Remetea Mare
Commune in Timiș, Romania From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Commune in Timiș, Romania From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remetea Mare (formerly Remetea Timișană;[4] Hungarian: Temesremete; German: Großeinsiedel or Großremete) is a commune in Timiș County, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Ianova and Remetea Mare (commune seat).
Remetea Mare | |
|---|---|
 Location in Timiș County | |
| Coordinates: 45°47′N 21°23′E | |
| Country | Romania |
| County | Timiș |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2024) | Ilie Golubov[1] (PSD) |
| Area | 58.15 km2 (22.45 sq mi) |
| Population (2021-12-01)[3] | 2,908 |
| • Density | 50/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Time zone | EET/EEST (UTC+2/+3) |
| Postal code | 307350–307353 |
| Vehicle reg. | TM |
| Website | www |
Remetea Mare is located in the center of Timiș County, 12 km (7.5 mi) east of Timișoara. It is crossed by DN6 (E70) and the Bega Canal. It borders Pișchia to the northeast, Recaș to the east, Bucovăț to the south and Giarmata to the west. The commune covers an area of 58.15 ha (143.7 acres).[2]

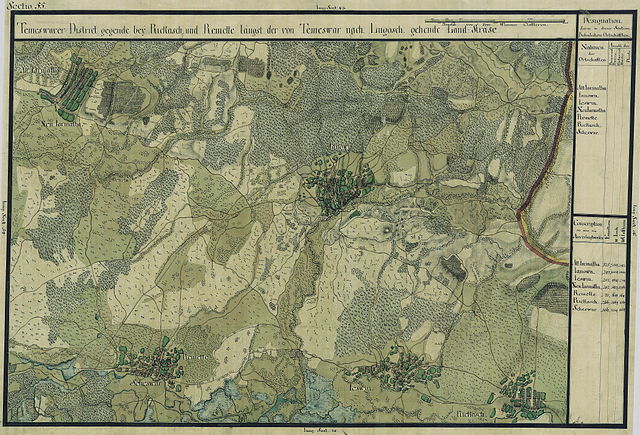
Remetea Mare was first mentioned in 1333 as Remete,[5] but most likely the village is much older. The area has been inhabited since the first Iron Age (Hallstatt culture, c. 1200–300 BC), as evidenced by recent archaeological discoveries.[6] The village was called Remetea Timișană, an alternative name used until now. In the Middle Ages, there would have been a town (market) called Sasvár, mentioned in the papal tithe records from 1332–1337. Sasvár was allegedly guarded by a fortress with a watchtower that aimed to protect the Timișoara Fortress from external attacks. The Sasvár Fortress, meaning "Fortress of the Eagles", was demolished immediately after the occupation of Banat by the Ottomans. Other details about this settlement are not known, but in popular parlance the name of a place known as Șușioara has been preserved.[7]
During the Turkish occupation of Banat, no information is known about the settlement. It is only on Count Mercy's map from 1723 that the name Remeta appears, designating the estates here, one of which belongs to the Ambrózy family.[8] The modern history of the locality is linked to the name of this family. Initially they sold the estate to other owners, but then they recovered it, and in 1720 Baron László Ambrózy built a mansion which is still preserved today. In 1848 this mansion served as a field hospital.[7]
Although located in the immediate vicinity of Timișoara, on the road that connected the capital of Banat with Lugoj, Remetea Mare was inhabited mainly by Romanians, although there were also inhabitants of other nationalities, especially Germans and Hungarians. In 1911, the Romanians built their new Orthodox church.
In the interwar period it was rounded to Plasa Chișoda, Timiș-Torontal County, it had a national house, a choir, a cultural society and the St. George Society.[7]
Ianova is about as old as Remetea Mare. The first recorded mention of Ianova dates from 1333 (Jenev).[5] The presence of Serbs was noticed very early here, probably in the 11th century. During the Middle Ages it was inhabited and ruled by various local noblemen, as evidenced by the numerous feudal documents of change of ownership. In Ianova are the ruins of a medieval fortification dating from the 14th–16th centuries and is located in the south of the village, in the place called "Turkish fortress" (Romanian: cetatea turcească).[9]
It was inhabited during the Ottoman occupation, as in 1690 it is mentioned as Jenovo.[5] On Count Mercy's map from 1723–1725 it is mentioned as Janova, being inhabited by Romanians. This name was kept until 1893 when it was changed to Margitfalva, in honor of the village owner, Margit, wife of István Károlyi.[7] Later it was also called Temesjenő.
In the mid-19th century, when Ianova was owned by the Csekonics family, the village was colonized with Germans and Hungarians. In 1968 it was incorporated in the commune of Remetea Mare, together with Bucovăț and Bazoșu Nou.
Remetea Mare had a population of 2,302 inhabitants at the 2011 census, up 9% from the 2002 census. Most inhabitants are Romanians (92.18%), with a minority of Hungarians (1.39%). For 5.73% of the population, ethnicity is unknown.[10] By religion, most inhabitants are Orthodox (86.4%), but there are also minorities of Roman Catholics (3.34%) and Pentecostals (2.65%). For 5.73% of the population, religious affiliation is unknown.[11]
| Census[12] | Ethnic composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Population | Romanians | Hungarians | Germans | Serbs |
| 1880 | 2,830 | 2,417 | 134 | 226 | 18 |
| 1890 | 3,254 | 2,374 | 359 | 411 | 76 |
| 1900 | 3,212 | 2,272 | 424 | 425 | 51 |
| 1910 | 3,196 | 2,236 | 512 | 396 | 47 |
| 1920 | 2,894 | 2,013 | 445 | 392 | – |
| 1930 | 2,913 | 2,200 | 349 | 301 | 17 |
| 1941 | 2,852 | 2,187 | 304 | 298 | – |
| 1956 | 2,629 | – | – | – | – |
| 1966 | 2,627 | 2,248 | 265 | 73 | 8 |
| 1977 | 2,581 | 2,310 | 198 | 45 | 2 |
| 1992 | 1,961 | 1,825 | 108 | 11 | 1 |
| 2002 | 2,111 | 1,982 | 88 | 11 | 1 |
| 2011 | 2,302 | 2,122 | 32 | 3 | 7 |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.