List of ancient Greek tribes
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The ancient Greek tribes (Ancient Greek: Ἑλλήνων ἔθνη) were groups of Greek-speaking populations living in Greece, Cyprus, and the various Greek colonies. They were primarily divided by geographic, dialectal, political, and cultural criteria, as well as distinct traditions in mythology and religion. Some groups were of mixed origin, forming a syncretic culture through absorption and assimilation of previous and neighboring populations into the Greek language and customs. Greek word for tribe was Phylē (sing.) and Phylai (pl.), the tribe was further subdivided in Demes (sing. Demos, pl. Demoi) roughly matching to a clan.
The name Pelasgians was used exclusively by the ancient Greek writers, who referred to the populations they considered the ancestors of the Greeks or "pre-Hellenic". Some, mainly later ones, use it to describe purely Greek populations.
With the dominion of land passing on from one tribe to the other, cultural exchange through art and trade, and frequent alliances toward common goals, the ethnic character of the different tribes had become primarily political by the dawn of the Hellenistic period. The Roman conquest of Greece, the subsequent division of the Roman Empire into Greek East and Latin West, as well as the advent of Christianity, molded the common ethnic and political Greek identity once and for all to the subjects of the Greek world by the 3rd century AD.
Ancestors

- Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers
- (?) Proto-Graeco-Phrygians (proposed subgroup of Proto-Graeco-Phrygian speakers)[1]
- (?) Proto-Graeco-Armenians (proposed subgroup of Proto-Graeco-Armenian speakers)[2]
- (?) Proto-Graeco-Aryans (proposed subgroup of Proto-Graeco-Aryan speakers)[3]
- Proto-Greeks (Proto-Greek speakers)
Greek tribes
Summarize
Perspective
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2018) |
Late Bronze Age: Homeric Age of the Iliad (circa 1200 BC)
Hellenes


- Achaeans/Argives/Danaans (Danaoi)/Hellenes/Panhellenes (used as synonym of Greeks by Homer in the Iliad) (Mycenaean Greece before Late Bronze Age collapse and Dorian Invasion)
- Central and Eastern Greek tribes (Aeolians, Achaeans and Ionians)
- Achaeans (Broader sense)
- Central Greek tribes (Aeolians and Achaeans)
- Aeolians
- Acarnanians, Pre-Dorian Acarnanians
- Dulichiumians/Doulicheis (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Taphians and Teleboans - in the Echinades Islands
- Cephallenians - Original dwellers of Cephalonia/Kefalonia, Ithaca (homeland of Odysseus), Leucas/Lefkada and Zakynthos (Southern Ionian Islands) (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Aenianes/Enienes - Pre-Dorian Aenianes of Aenis
- Boeotians
- Aones (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Curetes or Aetolians (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Dryopes - Pre-Dorian dwellers of Doris
- Locrians - Pre-Dorian Locrians (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Phoceans - Pre-Dorian Phoceans (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Thessalians
- Lapiths (Lapíthai) (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships) (Phlegyas was their mythical king)
- Myrmidons (Myrmidónes) (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships) (people of Achilles in the Iliad)
- Perrhaebi (Perraiboí) (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Acarnanians, Pre-Dorian Acarnanians
- Achaeans (Narrower sense) - Pre-Doric people of Peloponnese Peninsula (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Arcadians (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Argives - Pre-Doric people of Argos (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Epeans (el) of Elis (Epeioí) - Pre-Doric people of Elis (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Lacedaemonians - Pre-Doric people of Lacedaemonia, later doric Sparta (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Mycenaeans - Pre-Doric Myceneans, Mycenae was their main settlement (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Symians (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Aeolians
- Eastern Greek tribes (Ionians)
- Ionians
- Oldest tribes (Phylai)
- Agikoreis
- Argadeis
- Geleontes
- Hopletes
- Attics
- Athenians (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Euboeans
- Salamineans (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Oldest tribes (Phylai)
- Ionians
- Central Greek tribes (Aeolians and Achaeans)
- Achaeans (Broader sense)
- Western Greek tribes (Dorians and Magnetes)
- Dorians
- Oldest tribes (Phylai)
- Northwestern Doric Greek tribes
- Magnetes (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Dorians
- Central and Eastern Greek tribes (Aeolians, Achaeans and Ionians)
Iron Age: Archaic and Classical Greece (from circa 800 BC)
Archaic and Classical Greece after Late Bronze Age collapse and Dorian Invasion
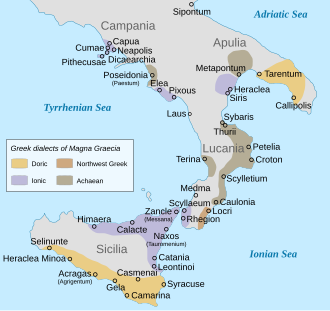
Distribution of Greek dialects in Greece in the classical period.[4]
|
Western group: |
Central group: |
Eastern group:
|
Distribution of Greek dialects in Magna Graecia (Southern Italy and Sicily) in the classical period.
|
Western group: |
Eastern group:
|








Hellenes
- Central and Eastern Greek tribes (Aeolians, Achaeans and Ionians)
- Achaeans (Broader sense) - They lived in Eastern, East Central and Southern Greece (Mycenean Greece) before Dorian migrations or Dorian invasions (after that most Achaeans were displaced or assimilated by Dorians in Southern Greece regions, except for Arcadia). They spoke Mycenean Greek that was the ancestor of Aeolic, Arcado-Cypriot and Ionic Greek dialects of Classical Greece.
- Central Greek tribes (Aeolians and Achaeans)
- Aeolians - They spoke Aeolic Greek dialects (archaic dialects that preserved some Mycenean Greek features).
- Boeotians - They lived in Boeotia (Aonia)
- Dryopes - They lived in Dryopis, later known as Doris (after driven out by the Malians, a Dorian tribe, many scattered to other Greek regions, mostly towards far southern of Euboea Island).
- Thessalians - They lived in Thessaly (Thessalia/Aeolia). Mount Olympus is on the border between Thessaly and Macedon.
- Achaeans, Phtiothis - They lived in Achaea Phthiotis.
- Dolopes? - They lived in Dolopia (mostly considered a Thessalian tribe)
- Histiaeoteans - They lived in Histiaeotis, Thessaly's Northwest district.
- Thessalians Proper - They lived in Thessaliotis.
- Aeolian Diaspora
- Asia Minor Aeolians - They lived in Aeolis, Northwestern Anatolian coast.
- Lesbians - They lived in Lesbos Island.
- Achaeans (Narrower sense) (Arcado-Cyprian tribes) - They spoke Arcado-Cypriot Greek dialects (archaic dialects that preserved some Mycenean Greek features).
- Arcadians - They lived in Arcadia (Central Peloponnese Peninsula) and were a pre-Dorian invasion or Dorian migration Greek tribal confederation.
- Azanes
- Triphylians - They were a group of three tribes (Tri - Three, Phylai -Tribes) that lived in Western Peloponnese, in southern part of Elis (south of Alpheiós river) but saw themselves as Arcadians and not Eleans.
- Amphidolians
- Letrinians
- Marganians
- Achaean Diaspora
- Cypriots - They lived in Cyprus Island
- Pamphylians - They lived in Pamphylia (South-West Anatolia).
- Arcadians - They lived in Arcadia (Central Peloponnese Peninsula) and were a pre-Dorian invasion or Dorian migration Greek tribal confederation.
- Aeolians - They spoke Aeolic Greek dialects (archaic dialects that preserved some Mycenean Greek features).
- Eastern Greek tribes (Ionians)
- Ionians - They spoke Ionic Greek dialects (basis of the Greek Koiné and its descendant Modern Greek).
- Oldest tribes (Phylai)
- Agikoreis
- Argadeis
- Geleontes
- Hopletes
- Attics - They lived in Attica (included ancient Athenians) (Marathon is in Attica)
- Aiantis (named after Ajax) (Aeschylus was a member of this tribe)
- Aigeis (named after Aegeus)
- Akamantis/Acamantis (named after Acamas) (Pericles was a member of this tribe)
- Antiochis (named after Antiochus, son of Heracles) (Socrates was a member of this tribe)
- Erechtheis (named after Erechtheus) (Critias may also have been a member of this tribe)
- Hippothontis (named after Hippothoon)
- Kekropis (named after Cécrops)
- Leontis (named after Leos, son of Orpheus) (Themistocles was a member of this tribe)
- Oineis (named after Oeneus)
- Pandionis (named after Pandion)
- Euboeans (West Ionians) - They lived in Euboea Island.
- Abantes
- Euboean Diaspora
- Chalcidicians, Euboean - They lived in the Peninsula of Chalcidicia (many were descendants from Euboean colonies from the cities of Chalcis and Eretria).
- Catanians - They lived in Catania, Magna Graecia (many were descendants from a Euboean colony from the city of Chalcis).
- Cumaeans - They lived in Cumae, that was founded by settlers from Euboea island (from Chalcis and Eretria cities) in Magna Graecia. It was one of the Greek colonies that most influenced ancient Etruscan and Roman cultures, namely by the introduction of the Alphabet. Cumae by itself was the Metropolis of other poleis in southern Italy coast, including Nea Polis (New City), today's Naples (it was to the West and close of Naples).
- Neapolitans - They lived in Naples (many were descendants from Rhodean and Ionic colonies, the last ones were more numerous).
- Ionians, Cycladian (Central Ionians) - They lived in Cyclades Islands. Delos Island that had the important Delos sanctuary was in this group of islands.
- Cycladian Diaspora
- Chalcidicians, Cycladian - They lived in the Peninsula of Chalcidicia (many were descendants of a colony from Andros Island).
- Cycladian Diaspora
- Salamineans - in Salamis/Salamina Island
- Ionian Diaspora
- Asia Minor Ionians (East Ionians) - They lived in Ionia, Western Anatolian coast.
- Oldest tribes (Phylai)
- Ionians - They spoke Ionic Greek dialects (basis of the Greek Koiné and its descendant Modern Greek).
- Central Greek tribes (Aeolians and Achaeans)
- Achaeans (Broader sense) - They lived in Eastern, East Central and Southern Greece (Mycenean Greece) before Dorian migrations or Dorian invasions (after that most Achaeans were displaced or assimilated by Dorians in Southern Greece regions, except for Arcadia). They spoke Mycenean Greek that was the ancestor of Aeolic, Arcado-Cypriot and Ionic Greek dialects of Classical Greece.
- Western Greek tribes (Dorians and Macedonians)
- Dorians - They spoke Doric Greek dialects (that were not descendants of Mycenean Greek but from a common Proto-Greek language).
- Northwestern Doric Greek tribes - They spoke North-West Doric Greek dialect
- Acarnanians, Northwestern Greek - They lived in Acarnania (this region had two groups of Greeks: the native Northwestern Greek Acarnanians and the Dorians Proper Acarnanians, many of whom were descendants from Corinthian colonies).
- Achaean Dorians - Many were Achaeans assimilated by Dorians. They spoke a Northwest Greek dialect but with a stronger Achaean Greek substrate. They spoke Achaean Doric Greek (not to be confused with Achaean Greek).
- Achaean Dorians of Peloponnese - They lived in Achaea (whose older name was Aegialus/Aegialea and was dwelt by Ionians) (North Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Achaean Dorians Diaspora
- Crotoneans - They lived in Crotone (Eastern Calabria coast), Magna Graecia (many were descendants from an Achaean colony from the city of Rhypes).
- Achaean Dorians Diaspora
- Achaean Dorians of the Islands
- Doulicheis - Older dwellers of Leucas/Lefkada Island (before Corinthian colonization).
- Ithacians - They lived in Ithaca Island (the land of the legendary Odysseus, the main character of the Odyssey and also one of the main ones in the Iliad whose author is traditionally thought to be Homer).
- Kefalloneis - They lived in Kephalonia Island.
- Zakynthians - They lived in Zakynthos Island.
- Achaean Dorians of Peloponnese - They lived in Achaea (whose older name was Aegialus/Aegialea and was dwelt by Ionians) (North Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Aenianians - They lived in Aeniania/Ainis.
- Aetolians/Curetes - They lived in Aetolia.
- Amphilochians - They lived in Amphilochia.
- Eleans - They lived in Elis (West Peloponnese Peninsula). Olympia, where the Ancient Olympic Games were held, was in Elis.
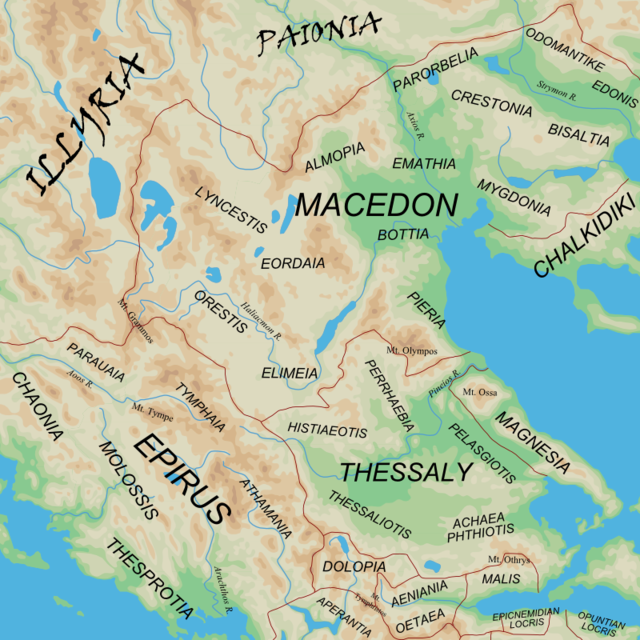
- Epirotes (Epirotic Dorians) - They lived in Epirus.
- Amantes[5] (?) (there is ongoing debate on if the tribe was Epirote Greek or Illyrian.)
- Atintanes[6] (?) (there is ongoing debate on if the tribe was Epirote Greek or Illyrian.)
- Chaonians - They lived in Chaonia.
- Subtribes or Clans: Dexaroi
- Molossians - A tribal confederation. They lived in Molossis/Molossia.
- Apheidantes - They were named after king Apheidas.
- Arktanoi[7]
- Athamanians (or Athamanes) - They lived in Athamania
- Dodonaioi or Selloi[8] - Dodona sanctuary and oracle was in their land.
- Orestaes - They lived in Orestis.
- Parauaei/Paroraioi - They lived in Parauaea, Northern Pindus Mountains.
- Paroraioi (Paroraei) - They lived in the western slopes of Mount Tymphe, Northern Pindus Mountains.
- Pelagones[9] - They lived in Pelagonia.
- Talares - They lived on Mount Pindus and in the neighborhood of Mount Tomarus.
- Tymphaeans - They lived in Tymphaea, eastern slopes of Mount Tymphe.
- Thesprotians - They lived in Thesprotia.
- Locrians - They lived in Locris.
- Malians - They lived in Malia/Malis. Thermopylae was in their land.
- Oetaeans - They lived in Oetaea, included Mount Oeta.
- Phoceans - They lived in Phocis. Delphi sanctuary and oracle was in their land (on the southern slopes of Mount Parnassus).
- Dorians Proper They spoke Doric Greek dialects.
- Oldest tribes (Phylai)
- Argives - They lived in Argolis (East Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Corinthians - They lived in Corinthia (Isthmus of Corinth and North-East Peloponnese Peninsula). Many Greek colonies were of Corinthian origin (i.e. Corinth was the Metropolis - Mother City, the origin of many Greek colonies).
- Corinthian Diaspora
- Acarnanians, Dorians Proper - They lived in Acarnania (this region had two groups of Greeks: the native Northwestern Greek Acarnanians and the Dorians Proper Acarnanians, many of whom were descendants from Corinthian colonies).
- Ambracians - Descendants of a Corinthian colony. They lived in Ambracia.
- Kerkyreans/Corcyraeans - Descendants of a Corinthian colony. They lived in Kerkyra/Corfu (Corcyra). (Phaeacians may have been the original inhabitants and called their island Scheria).
- Leucadians - Descendants of a Corinthian colony. They lived in Leucas (Lefkada) Island.
- Syracusans - They lived in Syracuse in South-East Sicily Island, Magna Graecia (many were descendants from a Corinthian colony).
- Corinthian Diaspora
- Cretans - They lived in Crete Island.
- Cythereans - They lived in Cythera (Kythera/Kythira) Island, south of Peloponnese Peninsula.
- Dorians (of Doris) - They lived in Doris (Upper Cephissus river valley). They were viewed as a people close to the land were Dorians originated - roughly south Epirus and Aetolia in Northwest Greece (when they migrated towards south).
- Laconians - They lived in Laconia (South Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Spartans-Lacedaemonians - They lived in Sparta/Lacedaemon a part of Laconia (South Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Spartan Diaspora
- Tarantinoi - They lived in Taranto, Magna Graecia (many were descendants from a Spartan colony).
- Spartan Diaspora
- Spartans-Lacedaemonians - They lived in Sparta/Lacedaemon a part of Laconia (South Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Megareans - They lived in Megaris.
- Messenians - They lived in Messenia (South-West Peloponnese Peninsula).
- Thereans - They lived in Thera/Thira Island (Santorini).
- Dorian Diaspora
- Northwestern Doric Greek tribes - They spoke North-West Doric Greek dialect
- Dorians - They spoke Doric Greek dialects (that were not descendants of Mycenean Greek but from a common Proto-Greek language).
- Macedonians-Magnetes
- Macedonians (Makedónes) - They lived in Ancient Macedonia and may have spoken a version of the Doric dialect.
- Argeads - According to their oral tradition their tribe originally came from Argos, in Argolis, Eastern Peloponnese Peninsula (Argeads = Argives) (origin of the Macedonian ruling dynasty - The Argeads - House of Argos).
- Elimiotai[9] - They lived in Elimiotis/Elimeia.
- Eordeans - They lived in Eordaia.
- Lyncestai - They lived in Lynkestis.
- Magnetes - They lived in Magnesia (most of Thessaly's coastal region). They were seen by ancient Greeks as a people that shared a common ancestor with the Macedonians.
- Macedonians (Makedónes) - They lived in Ancient Macedonia and may have spoken a version of the Doric dialect.
Pre-Greek and non-Greek tribes (later Hellenized)
Summarize
Perspective
Pre-Greek and non-Greek tribes who became hellenized and whom some of the later Greek tribes claimed descent from
- Anatolians?
- Cadmeans
- Eteocypriots ("True Cypriots") - They lived scattered through Cyprus island.
- Minoan Cretans (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Eteocretans? ("True Cretans") - They lived in the eastern region of Crete island.
- Bottiaeans? - They originally lived in Bottiaea, after Macedonian conquest many of them migrated to Bottike
- Minyans (Minyes) (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships)
- Mysians?
- Pelasgians (mentioned in Iliad's Catalogue of Ships and in Trojan Battle Order) - They lived scattered through several regions of ancient Greece (like Pelasgiotis) in enclaves.
- Aethices/Aethikes - They lived on Mount Pindus and in the neighborhood of Mount Tomarus.
- Attican Pelasgians - They lived in Attica in scattered communities. Later they were fully assimilated into an Attican Ionian Greek ethnic identity.
- Crestones - They lived in Crestonia (southern slopes of Bertiscus Mount, today's Vertiskos Mount; Vertiskos village is on the slopes), to the north of the Mygdonia, to the northeast of Thessalonika).
- Cretan Pelasgians - They lived in parts of Crete island along with other peoples of the island: Eteocretans ("True Cretans" or Cretans proper), Achaean and Dorian Greeks and the Cydonians (of the city of Cydonia/modern Chania).
- Hellespontus Pelasgians - They lived in the Thracian Chersonesus (today's Gallipoli Peninsula) and some parts on the coast of the other side of the Hellespontus or Dardanelles strait (on the Asian side) before the Thracian expansion and conquest of that peninsula.
- Lemnian Pelasgians - They lived in Lemnos island, in the North Aegean Sea. They were conquered by Athens at the end of the 6th century BC and later assimilated into an Ionian Greek identity. Some of them moved to the peninsula's promontory of Actē (today's Mount Athos).
- Cynurians - They lived in Cynuria (Cynuria had two enclaves, one on the coast of eastern Peloponnese Peninsula, between Laconia and Argolis, and another inland, in the far southwestern Arcadia, also called Parrhasia) but it is not certain if Cynurians of East Peloponnese coast and Cynurians of the inland (Arcadia) were the same people, two branches of an original people or even if they were directly related.
- Arcadian Cynurians/Inland Cynurians (Arcadian Pelasgians/Parrhasia Pelasgians) - They lived in far southwestern Arcadia (an inland region of Peloponnese), that was also called Parrhasia, around Mount Lykaion/Lycaeus.
- East Peloponnese Coastal Cynurians - They lived on the coast of eastern Peloponnese Peninsula, from the coast to the eastern slopes of Mount Parnon.
- Hyantes Pelasgians (legendary or partly based on a true people and historical events) - Former Pelasgians inhabitants of Boeotia, from which country they were expelled by the followers of Cadmus (Peck; Pliny's Natural History, iv.12).
- Pelasgiotes - They lived in Pelasgiotis (eastern Thessaly that included Thessaly's own capital Larissa).
- Propontis Pelasgians - They lived in some islands (Marmara, Aphousia) and parts of the southern coast of the Propontis (today's Marmara Sea), mostly in Cyzicus.
- Samothracian Pelasgians - They lived in the island of Samothrace in the North Aegean Sea, south of Thrace. They were conquered by Athens at the beginning of the 5th century BC and later assimilated into an Ionian Greek identity.
- Phrygians?
- Thracians?
- Pieres - They originally lived in Pieria, after Macedonian conquest many of them migrated to Pieris
- Tyrrhenians?
- Hellenistic Cultures
- Greco-Bactrians - A small Hellenistic Kingdom created after the conquest of Macedonia.
- Indo-Greeks - Another Hellenistic Kingdom which revolted against the Seleucid empire.
- Dayuans - The descendants of the Greco-Bactians. They were conquered by the Chinese and the Kossands.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.