The mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve is one of the sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V). It is located in the brainstem. It receives proprioceptive sensory information from the muscles of mastication and other muscles of the head and neck. It is involved in processing information about the position of the jaw/teeth. It is functionally responsible for preventing excessive biting that may damage the dentition, regulating tooth pain perception, and mediating the jaw jerk reflex (by means of projecting to the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve).[1]
| Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve | |
|---|---|
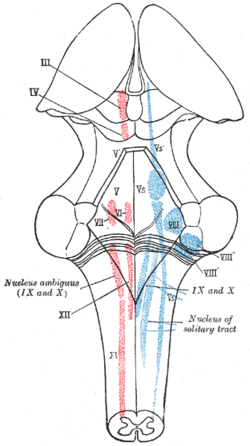 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue. (Trigeminal nerve nuclei are at "V".) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus mesencephalicus nervi trigemini |
| NeuroNames | 558 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1010 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.409 |
| TA2 | 5887 |
| FMA | 54568 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The axons of the neuron cell bodies of this nucleus provide sensory innervation to target tissues directly, whereas other sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve receive their sensory inputs by synapsing with primary sensory neurons in the trigeminal ganglion.[1]
Anatomy
The MNTN is located in the brainstem, more specifically (sources vary) spanning the length of the midbrain[2]/in the caudal midbrain and rostral pons.[1] It is situated (sources vary) near[1]/within[2] the periaqueductal gray, lateral to the cerebral aqueduct.[2]
The mesencephalic nucleus is the only structure in the central nervous system to contain the cell bodies of first order sensory neurons.[2] The mesencephalic nucleus can thus be considered functionally as a primary sensory ganglion embedded within the brainstem,[1] making it neuroanatomically unique.[3]
Microanatomy
Unlike many nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS), the mesencephalic nucleus contains no chemical synapses, neurons instead being electrically coupled.[4] Neurons of this nucleus are pseudounipolar, receiving proprioceptive afferent information from the mandible and sending efferent projections to the trigeminal motor nucleus to mediate the monosynaptic jaw jerk reflex.[5]
Development
The pseudounipolar neurons in the mesencephalic nucleus are embryologically derived from the neural crest. However, instead of joining the trigeminal ganglion, the neurons migrate into the brainstem.[6][7] The MNTN neurons directly receive sensory information, akin to neurons in the dorsal root ganglia.
Function
The MNTN is involved in reflex proprioception of the periodontium[8] and of the muscles of mastication in the jaw[9] that functions to prevent biting down hard enough to lose a tooth. To subserve this reflex protective function, mechanoreceptive nerves in the periodontal ligament sense tooth movement and project to the mesencephalic nucleus. Likewise, afferent fibers from muscle spindles, the sensory organs of skeletal muscle, are stimulated by the stretch of hard contraction of jaw muscles. The temporomandibular joint receptors and the Golgi tendon organs of the jaw muscles do not project to the mesencephalic nucleus.[10] The mesencephalic nucleus is one of four trigeminal nerve nuclei, three sensory and one motor. The other two sensory nuclei are the chief sensory nucleus mediating conscious facial touch and the spinal trigeminal nucleus, mediating pain and temperature in the head, and is of importance in headache. The trigeminal motor nucleus innervates the muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor veli palatini, and tensor tympani.
Clinical significance
Clinically, because of its reflex function, the mesencephalic nucleus can be tested with the jaw jerk reflex. Because of its function in oral proprioception, lesions of the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus cause effects on feeding.[11] The mesencephalic nucleus can be thought of simply as the "nucleus that keeps your teeth in" by preventing one from biting down hard enough to lose a tooth on foods containing e.g. bone, cherry seeds, apricot stones etc.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.
