Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Left coronary artery
Artery supplying blood to the left side of the heart muscle From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The left coronary artery (LCA, also known as the left main coronary artery, or left main stem coronary artery) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and supplies blood to the left side of the heart muscle.[citation needed] The left coronary artery typically runs for 10–25 mm, then bifurcates into the left anterior descending artery, and the left circumflex artery.[1]

The part that is between the aorta and the bifurcation only is known as the left main artery (LM), while the term "LCA" might refer to just the left main, or to the left main and all its eventual branches.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Structure
Variation
Sometimes, an additional artery arises at the bifurcation of the left main artery, forming a trifurcation; this extra artery is called the ramus or intermediate artery.[2]
A "first septal branch" is sometimes described.[3]
Additional images
This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. |
- Left coronary artery
- Cardiac vessels
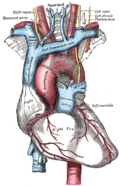
- The aortic arch and its branches
- Diagram of the arch
- Human heart with coronary arteries
- Heart left lateral coronaries diagram
- Diagram of a myocardial infarction
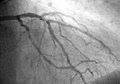
- A coronary angiogram that shows the LMCA, LAD, and LCX
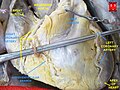
- Autopsy specimen showing the coronary ostia and proximal segments of the coronary arteries. Compare with Gray's Anatomy drawing above.
- Left coronary artery
- Left coronary artery. Plastination technique
- Left coronary artery. Plastination technique
Remove ads
See also
- Coronary circulation
- Pete Maravich – American basketball player whose congenital lack of a left coronary artery lead to his death at age 40
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads