Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of combat vehicles of World War I
List of WWI vehicles From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This is a list of combat vehicles of World War I, including conceptual, experimental, prototype, training and production vehicles. The vehicles in this list were either used in combat, produced or designed during the First World War. World War One saw the start of modern armoured warfare with an emphasis on using motor vehicles to provide support to the infantry.

Key
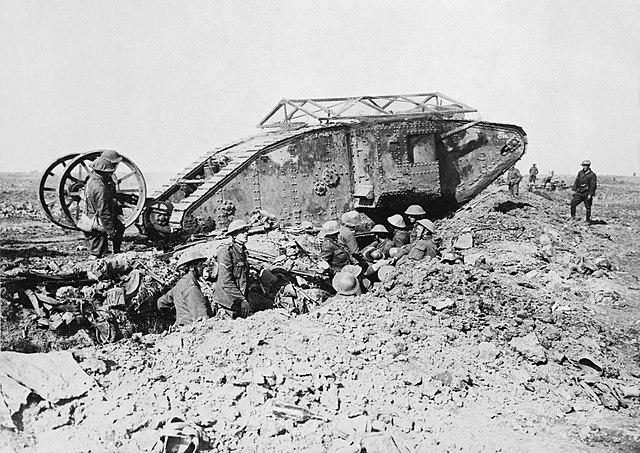
"Little Willie", the first ever completed tank prototype
Renault FT, the war's most produced tank
| * | Concept |
| † | Experimental prototypes |
| ‡ | Entered service post-war |
Tanks
Summarize
Perspective
Tanks came about as means to break the stalemate of trench warfare. They were developed to break through barbed wire and destroy enemy machine gun posts. The British and the French were the major users of tanks during the war; tanks were a lower priority for Germany as it assumed a defensive strategy. The few tanks that Germany built were outnumbered by the number of French and British tanks captured and reused.
- France
- Aubriot Gabet tank †[1]
- FCM A *[2]
- FCM 1A †[3]
- FCM 1B *[4]
- Peugeot tank †[5]
- Renault FT[6]
- Saint-Chamond[7]
- Saint-Chamond 25t *[8]
- Schneider CA1[9]
- Schneider CA2 and CA3 †[10]
- Schneider CA4 *[11]
- Germany
- A7V Sturmpanzerwagen[12]
- A7V-U-1 Sturmpanzerwagen †[13]
- K-Wagen †[14]
- Landpanzerkreuzer *[15]
- Leichter Kampfwagen I †[16]
- Leichter Kampfwagen II †[16]
- Leichter Kampfwagen III *[17]
- Sturmpanzerwagen Oberschlesien †[18]
- Orion Wagen II †[19]
- Orion Wagen III *[19]
- Italy
- Russia
- United Kingdom
- "Big Willie"/"Mother" † – the single tank "Mother" was the prototype of the British Mark I tank[26]
- Flotilla leader tank *[27]
- "Flying Elephant" * – project for a 100-ton well-armoured tank, not built.[28]
- Foster battletank *[27]
- Kupchak tank *[29]
- No.1 Lincoln Machine/"Little Willie" † – the predecessor to "Mother", single tank built[30]
- Macfie landship *[31]
- Mark I[32]
- Mark II – built for training but some used in France [32]
- Mark III – 50 built for training, only used in UK. [32]
- Mark IV – the most produced British tank[33]
- Mark V – improved engine and transmission, entered service late in war [34]
- Mark VI * – intended improved design with new hull, project cancelled in 1917 [35]
- Mark VII †[36]
- Mark X *[37]
- Medium Mark A Whippet[38]
- Medium Mark B[39]
- Medium Mark C ‡[39]
- Medium Mark D † – intended to be a relatively fast tank to take part in "Plan 1919", not developed until after the war.[40]
- United Kingdom & United States
- United States
- CLB 75 Tank †[42]
- Ford 3-Ton M1918 †[43]
- Ford Mark I †[44]
- Holt 200 ton trench destroyer *[45]
- Holt gas–electric tank †[42]
- M1917 light tank ‡[43]
- Skeleton tank †[42]
- Steam tank (tracked) †[42]
Remove ads
Armoured cars and trucks
Summarize
Perspective

Most of the armoured cars of the war were produced by building armoured bodywork over commercial large car and truck chassis.
- Austria-Hungary
- Austro-Daimler armoured car[46]
- Gonsior-Opp-Frank armoured car *[47]
- Junovicz P.A.1[48]
- Romfell armoured car[49]
- Belgium
- Minerva armoured car[50]
- SAVA armoured car[51]
- Canada
- Denmark
- HtK46 armoured car †[54]
- France
- Archer armoured car[55]
- Charron armoured car[56]
- Dion-Bouton armoured car 1914 †[55]
- Dion-Bouton armoured car 1916 †[55]
- Gasnier armoured car †[55]
- Hotchkiss armoured car[54]
- Latil armoured car[55]
- Panhard armoured car[55]
- Peugeot armoured car[57]
- Renault armoured car[57]
- Renault 47mm autocanon[55]
- Vinot Deguinguand armoured car †[55]
- White AM armoured car[55]
- Germany

- Büssing A5P[13]
- Daimler 15[13]
- Ehrhardt E-V/4[58]
- Mannesmann MULAG armoured truck[59]
- Marienwagen II armoured halftrack †[60]
- Italy
- Bianchi armoured car[61]
- Fiat-Terni armoured car[62]
- Lancia 1ZM[61]
- Pavesi 35 PS armoured car[63]
- Ottoman Empire
- Hotchkiss armoured car[54]
- Poland
- Pilsudski armoured car[64]
- Russia
- Armstrong Whitworth armoured car[65]
- Austin-Kegresse armoured car[66]
- Austin-Putilov armoured car[67]
- Fiat-Izorski armoured car[68]
- Izorski-White armoured car[69]
- Fiat-Omsky armoured car[70]
- Garford-Putilov armoured truck[71]
- Isotta-Fraschini-Mgebrov armoured car[72]
- Jeffery-Poplavko armoured truck[73]
- Renault-Mgebrov armoured car[74]
- Russo Balt Izorski C armoured car[75]
- White-Mgebrov armoured car[72]
- United Kingdom
- AC armoured car †[76]
- Austin armoured car[77]
- Delaunay-Belleville armoured car[78]
- Ford Model T armoured car[79]
- Isotta-Fraschini armoured car[80]
- Lanchester armoured car[81]
- Leyland armoured lorry[82]
- Peerless armoured car[83]
- Peerless armoured lorry[84]
- Pierce-Arrow armoured lorry[85]
- Rolls-Royce armoured car[86]
- Seabrook armoured lorry[87]
- Sheffield-Simplex armoured car[88]
- Sizaire-Berwick wind wagon †[89]
- Talbot armoured car[90]
- Wolseley armoured car[91]
- Wolseley CP armoured car[92]
- United States
- Davidson-Cadillac armored car[93]
- King armored car[94]
- Mack armored car †[95]
- White armored car[96]
Remove ads
Self-propelled artillery
- France
- Canon de 75 antiaérien on De Dion-Bouton truck[97][failed verification]
- Renault FT 75 BS[98]
- Renault FT self-propelled gun †[99]
- Renault FT STA self-propelled gun †[99]
- Renault FT STAV self-propelled gun †[99]
- Saint Chamond 120mm L self-propelled cannon †[100]
- Saint Chamond 155mm GPF self-propelled cannon †[100]
- Saint Chamond 194mm GPF self-propelled gun ‡[101] - 50 built from April 1918
- Obusier 220mm de St Chamond sur affût-chenilles St Chamond †[100] - 1 built and tested in July 1918
- Saint Chamond 280mm TR self-propelled mortar ‡[102]
- Canon de 220mm L Mle1917 Schneider †[103] - 1 built
- Germany
- A7V Flakpanzer †[104]
- Leichte Kraftwagengeschutze 7.7cm L-27 flak[105]
- Italy
- Russia

- United Kingdom
- Emplacement Destroyer No. 1, 1A, 2 & 3 *[79]
- Gun Carrier Mark I - carrier based on Mark I tank for 6-inch howitzer or 60-pdr gun.[109]
- Peerless armoured AA lorry[110]
- Pierce-Arrow armoured AA lorry[111] - 40mm QF 2-pounder gun on lorry chassis
- QF 13-pounder 6 cwt AA gun on Thornycroft J lorry[112]
- United States
- Holt 55-1 3-inch AA gun †[113] - delivered in 1917
- Holt Mark I (8-inch howitzer) †[113] - 3 built and tested in 1918
- Holt Mark II (155mm M1918 gun) †[113]
- Holt Mark III (240mm howitzer) †[113]
- Holt Mark IV (240mm howitzer) †[113]
- Christie 3-inch AA gun †[114]
- Christie 8-inch self-propelled howitzer †[114]
Remove ads
Armoured trains
- Austria-Hungary
- MAVAG Typ AE panzerzug[115]
- Belgium
- Light armoured train[116]
- Belgium & United Kingdom
- Heavy "Anglo-Belgian" armoured train[117]
- Germany
- Deutsches Heer armoured train[118]
- Russia
- Zaamurets armoured train[119]
- South Africa
- South African Engineer Corps armoured train[120]

- United Kingdom
- GNR(I) armoured train[120]
- LNWR armoured train ("Norma" and "Alice")[121]
- Royal Navy armoured train[121]
- Simplex armoured train[121]
- Uganda Railway armoured train[122]
Remove ads
Other vehicles
- Canada
- Saczeany tank *[123]

- France
- Aubriot Gabet armoured tractor †[1]
- Boirault machine I and II †[124]
- Breton-Prétot machine (armed tractor) †[124]
- Frot-Turmel-Laffly landship †[124]
- Renault FT TSF (radio tank)[125]
- Souain armoured tractor †[126]
- Germany
- Italy
- Gussalli assault car †[128]
- Russia
- United Kingdom
- AEC B type armoured lorry[130]
- Gun Carrier Mark II *[79]
- Killen-Strait armoured tractor †[131]
- Mark I converted to supply tank[132]
- Mark I fitted with wireless communications [132]
- Mark IX[133]
- Pedrail Machine †[134]
- Salvage Machine[135]
- United States
- Holt 150 ton field monitor *[45]
- Holt G9 armored tractor †[136]
- Steam Wheel "tank" †[137]
- Studebaker supply tank †[42]
Remove ads
See also
References
Bibliography
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads







