Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
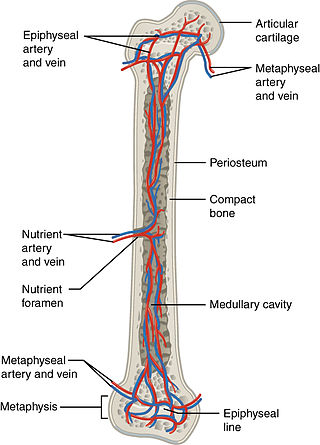
Nutrient artery
Artery entering bone marrow From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The nutrient artery (arteria nutricia, or central artery), usually accompanied by one or two nutrient veins, enters the bone through the nutrient foramen, runs obliquely through the cortex, sends branches upward and downward to the bone marrow, which ramify in the endosteum–the vascular membrane lining the medullary cavity–and give twigs to the adjoining canals. Nutrient arteries are the most apparent blood vessels of the bones.[1]
All bones possess larger or smaller foramina for the entrance of the nourishing blood-vessels; these are known as the nutrient foramina, and are particularly large in the shafts of the larger long bones, where they lead into a nutrient canal, which extends into the medullary cavity (bone marrow cavity).[2]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads