the definitions.
- The combination bz is described by Atkins as an "alveolar-labialised fricative".[35] The combination sounds approximately as [bʒ] or [bʒʲ]. Similarly ps is pronounced approximately as [pʃ] or [pʃʲ].
- The sounds written ch, k, p and t are pronounced less forcibly than the English equivalents and generally without aspiration. Stevick notes that in relaxed speech, the first three are sometimes replaced with the voiced fricatives [ʒ], [ɣ] and [β], and t can be heard as a voiced flap.[36] In the combination -ti (e.g. angáti? 'how many'), t may be lightly aspirated.
- h is also used in Chewa but mostly only in loanwords such as hotéra 'hotel', hátchi 'horse', mswahála 'monthly allowance given to chiefs'.
- j is described by Scotton and Orr as being pronounced "somewhat more forward in the mouth" than in English and as sounding "somewhere between an English d and j".[37]
- l and r are the same phoneme,[38] representing a retroflex tap [𝼈], approximately between [l] and [r]. According to the official spelling rules, the sound is written as 'r' after 'i' or 'e', otherwise 'l'. It is also written with 'l' after a prefix containing 'i', as in lilíme 'tongue'.[39][40]
- m is syllabic [m̩] in words where it is derived from mu, e.g. m'balé 'relative' (3 syllables), mphunzitsi 'teacher' (4 syllables), anáḿpatsa 'he gave him' (5 syllables). However, in class 9 words, such as mphátso 'gift', mbale 'plate', or mfíti 'witch', and also in the class 1 word mphaká 'cat', the m is pronounced very short and does not form a separate syllable. In Southern Region dialects of Malawi, the syllabic m in words like mkángo 'lion' is pronounced in a homorganic manner, i.e. [ŋ̍.ká.ᵑɡo] (with three syllables), but in the Central Region, it is pronounced as it is written, i.e. [m̩.ká.ᵑɡo].[41]
- n, in combinations such as nj, ntch, nkh etc., is assimilated to the following consonant, that is, it is pronounced [ɲ] or [ŋ] as appropriate. In words of class 9, such as njóka 'snake' or nduná 'minister' it is pronounced very short, as part of the following syllable. However, [n] can also be syllabic, when it is contracted from ndi 'it is' or ndí 'and', e.g. ń'kúpíta 'and to go'; also in the remote past continuous tense, e.g. ankápítá 'he used to go'. In some borrowed words such as bánki or íntaneti the combinations nk and nt with non-syllabic n can be found but not in native words.
- ng is pronounced [ŋɡ] as in 'finger' and ng’ is pronounced [ŋ] as in 'singer'. Both of these consonants can occur at the beginning of a word: ngoma 'kudu', ng'ombe 'cow or ox'.
- w in the combinations awu, ewu, iwu, owa, uwa (e.g. mawú 'voice', msewu 'road', liwú 'sound', lowa 'enter', duwa 'flower') although often written is generally not pronounced.[42] Combinations such as gwo or mwo are not found; thus ngwábwino (short for ndi wábwino)[43] 'he is good' but ngóípa (short for ndi wóípa) 'he is bad'; mwalá 'stone' but móto 'fire'.
- ŵ, a "closely lip-rounded [w] with the tongue in the close-i position",[44] was formerly used in Central Region dialects but is now rarely heard, usually being replaced by 'w'. ("It is doubtful whether the majority of speakers have [β] in their phoneme inventory" (Kishindo).)[45] The symbol 'ŵ' is generally omitted in current publications such as newspapers.[46] In the dialects that use the sound, it is found only before a, i, and e, while before o and u it becomes [w].[47] To some linguists (e.g. Watkins) it sounds similar to the Spanish [β].[47]
- zy (as in zyoliká 'be upside down like a bat') can be pronounced [ʒ].[48]
Tones
Like most other Bantu languages, Chewa is a tonal language; that is to say, the pitch of the syllables (high or low) plays an important role in it. Tone is used in various ways in the language. First of all, each word has its own tonal pattern, for example:[49]
- munthu [mu.ⁿtʰu] 'person' (Low, Low)
- galú [ɡă.𝼈ú] 'dog' (Rising, Mid)
- mbúzi [ᵐbû.zi] 'goat' (Falling, Low)
- chímanga [t͡ʃí.ma.ᵑɡa] 'maize' (High, Low, Low)
Usually there is only one high tone in a word (generally on one of the last three syllables), or none. However, in compound words there can be more than one high tone, for example:
- chákúdyá [t͡ʃá.kú.ɗʲá] 'food' (High, High, High; derived from chá + kudyá, 'a thing of eating')
A second important use of tone is in the verb. Each tense of the verb has its own characteristic tonal pattern (negative tenses usually have a different pattern from positive ones).[50] For example, the present habitual has high tones on the initial syllable and the penultimate, the other syllables being low:
- ndí-ma-thandíza 'I (usually) help'
The recent past continuous and present continuous, on the other hand, have a tone on the third syllable:
- ndi-ma-thándiza 'I was helping'
- ndi-ku-thándiza 'I am helping'
Tones can also indicate whether a verb is being used in a main clause or in a dependent clause such as a relative clause:[51][52]
- sabatá yatha 'the week has ended'
- sabatá yátha 'the week which has ended (i.e. last week)'
A third use of tones in Chewa is to show phrasing and sentence intonation. For example, immediately before a pause in the middle of a sentence the speaker's voice tends to rise up; this rise is referred to as a boundary tone.[53] Other intonational tones are sometimes heard, for example a rising or falling tone at the end of a yes-no question.[54][55]
Grammar
Summarize
Perspective
Noun classes
Chewa nouns are divided for convenience into a number of classes, which are referred to by the Malawians themselves by names such as "Mu-A-",[56] but by Bantu specialists by numbers such as "1/2", corresponding to the classes in other Bantu languages. Conventionally, they are grouped into pairs of singular and plural. However, irregular pairings are also possible, especially with loanwords; for example, bánki 'bank', which takes the concords of class 9 in the singular, has a plural mabánki (class 6).[57]
When assigning nouns to a particular class, initially the prefix of the noun is used. Where there is no prefix, or where the prefix is ambiguous, the concords (see below) are used as a guide to the noun class. For example, katúndu 'possessions' is put in class 1, since it takes the class 1 demonstrative uyu 'this'.[58]
Some nouns belong to one class only, e.g. tomáto 'tomato(es)' (class 1), mowa 'beer' (class 3), malayá 'shirt(s)' (class 6), udzudzú 'mosquito(es)' (class 14), and do not change between singular and plural. Despite this, such words can still be counted if appropriate: tomáto muwíri 'two tomatoes', mowa uwíri 'two beers', malayá amódzi 'one shirt', udzudzú umódzi 'one mosquito'.[59]
Class 11 (Lu-) is not found in Chewa. Words like lumo 'razor' and lusó 'skill' are considered to belong to class 5/6 (Li-Ma-) and take the concords of that class.[60]
- Mu-A- (1/2): munthu pl. anthu 'person'; mphunzitsi pl. aphunzitsi 'teacher'; mwaná pl. aná 'child'
(1a/2): galú pl. agalú 'dog'. Class 1a refers to nouns which have no m- prefix.
The plural a- is used only for humans and animals. It can also be used for respect, e.g. aphunzitsi áthu 'our teacher'
(1a/6): kíyi pl. makíyi 'key'; gúle pl. magúle 'dance'
(1a): tomáto 'tomato(es)'; katúndu 'luggage, furniture'; feteréza 'fertilizer' (no pl.) - Mu-Mi- (3/4): mudzi pl. midzi 'village'; mténgo pl. miténgo 'tree'; moyo pl. miyoyo 'life'; msika pl. misika 'village'
(3): mowa 'beer'; móto 'fire'; bowa 'mushroom(s)' (no pl.) - Li-Ma- (5/6): dzína pl. maína 'name'; vúto pl. mavúto 'problem'; khásu pl. makásu 'hoe'; díso pl. masó 'eye'
Often the first consonant is softened or omitted in the plural in this class.
(6): madzí 'water', mankhwála 'medicine', maló 'place' (no sg.) - Chi-Zi- (7/8): chinthu pl. zinthu 'thing'; chaká pl. zaká 'year'
(7): chímanga 'maize'; chikóndi 'love' (no pl.) - I-Zi- (9/10): nyumbá pl. nyumbá 'house'; mbúzi pl. mbúzi 'goat'
(10): ndevu 'beard'; ndíwo 'relish'; nzerú 'intelligence' (no sg.)
(9/6): bánki pl. mabánki 'bank' - Ka-Ti- (12/13): kamwaná pl. tianá 'baby'; kanthu pl. tinthu 'small thing'
(12): kasamalidwe 'method of taking care'; kavinidwe 'way of dancing' (no pl.)
(13): tuló 'sleep' (no sg.) - U-Ma- (14): usíku 'night time'; ulimi 'farming'; udzudzú 'mosquito(es)' (no pl.)
(14/6): utá pl. mautá 'bow'
Infinitive class:
- Ku- (15): kuóna 'to see, seeing'
Locative classes:
- Pa- (16): pakamwa 'mouth'
- Ku- (17): kukhosi 'neck'
- Mu- (18): mkamwa 'inside the mouth'
Concords
Pronouns, adjectives, and verbs have to show agreement with nouns in Chichewa. This is done by means of prefixes, for example:
- Uyu ndi mwaná wángá 'this is my child' (class 1)
- Awa ndi aná ángá 'these are my children' (class 2)
- Ichi ndi chímanga chánga 'this is my maize' (class 7)
- Iyi ndi nyumbá yángá 'this is my house' (class 9)
Class 2 (the plural of class 1) is often used for respect when referring to elders. According to Corbett and Mtenje, a word like bambo 'father', even though it is singular, will take plural concords (e.g. bambo anga akuyenda, ndikuwaona 'my father is walking, I see him'); they note that to use the singular object-marker -mu- would be 'grossly impolite'.[61]
The various prefixes are shown on the table below:
| noun | English | this | that | pron | subj | object | num | rem | of | of+vb | other | adj | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | mwaná | child | uyu | uyo | yé- | a- | mú/ḿ- | m/(mu)- | uja | wá | wó- | wína | wám- |
| 2 | aná | children | awa | awo | ó- | a- | -á/wá- | a- | aja | á | ó- | éna | áa- |
| 3 | mutú | head | uwu | uwo | wó- | u- | -ú- | u- | uja | wá | wó- | wína | wau- |
| 4 | mitú | heads | iyi | iyo | yó- | i- | -í/yí- | i- | ija | yá | yó- | ína | yái- |
| 5 | díso | eye | ili | ilo | ló- | li- | -lí- | li- | lija | lá | ló- | lína | láli- |
| 6 | masó | eyes | awa | awo | ó- | a- | -wá- | a- | aja | á | ó- | éna | áa- |
| 7 | chaká | year | ichi | icho | chó- | chi- | -chí- | chi- | chija | chá | chó- | chína | cháchi- |
| 8 | zaká | years | izi | izo | zó- | zi- | -zí- | zi- | zija | zá | zó- | zína | zázi- |
| 9 | nyumbá | house | iyi | iyo | yó- | i- | -í/yí- | i- | ija | yá | yó- | ína | yái- |
| 10 | nyumbá | houses | izi | izo | zó- | zi- | -zí- | zi- | zija | zá | zó- | zína | zázi- |
| 12 | kamwaná | baby | aka | ako | kó- | ka- | -ká- | ka- | kaja | ká | kó- | kéna | káka- |
| 13 | tianá | babies | iti | ito | tó- | ti- | -tí- | ti- | tija | tá | tó- | tína | táti- |
| 14 | utá | bow | uwu | uwo | wó- | u- | -ú- | u- | uja | wá | wó- | wína | wáu- |
| 15 | kugúla | buying | uku | uko | kó- | ku- | -kú- | ku- | kuja | kwá | kó- | kwína | kwáku- |
| 16 | pansí | underneath | apa | apo | pó- | pa- | -po | pa- | paja | pá | pó- | péna | pápa- |
| 17 | kutsogoló | in front | uku | uko | kó- | ku- | -ko | ku- | kuja | kwá | kó- | kwína | kwáku- |
| 18 | mkatí | inside | umu | umo | mó- | m/mu- | -mo | m/mu- | muja | mwá | mó- | mwína | mwám'- |
There are 17 different noun classes, but because some of them share concords there are in fact only 12 distinct sets of prefixes.
Examples of the use of concords
In the examples below, the concords are illustrated mainly with nouns of classes 1 and 2.
Demonstratives 'this' and 'that'
- uyu ndaní? 'who is this?'; awa ndaní? 'who are these?' (or: 'who is this gentleman?' (respectful))
- mwaná uyu (mwanáyu) 'this child'; aná awa (anáwa) 'these children'
- mwaná uyo (mwanáyo) 'that child'; aná awo (anáwo) 'those children'
The shortened forms are more common.
Pronominal yé, (w)ó etc.
Prefixed by a supporting vowel, or by ná 'with' or ndi 'it is', these make the pronouns 'he/she' and 'they':
- iyé 'he/she'; iwó 'they' (or 'he/she' (respectful))
- náye 'with him/her'; náwo 'with them' (or 'with him/her' (respectful))
- ndiyé 'it is he/she'; ndiwó 'it is they'
For classes other than classes 1 and 2, a demonstrative is used instead of a freestanding pronoun, for example in class 6 ichi or icho. But forms prefixed by ná- and ndi- such as nácho and ndichó are found.
yénse, yékha, yémwe
The three pronominal adjectives yénse 'all', yékha 'alone', yémwe 'that same' (or 'who') have the same pronominal concords yé- and (w)ó-, this time as prefixes:
- Maláwi yénse 'the whole of Malawi'
- aná ónse 'all the children'
- yékha 'on his/her own'
- ókha 'on their own'
- mwaná yemwéyo 'that same child'
- aná omwéwo 'those same children'
In classes 2 and 6, ó- often becomes wó- (e.g. wónse for ónse etc.).
The commonly used word álíyensé 'every' is compounded from the verb áli 'who is' and yénse 'all'. Both parts of the word have concords:
- mwaná álíyensé 'every child'
- aná awíri álíonsé 'every two children'
- nyumbá ílíyonsé 'every house' (class 4)
- chaká chílíchonsé 'every year' (class 7)
Subject prefix
As with other Bantu languages, all Chewa verbs have a prefix which agrees with the subject of the verb. In modern Chewa, the class 2 prefix (formerly ŵa-) has become a-, identical with the prefix of class 1:
- mwaná ápita 'the child will go'; aná ápita 'the children will go'
The perfect tense (wapita 'he/she has gone', apita 'they have gone') has different subject prefixes from the other tenses (see below).
améne 'who'
The relative pronoun améne 'who' and demonstrative améneyo use the same prefixes as a verb:
- mwaná améne 'the child who'
- aná améne 'the children who'
- mwaná améneyo 'that child'
- aná aménewo 'those children'
- nyumbá iméneyo 'that house'
- nyumbá ziménezo 'those houses'
Object infix
The use of an object infix is not obligatory in Chewa (for example, ndagula means 'I have bought (them)'). If used, it comes immediately before the verb root, and agrees with the object:
- ndamúona 'I have seen him/her'; ndawáona 'I have seen them' (sometimes shortened to ndaáona).
The object infix of classes 16, 17, and 18 is usually replaced by a suffix: ndaonámo 'I have seen inside it'.
The same infix with verbs with the applicative suffix -ira represents the indirect object, e.g. ndamúlembera 'I have written to him'.
Numeral concords
Numeral concords are used with numbers -módzi 'one', -wíri 'two', -tátu 'three', -náyi 'four', -sanu 'five', and the words -ngáti? 'how many', -ngápo 'several':
- mwaná mmódzi 'one child'; aná awíri 'two children'; aná angáti? 'how many children?'
The class 1 prefix m- becomes mu- before -wiri: tomáto muwíri 'two tomatoes'.
The number khúmi 'ten' has no concord.
Demonstratives uja and uno
The demonstrative pronouns uja 'that one you know' and uno 'this one we are in' take the concords u- and a- in classes 1 and 2. For semantic reasons, class 1 uno is rare:
- mwaná uja 'that child (the one you know)'; aná aja 'those children' (those ones you know)
- mwezí uno 'this month (we are in)' (class 3); masíkú ano 'these days'; ku Maláwí kuno 'here in Malawi (where we are now)' (class 17).
Perfect tense subject prefix
The same concords w- (derived from u-) and a-, combined with the vowel a, make the subject prefix of the perfect tense. In the plural the two prefixes a-a- combine into a single vowel:
- mwaná wapita 'the child has gone; aná apita 'the children have gone'
Possessive concord
The concords w- (derived from u-) and a- are also found in the word á 'of':
- mwaná wá Mphátso 'Mphatso's child'; aná á Mphátso 'Mphatso's children'
The same concords are used in possessive adjectives -ánga 'my', -áko 'your', -áke 'his/her/its/their', -áthu 'our', -ánu 'your (plural or respectful singular), -áwo 'their'/'his/her' (respectful):
- mwaná wángá 'my child'; aná ángá 'my children'
-áwo 'their' is used only of people (-áke is used for things).
Wá 'of' can be combined with nouns or adverbs to make adjectives:
- mwaná wánzérú 'an intelligent child'; aná ánzérú 'intelligent children'
- mwaná ábwino a good child'; aná ábwino 'good children'
In the same way wá 'of' combines with the ku- of the infinitive to make verbal adjectives. Wá + ku- usually shortens to wó-, except where the verb root is monosyllabic:
- mwaná wókóngola 'a beautiful child'; aná ókóngola 'beautiful children'
- mwaná wákúbá 'a thieving child'; aná ákúbá 'thieving children'
-ína 'other' and -ení-éní 'real'
The same w- and a- concords are found with the words -ína 'other' and -ení-éní 'real'. In combination with these words the plural concord a- is converted to e-:
- mwaná wína 'a certain child, another child'; aná éna 'certain children, other children'
- mwaná weníwéní 'a real child'; aná eníéní 'real children'
Double-prefix adjectives
Certain adjectives (-kúlu 'big', -ng'óno 'small'; -(a)múna 'male', -kázi 'female'; -táli 'long', 'tall', -fúpi 'short'; -wisi 'fresh') have a double prefix, combining the possessive concord (wá-) and the number concord (m- or mw-):
- mwaná wáḿkúlu 'a big child'; aná áákúlu 'big children'
- mwaná wáḿng'óno 'a small child'; aná ááng'óno 'little children'
- mwaná wámwámúna 'a male child'; aná áámúna 'male children'
- mwaná wáḿkázi 'a female child'; aná áákázi 'female children'
Historic changes
Early dictionaries, such as those of Rebmann, and of Scott and Hetherwick, show that formerly the number of concords was greater. The following changes have taken place:
- Class 2 formerly had the concord ŵa- (e.g. ŵanthu aŵa 'these people'), but this has now become a- for most speakers.
- Class 8, formerly using dzi- (Southern Region) or bzi/bvi/vi- (Central Region) (e.g. bzaká bziŵíri 'two years'),[62] has now adopted the concords of class 10.
- Class 6, formerly with ya- concords (e.g. mazira aya 'these eggs'),[63] now has the concords of class 2.
- Class 11 (lu-) had already been assimilated to class 5 even in the 19th century, although it still exists in some dialects of the neighbouring language Tumbuka.
- Class 14, formerly with bu- concords (e.g. ufá bwángá 'my flour'),[64] now has the same concords as class 3.
- Class 13 (ti-) had tu- in Rebmann's time (e.g. tumpeni utu 'these small knives'). This prefix still survives in words like tuló 'sleep'.
In addition, classes 4 and 9, and classes 15 and 17 have identical concords, so the total number of concord sets (singular and plural) is now twelve.
Verbs
Summarize
Perspective
Formation of tenses
Tenses in Chichewa are differentiated in two ways, by their tense-marker (or tense-infix), and by their tonal pattern. Sometimes two tenses have the same tense-marker and differ in their tonal pattern alone. In the following examples, the tense-marker is underlined:[65][66]
- ndi-ku-gúla 'I am buying'
- ndí-ma-gúla 'I usually buy'
- ndi-ma-gúla 'I was buying', 'I used to buy'
- ndí-dzá-gula 'I will buy (tomorrow or in future)'
- ndí-ká-gula 'I will buy (when I get there)'
One tense has no tense-marker:
- ndí-gula 'I will buy (soon)'
Tenses can be modified further by adding certain other infixes, called 'aspect-markers', after the tense-marker. These are -má- 'always, usually' -ká- 'go and', -dzá 'come and' or 'in future', and -ngo- 'only', 'just'. These infixes can also be used on their own, as tense-markers in their own right (compare the use of -ma- and -dza- in the list of tenses above). For example:
- ndi-ku-má-gúlá 'I am always buying'[67]
- ndi-ná-ká-gula 'I went and bought'[68]
- ndí-má-ngo-gúla 'I just usually buy'[69]
Compound tenses, such as the following, are also found in Chichewa:[70]
- nd-a-khala ndí-kú-gúla 'I have been buying'
Subject-marker
Chichewa verbs (with the exception of the imperative mood and infinitive) begin with a prefix agreeing grammatically with the subject.[71] This prefix is referred to by some grammarians as the 'subject-marker'.[72]
- (ife) ti-ku-píta 'we are going'
- mténgo w-a-gwa (for *u-a-gwa) 'the tree has fallen'[73]
The subject-marker can be:
- Personal: ndi- 'I', u- 'you (singular)', a- 'he, she', ti- 'we', mu- 'you (plural or polite)', a- 'they'; 'he/she (respectful or polite). (In the perfect tense, the subject-marker for 'he, she' is w-: w-a-pita 'he has gone'.)[74]
- Impersonal: a- (class 1, 2 or 6), u- (class 3 or 14), i- (class 4 or 9), li- (class 5), etc.
- Locative: ku-, pa-, mu-
An example of a locative subject-marker is:
- m'madzí muli nsómba 'in the water there are fish'[75]
Both the 2nd and the 3rd person plural pronouns and subject-markers are used respectfully to refer to a single person:[76]
- mukupíta 'you are going' (plural or respectful)
- apita 'they have gone' or 'he/she has gone' (respectful)
Except in the perfect tense, the 3rd person subject marker when used of people is the same whether singular or plural. So in the present tense the 3rd person subject-marker is a-:
- akupíta 'he/she is going'
- akupíta 'they are going', 'he/she is going' (respectful)
But in the perfect tense wa- (singular) contrasts with a- (plural or respectful):
- wapita 'he/she has gone'
- apita 'they have gone', 'he/she has gone' (respectful)
When the subject is a noun not in class 1, the appropriate class prefix is used even if referring to a person:
- mfúmu ikupíta 'the chief is going' (class 9)
- tianá tikupíta 'the babies are going' (class 13)
Object-marker
An object-marker can also optionally be added to the verb; if one is added it goes immediately before the verb-stem.[77] The 2nd person plural adds -ni after the verb:
- ndí-ma-ku-kónda 'I love you' (ndi = 'I', ku = 'you')
- ndí-ma-ku-kónda-ni 'I love you' (plural or formal)
The object-marker can be:
- Personal: -ndi- 'me', -ku- 'you', -mu- or -m'- 'him, her', -ti- 'us', -wa- or -a- 'them', 'him/her (polite)'.
- Impersonal: -mu- (class 1), -wa- (class 2), -u- (class 3 or 14), etc.
- Locative: e.g. m'nyumbá mu-ku-mú-dzíwa 'you know the inside of the house';[78] but usually a locative suffix is used instead: nd-a-oná-mo 'I have seen inside it'
- Reflexive: -dzi- 'himself', 'herself', 'themselves', 'myself', etc.
When used with a toneless verb tense such as the perfect, the object-marker has a high tone, but in some tenses such as the present habitual, the tone is lost:[79]
- nd-a-mú-ona 'I have seen him'
- ndí-ma-mu-óna 'I usually see him'
With the imperative or subjunctive, the tone of the object-marker goes on the syllable following it, and the imperative ending changes to -e:[80]
- ndi-pátse-ni mpungá 'could you give me some rice?'
- ndi-thándízé-ni! 'help me!'
- mu-mu-thándízé 'you should help him'
Variety of tenses
Chewa has a large number of tenses, some of which differ in some respects from the tenses met with in European languages. The distinction between one tense and another is made partly by the use of infixes, such as -na- and -ku-, and partly by the intonation of the verb, since each tense has its own particular tonal pattern.
Near vs. remote
There are five time-frames (remote past, near past, present, near future, and remote future). The distinction between near and remote tenses is not exact. The remote tenses are not used of events of today or last night, but the near tenses can sometimes be used of events of earlier or later than today:
- ndi-ná-gula 'I bought (yesterday or some days ago)' (remote perfect)
- nd-a-gula 'I have bought (today)' (perfect)
- ndi-ku-gúla 'I am buying (now)' (present)
- ndí-gula 'I'll buy (today)' (near future)
- ndi-dzá-gula 'I'll buy (tomorrow or later)' (remote future)
Perfect vs. past
Another distinction is between perfect and past.[81][82] The two perfect tenses imply that the event described had an outcome which still obtains now. The two past tenses usually imply that the result of the action has been reversed in some way:
Recent time (today):
- nd-a-gula 'I have bought it' (and still have it) (Perfect)
- ndi-na-gúla 'I bought it (but no longer have it)' (Recent Past)
Remote time (yesterday or earlier):
- ndi-ná-gula or ndi-dá-gula 'I bought it' (and still have it) (Remote Perfect)
- ndí-ná-a-gúla or ndí-dá-a-gúla 'I bought it (but no longer have it)' (Remote Past)
When used in narrating a series of events, however, these implications are somewhat relaxed: the Remote Perfect is used for narrating earlier events, and the Recent Past for narrating events of today.[83]
Perfective vs. imperfective
Another important distinction in Chewa is between perfective and imperfective aspect. Imperfective tenses are used for situations, events which occur regularly, or events which are temporarily in progress:
- ndi-nká-gúlá 'I used to buy', 'I was buying (a long time ago)'
- ndi-ma-gúla 'I was buying (today)', 'I used to buy (a long time ago)'
- ndí-zi-dza-gúla 'I will be buying (regularly)'
In the present tense only, there is a further distinction between habitual and progressive:
- ndí-ma-gúla 'I buy (regularly)'
- ndi-ku-gúla 'I am buying (currently)'
Other tenses
One future tense not found in European languages is the -ká- future, which 'might presuppose an unspoken conditional clause':[84]
- ndí-ká-gula 'I will buy' (if I go there, or when I get there)
There are also various subjunctive and potential mood tenses, such as:
- ndi-gulé 'I should buy'
- ndi-zí-gúlá 'I should be buying'
- ndi-dzá-gúlé 'I should buy (in future)'
- ndi-nga-gule 'I can buy'
- ndi-kadá-gula 'I would have bought'
Negative tenses
Negative tenses, if they are main verbs, are made with the prefix sí-. They differ in intonation from the positive tenses.[85] The negative of the -ná- tense has the ending -e instead of -a:
- sí-ndí-gula 'I don't buy'
- sí-ndi-na-gúle 'I didn't buy'
Tenses which mean 'will not' or 'have not yet' have a single tone on the penultimate syllable:
- si-ndi-dza-gúla 'I won't buy'
- si-ndi-na-gúle 'I haven't bought (it) yet'
Infinitives, participial verbs, and the subjunctive make their negative with -sa-, which is added after the subject-prefix instead of before it. They similarly have a single tone on the penultimate syllable:
- ndi-sa-gúle 'I should not buy'[86]
- ku-sa-gúla 'not to buy'
Dependent clause tenses
The tenses used in certain kinds of dependent clauses (such as relative clauses and some types of temporal clauses) differ from those used in main clauses. Dependent verbs often have a tone on the first syllable. Sometimes this change of tone alone is sufficient to show that the verb is being used in a dependent clause.[87][51] Compare for example:
- a-ku-gúla 'he is buying'
- á-kú-gúla 'when he is buying' or 'who is buying'
Other commonly used dependent tenses are the following:
- ndí-tá-gúla 'after I bought/buy'
- ndí-sa-na-gúle 'before I bought/buy'
There is also a series of tenses using a toneless -ka- meaning 'when' of 'if', for example:[88][89]
- ndi-ka-gula 'when/if I buy'
- ndi-ka-dzá-gula 'if in future I buy'
- ndi-ka-má-gúlá 'whenever I buy'
- ndí-ka-da-gúla 'if I had bought'
Verb extensions
After the verb stem one or more extensions may be added. The extensions modify the meaning of the verb, for example:
- gul-a 'buy'
- gul-ir-a 'buy for' or 'buy with' (applicative)
- gul-ir-an-a 'buy for one another' (applicative + reciprocal)
- gul-ik-á 'get bought', 'be for sale' (stative)
- gul-its-a 'cause to get bought, i.e. sell' (causative)
- gul-its-idw-a 'be sold (by someone)' (causative + passive)
The extensions -ul-/-ol- and its intransitive form -uk-/-ok- are called 'reversive'. They give meanings such as 'open', 'undo', 'unstick', 'uncover':
- tseg-ul-a 'open (something)'
- tseg-uk-á 'become open'
- thy-ol-a 'break something off'
- thy-ok-á 'get broken off'
- mas-ul-a 'undo, loosen'
- mas-uk-á 'become loose, relaxed'
Most extensions, apart from the reciprocal -an- 'one another', have two possible forms, e.g. -ir-/-er-, -idw-/-edw-, -its-/-ets-, -iz-/-ez-, -ul-/-ol-, -uk-/-ok-. The forms with i and u are used when the verb stem has a, i, or u. u can also follow e:
- kan-ik-á 'fail to happen'
- phik-ir-a 'cook for someone'
- gul-its-a 'sell'
- sungun-ul-a 'melt (transitive)'
- tseg-ul-a 'open'
The forms with e are used if the verb stem is monosyllabic or has an e or o in it:[90]
- dy-er-a 'eat with'
- bwer-ez-a 'repeat'
- chok-er-a 'come from'
Extensions with o are used only with a monosyllabic stem or one with o:
- thy-ok-á 'get broken off'
- ton-ol-a 'remove grains of corn from the cob'
The extension -its-, -ets- with a low tone is causative, but when it has a high tone it is intensive. The high tone is heard on the final syllable of the verb:
- yang'an-its-its-á 'look carefully'
- yes-ets-á 'try hard'
The applicative -ir-, -er- can also sometimes be intensive, in which case it has a high tone:
- pit-ir-ir-á 'carry on, keep going'
Verbs with -ik-, -ek-, -uk-, -ok- when they have a stative or intransitive meaning also usually have a high tone:
- chit-ik-á 'happen'
- sungun-uk-á 'melt (intransitive), get melted'
However, there are some low-toned exceptions such as on-ek-a 'seem' or nyam-uk-a 'set off'.[91]
Oral literature
Summarize
Perspective
In 1907, Robert Sutherland Rattray, who learned the Chinyanja language with the help of Alexander Hetherwick (author of A Practical Manual of the Nyanja language), published Some Folklore Stories and Songs in Chinyanja, a collection of texts in the Chinyanja language,[92] accompanied by English translations, reflecting the language heard in what was then Central Angoniland in the British Central Africa Protectorate, now Malawi. The texts include cultural and historical narratives, along with folktales, including several stories about Kamba, the trickster tortoise, and Kalulu, the trickster rabbit (hare). These are some of the riddles:[93]
- "Kantu kosanyamulika 'i? Chitunzilunzi." "A little thing, yet that cannot be lifted. A shadow." (#7)
- "Ndamanga nyumba ndi mzati umodzi, n'chiani? Boa." "I built a hut with only one post to prop up the roof. What is that? A mushroom." (#11)
- "Nyumba yopanda komo. Dzira." "A hut without a doorway. An egg." (#19)
- "Mtengo adula lero, m'mawa mwache yuamba kupuka. Tsitsi." "A tree which you cut down today, and the next it begins to sprout. Hair." (#23)
- "Kungatarikitsa, lero lomwe ukafika, n'chiani? Mtima." "However far away it be, this very day this thing reaches there. Memories." (#24)
- "Pita uku, nanenso, ndipite uko, tikomane. Mkuzi." "You go in this direction, I go in that, and we must meet. Belt." (#25)
At the end of the riddle section, Rattray includes a version of the conundrum about the man who must cross a river with a goat, a leopard, and some maize, a traditional African form of the river-crossing puzzle.[94]
Literature
Story-writers and playwrights
The following have written published stories, novels, or plays in the Chewa language:
- William Chafulumira[95]
- Samuel Josia Ntara or Nthala[96]
- John Gwengwe[97]
- E.J. Chadza
- Lula Pensulo[98]
- Steve Chimombo
- Whyghtone Kamthunzi
- Francis Moto
- Bonwell Kadyankena Rodgers
- Willie Zingani
- Barnaba Zingani
- Jolly Maxwell Ntaba[99]
Poets
Town Nyanja (Zambia)
Summarize
Perspective
An urban variety of Nyanja, sometimes called Town Nyanja, is the lingua franca of the Zambian capital Lusaka and is widely spoken as a second language throughout Zambia. This is a distinctive Nyanja dialect with some features of Nsenga, although the language also incorporates large numbers of English-derived words, as well as showing influence from other Zambian languages such as Bemba. Town Nyanja has no official status, and the presence of large numbers of loanwords and colloquial expressions has given rise to the misconception that it is an unstructured mixture of languages or a form of slang.
The fact that the standard Nyanja used in schools differs dramatically from the variety actually spoken in Lusaka has been identified as a barrier to the acquisition of literacy among Zambian children.[100]
The concords in Town Nyanja differ from those in Chichewa described above. For example, classes 5 and 6 both have the concord ya- instead of la- and a-; class 8 has va- instead of za-; and 13 has twa- instead of ta-.[101] In addition, the subject and object marker for "I" is ni- rather than ndi-, and that for "they" is βa- (spelled "ba-") rather than a-.[102]
Sample phrases
| English | Chewa (Malawi and Mashonaland(Zimbabwe))[103] | Town Nyanja (Lusaka)[104] |
|---|---|---|
| How are you? | Muli bwanji? | Muli bwanji? |
| I'm fine | Ndili bwino | Nili bwino / Nili mushe |
| Thank you | Zikomo | Zikomo |
| Yes | Inde | Ee |
| No | Iyayi/Ayi | Iyayi |
| What's your name? | Dzina lanu ndani?[105] | Zina yanu ndimwe bandani? |
| My name is... | Dzina langa ndine... | Zina yanga ndine... |
| How many children do you have? | Muli ndi ana angati? | Muli na bana bangati? ('b' = [ŵ]) |
| I have two children | Ndili ndi ana awiri | Nili na bana babili |
| I want... | Ndikufuna... | Nifuna... |
| Food | Chakudya | Vakudya |
| Water | Madzi | Manzi |
| How much is it? | Ndi zingati? | Ni zingati? |
| See you tomorrow | Tionana mawa | Tizaonana mailo |
| I love you | Ndimakukonda | Nikukonda |
References
Bibliography
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
