Kamuysaurus
Genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Kamuysaurus is a genus of herbivorous edmontosaurin saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaur from Late Cretaceous Maastrichtian marine deposits of the Yezo Group (Hakobuchi Formation) in the Hobetsu area near the town of Mukawa, Hokkaido in Japan.[1][2]
| Kamuysaurus Temporal range: Early Maastrichtian, | |
|---|---|
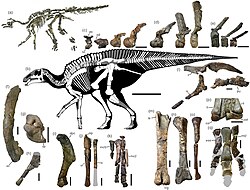 | |
| Known remains of Kamuysaurus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | †Ornithischia |
| Clade: | †Ornithopoda |
| Family: | †Hadrosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Saurolophinae |
| Tribe: | †Edmontosaurini |
| Genus: | †Kamuysaurus Kobayashi et al., 2019 |
| Type species | |
| †Kamuysaurus japonicus Kobayashi et al., 2019 | |
Discovery
Summarize
Perspective

In 2003, amateur paleontologist Yoshiyuki Horita at the Shirafunezawa Creek discovered the tail of a euornithopod. An entire skeleton was in 2013 and 2014 uncovered by teams of the Hobetsu Museum and the Hokkaido University Museum.[1] The find was nicknamed Mukawaryu,[3] the "Dragon of Mukawa".
In 2019, the type species Kamuysaurus japonicus was named and described by Professor Yoshitsugu Kobayashi, Tomohiro Nishimura, Ryuji Takasaki, Kentaro Chiba, Anthony Ricardo Fiorillo, Kohei Tanaka, Tsogtbaatar Chinzorig, Tamaki Sato and Kazuhiko Sakurai. The generic name is derived from kamuy, meaning "deity" in Ainu, the language of the original inhabitants of Hokkaido. The specific name japonicus, "japanese" in Neo-Latin, refers to the provenance from Japan.[1]
The holotype, HMG-1219, has been found in a marine layer of the Hakobuchi Formation, part of the Yezo Group, dating from the early Maastrichtian, between 72.1 and 70.6 million years old. It consists of a nearly complete skeleton with skull, only missing the snout, parts of the sacral vertebrae and phalanges.[1] Containing over 60% of the skeletal elements and 80% of the bone mass, it is, together with the smaller skeleton of Fukuivenator, one of the most complete dinosaur skeletons found in Japan.[3] The bones were found on a surface of seven by four metres (23 by 13 ft) and were partially articulated, though sometimes damaged by erosion. The holotype represents an adult individual of at least nine years of age. It was likely washed into the sea as a carcass.[1]
Description

Kamuysaurus was about eight metres (26 ft) long. From the width of its thighbone, its weight has been estimated at 4 or 5.3 tonnes (3.9 or 5.2 long tons; 4.4 or 5.8 short tons), dependent on its having been bipedal or quadrupedal respectively.[1][3]

The describing authors indicated some distinguishing traits. Three of these were autapomorphies, unique derived characters. On the quadrate bone, the notch at the opening separating it from the quadratojugal bone, is located at a very low position, at three quarters of the shaft length measured from the top of the element. This is unique for the Hadrosauridae as a whole. The surangular bone of the lower jaw has only a short ascending branch, not reaching the coronoid process. The sixth tot thirteenth back vertebrae have neural spines that are inclined to the front.[1]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
