Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of refractive indices
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
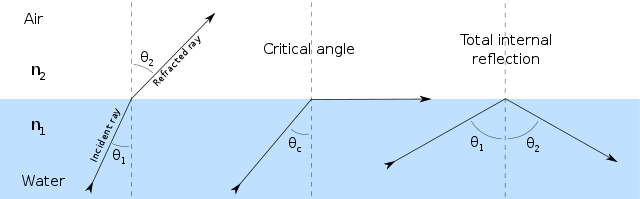
Most of the materials have a well-characterized refractive index, but these indices often depend strongly upon the frequency of light, causing optical dispersion. Standard refractive index measurements are taken at the "yellow doublet" sodium D line, with a wavelength (λ) of 589 nanometers.

There are also weaker dependencies on temperature, pressure/stress, etc., as well on precise material compositions (presence of dopants, etc.); for many materials and typical conditions, however, these variations are at the percent level or less. Thus, it's especially important to cite the source for an index measurement if precision is required.
In general, an index of refraction is a complex number with both a real and imaginary part, where the latter indicates the strength of absorption loss at a particular wavelength—thus, the imaginary part is sometimes called the extinction coefficient . Such losses become particularly significant, for example, in metals at short (e.g. visible) wavelengths, and must be included in any description of the refractive index.
Remove ads
List
Summarize
Perspective
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

