N,N′-Di-2-butyl-1,4-phenylenediamine is an aromatic amine used industrially as an antioxidant to prevent degradation of turbine oils, transformer oils, hydraulic fluids, lubricants, waxes, and greases. It is particularly effective for hydrocarbon products produced by cracking or pyrolysis, which are characterized by high alkene content. It is also used as an polymerisation inhibitor in production of various vinyl monomers such as acrylates.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
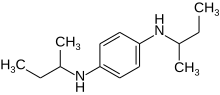
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N′-Di(butan-2-yl)benzene-1,4-diamine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.721 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H24N2 | |
| Molar mass | 220.360 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.942 g/mL at 20 °C[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N,N′-Di-2-butyl-1,4-phenylenediamine has the appearance of a red liquid. It is a skin sensitizer and can be absorbed through skin. It is toxic.
N,N′-Di-2-butyl-1,4-phenylenediamine is the active component of e.g. AO-22, AO-24, AO-29, and VANLUBE antioxidant mixtures, and Santoflex 44PD inhibitor.
References
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.
