Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas.[1] Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness.[1] Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness.[1] Some forms are slow-growing while others are fast-growing.[1] Unlike Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads contiguously, NHL is largely a systemic illness.[6]
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Non-Hodgkin disease |
 | |
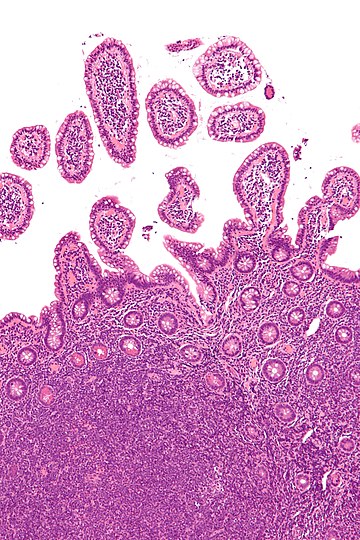
| Micrograph of mantle cell lymphoma, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Terminal ileum. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Hematology and oncology |
| Symptoms | Enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, tiredness, itching[1] |
| Usual onset | 65–75 years old[2] |
| Risk factors | Poor immune function, autoimmune diseases, Helicobacter pylori infection, hepatitis C, obesity, Epstein-Barr virus infection[1][3] |
| Diagnostic method | Bone marrow or lymph node biopsy[1] |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, stem cell transplantation, surgery, watchful waiting[1] |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate 71% (USA)[2] |
| Frequency | 4.3 million (affected during 2015)[4] |
| Deaths | 231,400 (2015)[5] |
Lymphomas are types of cancer that develop from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.[2] Risk factors include poor immune function, autoimmune diseases, Helicobacter pylori infection, hepatitis C, obesity, and Epstein–Barr virus infection.[1][3] The World Health Organization classifies lymphomas into five major groups, including one for Hodgkin lymphoma.[7] Within the four groups for NHL are over 60 specific types of lymphoma.[8][9] Diagnosis is by examination of a bone marrow or lymph node biopsy.[1] Medical imaging is done to help with cancer staging.[1]
Treatment depends on whether the lymphoma is slow- or fast-growing and if it is in one area or many areas.[1] Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, stem-cell transplantation, surgery, or watchful waiting.[1] If the blood becomes overly thick due to high numbers of antibodies, plasmapheresis may be used.[1] Radiation and some chemotherapy, however, increase the risk of other cancers, heart disease, or nerve problems over the subsequent decades.[1]
In 2015, about 4.3 million people had non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and 231,400 (5.4%) died.[4][5] In the United States, 2.1% of people are affected at some point in their life.[2] The most common age of diagnosis is between 65 and 75 years old.[2] The five-year survival rate in the United States is 71%.[2]
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma vary depending upon its location within the body. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow growing, while others are fast growing.[1] Enlarged lymph nodes may cause lumps to be felt under the skin when they are close to the surface of the body. Lymphomas in the skin may also result in lumps, which are commonly itchy, red, or purple. Lymphomas in the brain can cause weakness, seizures, problems with thinking, and personality changes.[10]
While an association between non-Hodgkin lymphoma and endometriosis has been described,[11] these associations are tentative.[12]
Diagnosis
Tests for non-Hodgkin lymphoma include;
- Complete blood count (CBC).
- Blood chemistry studies.
- Hepatitis B and hepatitis C test.
- HIV test.
- CT scan (CAT scan).
- PET scan (positron emission tomography scan).
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
If cancer is found, the following tests may be done to study the cancer cells:
- Immunohistochemistry.
- Cytogenetic analysis.
- Immunophenotyping.
Other tests and procedures may be done depending on the signs and symptoms seen and where the cancer forms in the body.[13][14]
Causes
The many different forms of lymphoma probably have different causes. These possible causes and associations with at least some forms of NHL include:
- Infectious agents:
- Epstein–Barr virus: associated with Burkitt's lymphoma, follicular dendritic cell sarcoma, extranodal NK-T-cell lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.[15]
- Human T-cell leukemia virus: associated with adult T-cell lymphoma.
- Helicobacter pylori: associated with gastric lymphoma.
- HHV-8: associated with primary effusion lymphoma, multicentric Castleman disease.
- Hepatitis C virus: associated with splenic marginal zone lymphoma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.[16]
- HIV infection.[17]
- Some chemicals, like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs),[18][19][20] diphenylhydantoin, dioxin, and phenoxy herbicides.
- Medical treatments, like radiation therapy and chemotherapy.[citation needed]
- Genetic diseases, like Klinefelter syndrome, Chédiak–Higashi syndrome, ataxia–telangiectasia syndrome.[citation needed]
- Autoimmune diseases, like Sjögren syndrome, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus.[21][22]
- Bone trauma and microfractures associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma originating in bone marrow.[23][24]
- Implants, made from hard metals or silicone, associated with anaplastic large cell lymphoma.[25][26]
Familial component
Familial lymphoid cancer is rare. The familial risk of lymphoma is elevated for multiple lymphoma subtypes, suggesting a shared genetic cause. However, a family history of a specific subtype is most strongly associated with risk for that subtype, indicating that these genetic factors are subtype-specific. Genome-wide association studies have successfully identified 67 single-nucleotide polymorphisms from 41 loci, most of which are subtype specific.[27]
HIV/AIDS
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) included certain types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma as AIDS-defining cancers in 1987.[28] Immune suppression rather than HIV itself is implicated in the pathogenesis of this malignancy, with a clear correlation between the degree of immune suppression and the risk of developing NHL. Additionally, other retroviruses, such as HTLV, may be spread by the same mechanisms that spread HIV, leading to an increased rate of co-infection.[29] The natural history of HIV infection has greatly changed over time. As a consequence, rates of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in people infected with HIV has significantly declined in recent years.[17]
Treatment
The traditional treatment of NHL includes chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and stem-cell transplants.[30][31] There have also been developments in immunotherapy used in the treatment of NHL.[32]
Chemotherapy
The most common chemotherapy used for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is R-CHOP, which is a regimen of four drugs (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) plus rituximab.[33]
R-CHP with polatuzumab vedotin, an antibody-drug conjugate, was included as a category 1 preferred regimen for first-line DLBCL by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network in 2023.[34]
Treatment complications
If participants receive stem-cell transplants, they can develop a graft-versus-host disease. When compared with placebo for treating immune mediated inflammation post transplantation and in autoimmunity, mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) may reduce the all-cause mortality if they are used for a therapeutic reason.[35] Moreover, the therapeutic use of MSCs may increase the complete response of acute and chronic GvHD, but the evidence is very uncertain.[35] The evidence suggests that MSCs for prophylactic reason result in little to no difference in the all-cause mortality, in the relapse of malignant diseases, and in the incidence of acute GvHD.[35] The evidence suggests that MSCs for prophylactic reason reduce the incidence of chronic GvHD.[35]
Platelet transfusions may be necessary for those who receive chemotherapy or undergo a stem cell transplantation due to the higher risk for bleeding. When comparing therapeutic/non-prophylactic platelet transfusions to prophylactic platelet transfusions there is little to no difference in the mortality secondary to bleeding and they may result in a slight reduction in the number of days on which a significant bleeding event occurred.[36] The evidence suggests that therapeutic platelet transfusions result in a large increase in the number of people with at least one significant bleeding event and they likely result in a large reduction in the number of platelet transfusions.[36][37]
Other
It is unclear if including aerobic physical exercise, in addition to the standard treatment for adult patients with haematological malignancies, is effective at reducing anxiety and serious adverse effects.[38] Aerobic physical exercises may result in little to no difference in the mortality, in the quality of life and in the physical functioning.[38] These exercises may result in a slight reduction in depression and most likely reduce fatigue.[38]
Prognosis
Prognosis depends on the subtype, the staging, a person's age, and other factors. Across all subtypes, 5-year survival for NHL is 71-74%.[39][40][41]
Epidemiology
Globally, as of 2010, there were 210,000 deaths, up from 143,000 in 1990.[42]
Rates of non-Hodgkin lymphoma increase steadily with age.[21] Up to 45 years NHL is more common among males than females.[43]
Australia
Around 6600 people are diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma in Australia each year.[44]
Canada
In Canada NHL is the fifth most common cancer in males and sixth most common cancer in females. The lifetime probability of developing a lymphoid cancer is 1 in 44 for males, and 1 in 51 for females.[45]
United Kingdom
On average, according to data for the 2014–2016 period, around 13,900 people are diagnosed with NHL yearly. It is the sixth most common cancer in the UK, and is the eleventh most common cause of cancer death accounting for around 4,900 deaths per year.[46]
United States
Age adjusted data from 2012 to 2016 shows about 19.6 cases of NHL per 100,000 adults per year, 5.6 deaths per 100,000 adults per year, and around 694,704 people living with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. About 2.2 percent of men and women will be diagnosed with NHL at some point during their lifetime.[47]
The American Cancer Society lists non-Hodgkin lymphoma as one of the most common cancers in the United States, accounting for about 4% of all cancers.[48]
History
While consensus was rapidly reached on the classification of Hodgkin lymphoma, there remained a large group of very different diseases requiring further classification. The Rappaport classification, proposed by Henry Rappaport in 1956 and 1966, became the first widely accepted classification of lymphomas other than Hodgkin. Following its publication in 1982, the Working Formulation became the standard classification for this group of diseases. It introduced the term non-Hodgkin lymphoma or NHL and defined three grades of lymphoma.[citation needed]
NHL consists of many different conditions that have little in common with each other. They are grouped by their aggressiveness. Less aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas are compatible with a long survival while more aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas can be rapidly fatal without treatment. Without further narrowing, the label is of limited usefulness for people or doctors. The subtypes of lymphoma are listed there.[citation needed]
Nevertheless, the Working Formulation and the NHL category continue to be used by many. To this day, lymphoma statistics are compiled as Hodgkin's versus non-Hodgkin lymphomas by major cancer agencies, including the US National Cancer Institute in its SEER program, the Canadian Cancer Society and the IARC.[citation needed]
References
External links
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.