Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds.[1] While flavonoids (in the narrow sense) have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, neoflavonoids have the 4-phenylchromen backbone with no hydroxyl group substitution at position 2.

Types
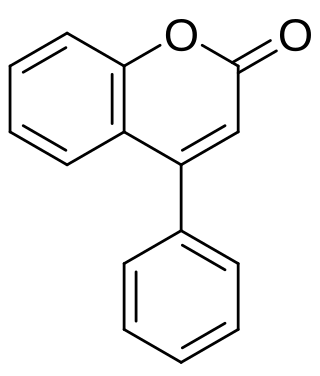
Neoflavonoids include 4-arylcoumarins (neoflavones), 4-arylchromanes, dalbergiones and dalbergiquinols.
- Neoflavones[1] are derived from the 4-phenylcoumarin (or 4-aryl-coumarin) backbone (C15H12O2).[2] The first neoflavone isolated from natural sources was calophyllolide from Calophyllum inophyllum seeds (1951).[3] It is also found in the bark and timber of the plant Mesua thwaitesii, endemic to Sri Lanka.[4]
- Neoflavenes possess the 4-phenylchromen backbone (C15H10O2). Dalbergichromene, extracted from the stem-bark and heartwood of Dalbergia sissoo, is an example of such compounds[5]
Other examples
- Coutareagenin (5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2H-benzo-1-pyran-2-on) found in Hintonia latiflora[6]
- Dalbergin
- Nivetin isolated from Echinops niveus[7]
References
External links
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.