Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
2007 Atlantic hurricane season
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was the first season since 2003 to feature tropical activity both before and after the official bounds of the season. There were an above-average number of named storms during the season – 15, most of them were weak and short-lived. Despite the predominance of weak systems, this was the first season on record to feature more than one Category 5 landfalling hurricane. This would not happen again until 2017. It produced 17 tropical cyclones, 15 tropical storms, six hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. It officially started on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean, although as shown by Subtropical Storm Andrea and Tropical Storm Olga in early May and early December, respectively, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. The first system, Subtropical Storm Andrea, developed on May 9, while the last storm, Tropical Storm Olga, dissipated on December 13. The most intense hurricane, Dean, was, at the time, the third most intense landfalling Atlantic storm on record. It was the second on record in which an Atlantic hurricane, Felix, and an eastern Pacific hurricane, Henriette, made landfall on the same day. September had a then record-tying eight storms, until it was surpassed in 2020. However, the strengths and durations of most of the storms were low.
Remove ads
Pre-season forecasts by Colorado State University called for 14 named storms and 7 hurricanes, of which three were expected to attain major hurricane status. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) later issued its initial forecast, which predicted 13 to 17 named storms, 7 to 10 hurricanes and three to five major hurricanes. After several revisions in the projected number of storms, NOAA and CSU lowered their forecasts by the middle of the season.
Several storms made landfall or directly affected land. Hurricanes Dean and Felix made landfall at Category 5 intensity, causing severe damage in parts of Mexico and Central America, respectively. Both storm names, as well as Noel, the name of a hurricane that affected the Caribbean, were retired from the naming list of Atlantic hurricanes. The United States was affected by five cyclones, although the storms were generally weak; three tropical depressions and only two tropical storms, Barry and Gabrielle, and one hurricane, Humberto, made landfall in the country. Elsewhere, three storms directly affected Canada, although none severely. The combined storms killed at least 478 people and caused about $3.42 billion (2007 USD, 5.19 billion 2025 USD) in damage.[nb 1]
Remove ads
Seasonal forecasts
Summarize
Perspective
| Source | Date | Named storms |
Hurricanes | Major hurricanes |
| CSU | Average (1950–2000)[1] | 9.6 | 5.9 | 2.3 |
| NOAA | Average (1950–2005)[2] | 11.0 | 6.2 | 2.7 |
| Record high activity[3] | 30 | 15 | 7 | |
| Record low activity[3] | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| CSU | December 8, 2006 | 14 | 7 | 3 |
| CSU | April 3, 2007 | 17 | 9 | 5 |
| NOAA | May 22, 2007 | 13–17 | 7–10 | 3–5 |
| CSU | May 31, 2007 | 17 | 9 | 5 |
| UKMO | June 19, 2007 | 10* | N/A | N/A |
| CSU | August 3, 2007 | 15 | 8 | 4 |
| NOAA | August 9, 2007 | 13–16 | 7–9 | 3–5 |
| CSU | September 4, 2007 | 15 | 7 | 4 |
| CSU | October 2, 2007 | 17 | 7 | 3 |
| Actual activity | 15 | 6 | 2 | |
| * July–November only: 12 storms observed in this period. | ||||
Philip J. Klotzbach, William M. Gray, and their associates at Colorado State University issue forecasts of hurricane activity each year, separately from NOAA. Klotzbach's team, formerly led by Gray, determined the average number of storms per season between 1950 and 2000 to be 9.6 tropical storms, 5.9 hurricanes, and 2.3 major hurricanes (storms exceeding Category 3 on the Saffir–Simpson scale).[1] A normal season, as defined by NOAA, has 9 to 12 named storms, of which five to seven reach hurricane strength, and one to three become major hurricanes.[2]
Pre-season forecasts
On December 8, 2006, Klotzbach's team issued its first extended-range forecast for the 2007 season, predicting above-average activity (14 named storms, seven hurricanes, three of Category 3 or higher).[1] It listed a 64 percent chance of at least one major hurricane striking the U.S. mainland. This included a 40 percent chance of at least one major hurricane strike on the East Coast, including the Florida peninsula, and a 40 percent chance of at least one such strike on the Gulf Coast from the Florida Panhandle westward. The potential for major hurricane activity in the Caribbean was forecast to be above average, and the team predicted that El Niño, associated with reduced hurricane activity in the Atlantic, would dissipate by the active portion of the season.[1]
On April 3 a new forecast was issued, calling for a very active hurricane season of 17 named storms, nine hurricanes and five intense hurricanes.[4] The increase in the forecast was attributed to the rapid dissipation of El Niño conditions. The team also forecast a neutral or weak-to-moderate La Niña and noted that sea surface temperatures were much higher than average.[5] The estimated potential for at least one major hurricane to affect the U.S. was increased to 74 percent; the East Coast potential increased to 50 percent, and from the Florida Panhandle westward to Brownsville, Texas, the probability rose to 49 percent.[5] However, the team's report noted that while they predicted an active season, it was not suggesting that 2007 would be "as active as the 2004 and 2005 seasons".[4]
Midseason outlooks
On June 19 the UK Met Office (UKMO) issued a forecast of 10 tropical storms in the July to November period with a 70 percent chance that the number would be in the range of 7 to 13.[6] On August 3, 2007, Klotzbach's team lowered its season estimate to 15 named storms, of which eight were to become hurricanes and four to become major hurricanes. Team members noted that conditions had become slightly less favorable for storms than earlier in the year. Sea surface temperature anomalies were cooler, and several Saharan Air Layer events had suppressed development of tropical cyclones. El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) conditions were also noted to have been slightly cooler.[7]
On August 9, 2007, NOAA revised its season estimate slightly downwards to 13 to 16 named storms, of which seven to nine were to be hurricanes, and three to five major hurricanes. However, the agency reaffirmed its prediction of an above-average season, citing warmer-than-normal sea surface temperatures in parts of the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean and the likelihood of La Niña conditions during the peak of the season.[8]
Remove ads
Seasonal summary
Summarize
Perspective

Only two major hurricanes—storms of Category 3 intensity or higher—formed during the season, the least since the 1997 season, although tied with the 2006 and 2002 seasons. Named storms were active for 33.50 days during the season, the lowest number of active days since the 1994 season. There were only 11.25 days with active hurricanes, the lowest value since the 2002 season. Despite this, the number of days with major hurricanes was above the long-term average. Four named storms made landfall on the U.S. during the year, but damage from those storms totaled to only about $82 million (2007 USD); this was the least damage the U.S. saw from any Atlantic hurricane season since the 1990 season.[9] The season was one of only eight Atlantic hurricane seasons to produce two Category 5 equivalent hurricanes, the others being the 1932, 1933, 1961, 2005, 2017, 2019 and 2024 seasons. The two Category 5 hurricanes, Dean and Felix, both reached Category 5 strength on two separate occasions, and both made landfall at Category 5 intensity, making the 2007 season the first to feature two hurricanes doing each, both of which would not be repeated until 2017. When Hurricane Felix was upgraded to a Category 5 storm on September 2, it became the eighth to form in this basin since 2000. This gave the decade more hurricanes of such strength than any other on record.[10] Hurricane Humberto was the first hurricane to make landfall in Texas since Hurricane Claudette in 2003.[9]
Overall, the season's activity was reflected with a cumulative accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) rating of 74, which is below the long-term average of 93, and the lowest since 2002.[11] ACE is, broadly speaking, a measure of the power of the hurricane multiplied by the length of time it existed, so storms that last a long time, as well as particularly strong hurricanes, have high ACEs. ACE is only calculated for full advisories on tropical systems at or exceeding 34 knots (39 mph, 63 km/h) or tropical storm strength. Although officially, subtropical cyclones, such as Andrea or the initial portions of Gabrielle, Jerry, and Olga, are excluded from the total,[12] the figure above includes periods when storms were in a subtropical phase.
Remove ads
Systems
Summarize
Perspective
Subtropical Storm Andrea
The first storm of the season, Subtropical Storm Andrea, originated from a large extratropical cyclone that formed off the mid-Atlantic coast on May 6. It deepened steadily along a cold front that pushed through Florida. When the system lost most of its baroclinic support, development ceased until its low moved into warmer waters near the Bahamas. However, interaction between the low and a strong high-pressure system to the north generated hurricane-force winds in the system. Decreasing vertical wind shear allowed the storm to generate deeper convection much closer to the center.[13] By May 9 the previously extratropical cyclone had transformed into Subtropical Storm Andrea while located about 140 miles (225 km) southeast of Savannah, Georgia.[14] Andrea began its subtropical phase as it was weakening, and continued this deterioration as it moved southward into an environment with higher wind shear. By May 11, Andrea had lost all significant convection and degenerated into a remnant low. Though it produced intermittent bursts of convection, Andrea's chance of regeneration was extinguished when an advancing cold front pushed it northward and eventually absorbed the system.[13]
Andrea was short-lived, dissipating on May 11. It was the first pre-season storm to develop since Tropical Storm Ana in April 2003 and the first Atlantic named storm in May since Tropical Storm Arlene in 1981. Six people drowned along the Southeast U.S. Coast.[13] However, because Andrea never made landfall, most of the resulting damage was associated with large waves, higher than normal tides, associated coastal flooding, and beach erosion caused by the storm.[13]
Tropical Storm Barry
On June 1, Tropical Storm Barry developed on the first day of the hurricane season. It originated from a trough of low pressure in the southeastern Gulf of Mexico that previously formed in the northwestern Caribbean. It accelerated to the northeast before reaching a peak intensity of 997 mbar and making landfall on Florida.[15] Barry dissipated on June 2.[15][16] In Florida, the rainfall resulted in slick roads, which caused two traffic-related deaths, and a woman was killed after being injured by rough surf.[16]
Tropical Storm Chantal
After two months of inactivity, an area of low pressure formed near the Bahamas on July 28 and gradually began to organize while moving north-northeast. On July 30 it was classified as Tropical Depression Three and was named Tropical Storm Chantal shortly thereafter while south of Nova Scotia. The storm weakened on August 1 and made landfall on Newfoundland; it later tracked into the North Atlantic as an extratropical storm.[17]
Chantal moved over the Avalon Peninsula of Newfoundland where flooding was observed,[17] where about 4 inches (100 mm) of rain caused the postponement of the annual Royal St. John's Regatta.[18] Insured damage across the area totaled $5.8 million (2007 CAD; $5.5 million 2007 USD$, 8.34 million 2025 USD).[19]
Hurricane Dean
On August 11, a tropical wave moved off the west coast of Africa, and, encountering favorable conditions, quickly spawned Tropical Depression Four, roughly 520 miles (835 km) west-southwest of Cape Verde.[20] The depression moved briskly westward, south of a deep layered ridge,[21] and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Dean on August 14.[20] The storm continued to strengthen overnight as it gained organization,[22] and became the first hurricane of the season on August 16.[20] On August 17 the eye of the hurricane passed into the Caribbean between the islands of Martinique and Saint Lucia as a Category 2 hurricane.[23]
In the warm waters of the Caribbean, Dean rapidly strengthened into a Category 5 hurricane with 165 mph (266 km/h) sustained winds. This made it the strongest Atlantic hurricane since Hurricane Wilma—and it was tied for the seventh most intense Atlantic storm of all time. An eyewall replacement cycle weakened Dean, which then passed just south of Jamaica as a Category 4 hurricane. Dean regained Category 5 status late on August 20 and at that strength it made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico near Costa Maya on August 21.[20] Dean was the first storm to make landfall as a Category 5 hurricane in the Atlantic basin since Hurricane Andrew in 1992. A dropsonde in the eye of the storm estimated a central pressure of 905 mbar, tying Dean with Hurricane Mitch for the seventh most intense Atlantic hurricane ever recorded. Dean was the third most intense landfalling Atlantic storm in history (after the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935 and Hurricane Gilbert of 1988).[20] Dean weakened over land, but re-intensified slightly in the Gulf of Mexico. It made its final landfall near Tecolutla, Veracruz on August 22, dissipating the next day.[20]
In Hispaniola, Dean killed 15 people and destroyed hundreds of homes.[24][25] Dean also left $616 million (2007 USD$, 934 million 2025 USD) in damage on Martinique and $154 million (2007 USD$, 234 million 2025 USD) on Guadeloupe.[26] In Mexico, Hurricane Dean made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula on August 21 as a Category 5 hurricane.[27] Throughout its track, Dean killed 44 people[9] and caused several billion dollars in damage.[20][28][29][30][31]
Tropical Storm Erin
Tropical Storm Erin formed on August 16 in the Gulf of Mexico from a persistent area of convection.[32] Based on reconnaissance data received from an NOAA plane investigating the depression, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Erin on August 15. It weakened to a tropical depression as it made landfall near Lamar, Texas, on August 16,[33] and the NHC issued its last advisory on the system shortly thereafter as it moved inland.[34] Early on August 19 after entering Oklahoma, the remnants of Erin suddenly re-intensified to maximum sustained winds of 60 mph (95 km/h) a short distance west of Oklahoma City.[32]
The storm flooded more than 40 homes and businesses. Along its path into the central states, Erin killed 16 people—9 directly—and left about $25 million (2007 USD$, 37.9 million 2025 USD) in total damage.[33]
Hurricane Felix
An area of disturbed weather east of the Windward Islands was designated Tropical Depression Six on August 31. Early on September 1, it was named Tropical Storm Felix, and it was upgraded to a hurricane later that day. Tracking generally westward, it rapidly intensified to Category 5, and after fluctuating in strength, made landfall on Nicaragua with 160 mph (260 km/h) winds. At least 133 deaths and more than $50 million (2007 USD) in damage have been attributed to Felix.[35] With Felix, the 2007 Atlantic hurricane season became the first known to include two hurricanes making landfall at Category 5;[36] hurricanes Irma and Maria made landfall at Category 5 intensity during the 2017 Atlantic season.[37]
Felix took a similar path as Hurricane Dean though a bit further south, although its effects were not severe; damage on Tobago was estimated at $250,000 (2007 TTD; $40,000 2007 USD$, 60,658 2025 USD).[38] Felix made landfall just south of the border between Nicaragua and Honduras, in a region historically known as the Mosquito Coast, as a Category 5 hurricane with 160 mph (260 km/h) winds on September 4.[36] Residents of the region were reported to have been given little warning of the oncoming hurricane, which left many fisherman stranded at sea.[39] In all, Felix killed at least 130 people,[36] and damage in Nicaragua totaled C$869.3 million (2007 NIO; $46.7 million 2007 USD$, 70.8 million 2025 USD).[35]
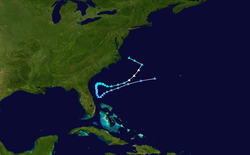
Tropical Storm Gabrielle
A cold front that moved off the southeastern coast of the United States on September 1 developed a weak low over the waters near Georgia. The low drifted eastward and weakened over the next few days until it joined with convection from an upper-level trough that had been moving over the western Atlantic.[40] On September 8, the center of circulation became sufficiently organized to be declared Subtropical Storm Gabrielle, about 360 nautical miles (670 km) southeast of Cape Hatteras.[41] For the next twelve hours, the system's strongest winds and thunderstorms remained separated from the center. On September 8 new convection eventually united with the center, leading the transition of Gabrielle into a tropical storm. Gabrielle gradually strengthened as it traveled northwest towards North Carolina and Virginia. The storm reached its peak intensity of 60 mph (95 km/h) just before it arrived in Cape Lookout, though strong wind shear kept most of the convection and surface winds offshore.[40] Gabrielle weakened over land, and moved back into the Atlantic on September 10. The circulation deteriorated further, and the storm dissipated southwest of Nova Scotia the next day.[42]
In advance of the storm, tropical cyclone watches and warnings were issued for coastal areas,[40] while rescue teams and the U.S. Coast Guard were put on standby.[43] The storm dropped heavy rainfall near its immediate landfall location but little precipitation elsewhere. Along the coast, high waves, rip currents, and storm surge were reported. Slight localized flooding was reported. Gusty winds also occurred, though no wind damage was reported. Overall damage was minor, and there were no fatalities.[40]
Tropical Storm Ingrid
A large tropical wave exited Africa on September 6 and initially failed to develop due to strong easterly shear. On September 9, a broad low-pressure area developed about midway between Africa and the Lesser Antilles.[44] The wind shear slowly weakened, and early on September 12 Tropical Depression Eight developed about 1125 miles (1815 km) east of the Lesser Antilles. The system moved west-northwestward due to a ridge to its north, and with continued wind shear, it remained a tropical depression for 24 hours before convection increased further. Early on September 13 it intensified into Tropical Storm Ingrid, reaching peak winds of 45 mph (75 km/h).[44] Operationally, it was not upgraded to a tropical storm until that evening.[45]
Ingrid remained a tropical storm until September 15, when it weakened to a tropical depression due to high shear from a strong tropical upper tropospheric trough.[44] Gradual weakening continued as it passed northeast of the Leeward Islands.[46] Ingrid briefly reorganized on September 16,[47] before weakening further and degenerating into an open wave early on September 17.[48] The remnants turned northwestward within the low-level steering flow, and dissipated on September 18 without redevelopment. There were no reports of damage or casualties associated with Ingrid because the storm never threatened land.[44]
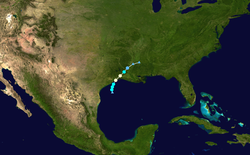
Hurricane Humberto
On September 12, an area of thunderstorm activity in the Gulf of Mexico organized into Tropical Depression Nine, about 60 mi (97 km) southeast of Matagorda, Texas. Within three hours of forming, it was named Tropical Storm Humberto, and it turned to the north-northeast before rapidly intensifying.[49] In the early morning hours of September 13, a Hurricane Hunter aircraft found that Humberto had strengthened into a hurricane while located about 15 miles (20 km) off the coast of Texas.[50] Humberto quickly weakened and entered Southwest Louisiana as a tropical storm during the afternoon of September 13,[51] dissipating the next day.[49]
Humberto caused some structural damage on High Island and widespread tree and power line damage in the Beaumont–Port Arthur area. Power outages caused four oil refineries to halt production in Beaumont. One person was reported dead as a result of the storm, a Bridge City man killed when his carport crashed on him outside his house.[52] Damage was estimated at $50 million.[49]
Tropical Depression Ten
A subtropical depression formed on September 21 in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico from the interaction of a tropical wave, the tail end of a cold front, and an upper-level low. Initially containing a poorly defined circulation and intermittent thunderstorm activity, the system transitioned into a tropical depression after convection increased over the center. Tracking northwestward, the depression moved ashore near Fort Walton Beach early on September 22, and shortly thereafter it dissipated over southeastern Alabama.[53]
It was the first tropical cyclone to threaten the New Orleans area after the destructive 2005 hurricane season and Hurricane Katrina.[54] Overall impact from the cyclone was minor and largely limited to light rainfall.[55] However, the precursor system spawned a damaging tornado in Eustis, Florida, where 20 houses were destroyed and 30 more were damaged.[56] Damage was estimated at $6.2 million.[53]
Tropical Storm Jerry
The origins of Jerry were from a non-tropical low-pressure area over the central Atlantic on September 21. The system meandered for two days, gradually developing deeper convection and gaining organization. On September 23, the National Hurricane Center declared it a subtropical depression, as a warm core had developed but the system was still involved with an upper-level low, and its strongest winds were well removed from the center.[57] Early on September 23, both satellite estimates and QuikScat data determined that the depression had strengthened into Subtropical Storm Jerry, despite the lack of a well-defined inner core.[58]
The storm slowly acquired tropical characteristics including a better-defined warm core,[59] and Jerry became fully tropical that evening as a weak and sheared tropical storm with 40 mph (65 km/h) winds over a small radius.[57][60] It accelerated northeastward over cooler waters with sea surface temperatures below 75 °F (24 °C).[61] On September 24, it weakened to a tropical depression ahead of a powerful cold front with little deep convection remaining in the system.[62] That evening, a QuikScat pass determined that Jerry opened up into a trough, which was being absorbed into the larger frontal system.[63] It completely dissipated by early on September 25. Jerry never approached land during its lifespan, and no damage or casualties were reported.[57]
Hurricane Karen
A very large tropical wave accompanied by a large envelope of low pressure emerged from the coast of Africa on September 21. As it moved westward, deep convection gradually increased over the disturbance as its broad low-level circulation became better-defined. By September 24, as the system traveled northwestward it organized enough to become a tropical depression.[64] Six hours later the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Karen.[65]
Karen's organization and intensity remained steady for the next day. Early on September 26, however, the storm strengthened significantly. In post-operational analysis the cyclone was determined to have reached hurricane-strength for about twelve hours.[64] However, strengthening was short-lived because a sharp upper-level trough to the west of Karen increased the amount of vertical wind shear over the hurricane. By September 28 these unfavorable conditions had weakened Karen to a marginal tropical storm and left its large low-level circulation exposed.[66] Meanwhile, the storm began heading northward and experiencing intermittent bursts of deep convection. However, the relentless wind shear exposed the system's circulation until it dissipated in the mid-Atlantic on September 29. Karen's remnants lingered near the Leeward Islands for the next few days, although the system never directly affected land. As a result, no reported damages or casualties were associated with Karen.[64]
Hurricane Lorenzo
A tropical wave moved off the western coast of Africa on September 11,[67] traversed the Caribbean and crossed the Yucatán on September 21. The disturbance developed a small surface low on September 24 while moving erratically over the southwestern Gulf of Mexico.[67] Strong upper-level winds initially prevented the system from developing convection; however, the shear relaxed on the following day and convection increased.[67][68] On the evening of September 25, a hurricane hunter aircraft found evidence that the low qualified as a tropical depression.[69] Under weak steering currents, the depression drifted south and southwest, executing a small cyclonic loop into the Bay of Campeche. Upper-level winds gave way to an anticyclone above the depression, and the system became Tropical Storm Lorenzo on September 27 about 130 nautical miles (240 km) east of Tuxpan.[67] Rapid intensification brought Lorenzo to hurricane status early that evening, less than twelve hours after becoming a tropical storm. Lorenzo reached its peak intensity on September 28, then weakened slightly before making landfall near Tecolutla, Mexico as a minimal hurricane. The small circulation weakened rapidly after landfall, and the system dissipated the next day.[67]
Six deaths in Mexico were attributed to Lorenzo, mostly due to flash floods and mudslides. The states of Puebla and Veracruz reported damage from rain and high winds. Two hundred people were forced to evacuate in Hidalgo when the San Lorenzo River overflowed its banks. Lorenzo made landfall in virtually the same location that Hurricane Dean had struck a month earlier.[67] Damage was estimated at $1 billion (2007 MXN; $92 million 2007 USD$, 140 million 2025 USD).[70]
Tropical Storm Melissa
On September 26, a tropical wave exited Africa and quickly developed a low-pressure area. Following a convective increase and better-defined outflow, it developed into Tropical Depression Fourteen about 115 miles (185 km) west-southwest of the southernmost Cape Verde Islands early on September 28.[71][72] Because the depression was isolated from the subtropical ridge, the depression drifted west-northwestward.[71] Westerly wind shear prevented significant development,[73] but following an increase in convection, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Melissa early on September 29.[74] Similar to previous storms Ingrid and Karen, high wind shear in the deep tropics hindered Melissa's development,[75] and its peak winds were only 40 mph (65 km/h);[71] operationally, satellite imagery suggested the storm reached 45 mph (72 km/h).[76] By September 30, the shear and cooler waters weakened Melissa to a tropical depression with a poorly defined surface center.[77] The system lost its deep convection and by that afternoon, Melissa degenerated into a remnant low.[78] It continued west-northwestward, producing intermittent convection, until being absorbed by a front northeast of the Lesser Antilles on October 5. There were no reports of damage or casualties associated with Melissa.[71]
Tropical Depression Fifteen
An area of disturbed weather extended from the northwestern Caribbean to the western Atlantic Ocean on October 4,[79] possibly related to the remnants of Hurricane Karen.[80] The system slowly organized, developing a surface low pressure on October 8 to the northeast of the Turks and Caicos Islands. Convection associated with the storm steadily increased as the low moved towards the northeast.[79] By October 11, the low organized into Tropical Depression Fifteen about 740 mi (1,190 km) east-southeast of Bermuda,[81] after the convection had persisted for about 12 hours. An upper-level low to the west caused strong southwesterly wind shear, which inhibited development.[80]
On October 12, a building ridge caused the depression to slow at the same time as the convection began decreasing.[82] The storm's center became exposed as the deep convection became limited to a few small cells north of the center.[83] By that afternoon, the depression degenerated into a remnant low.[84] The remnant low persisted for the next several days while picking up speed and taking a gradual turn towards the northeast. The low transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on October 14 and intensified, moving through the Azores with gale-force winds. It reached winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) before being absorbed by a larger extratropical storm on October 18.[79]
Hurricane Noel
During the evening of October 27, a low-pressure system that had been slowly developing over the eastern Caribbean organized into Tropical Depression Sixteen. On the next day, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Noel, and made landfall on Haiti on October 29. Noel meandered across the western Caribbean for the next three days, intensifying into a hurricane on November 1. Tracking northward, Noel began its transition into an extratropical cyclone on November 2, becoming fully extratropical on November 4 while over Labrador. As a powerful extratropical cyclone, Noel crossed back into the Atlantic and began a track towards western Greenland.[85]
Throughout the Caribbean, Hurricane Noel caused severe damage. Torrential rainfall and mudslides caused by the storm killed at least 87 people in the Dominican Republic and at least 73 in Haiti.[85] Noel generated winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) in the Wreckhouse region of Newfoundland and Labrador.[86]
Tropical Storm Olga
In the second week of December, after the official end of the hurricane season, a low developed east of the northernmost Lesser Antilles. It slowly acquired tropical characteristics, and late on December 10, the National Hurricane Center declared it Subtropical Storm Olga while just north of Puerto Rico. It is the first post-season storm since Tropical Storm Zeta in the 2005 season. Olga was only one of a few out of season tropical cyclones to make landfall. The storm made landfall on December 11 on the eastern tip of the Dominican Republic. Later that evening, Olga transitioned into a tropical storm just after making landfall. Olga tracked over Hispaniola and emerged in the Caribbean. Strong wind shear and dry air caused Olga to weaken into a remnant low early on December 13.[87]
The storm impacted many areas affected by Tropical Storm Noel a month earlier. In Puerto Rico, moderate rainfall caused one death. According to the National Hurricane Center's Tropical Cyclone Report on Olga, at least 22 occurred due to the release of floodgates at a dam in Santiago Province. Two deaths were also reported in Haiti, and one fatality was confirmed in Puerto Rico. Almost 12,000 homes were damaged, of which 370 were completely destroyed.[87]
Remove ads
Storm names
The following list of names was used for named storms that formed in the North Atlantic in 2007.[88] This is the same list used for the 2001 season, except for Andrea, Ingrid, and Melissa, which replaced Allison, Iris, and Michelle, respectively.[89] Each of the new names was used for the first time in 2007.
|
Retirement
On May 13, 2008, at the 30th Session of the World Meteorological Organization's Regional Association IV Hurricane Committee, the WMO retired the names Dean, Felix, and Noel from its Atlantic hurricane name lists, and they will not be used again for another Atlantic hurricane. They were replaced with Dorian, Fernand, and Nestor for the 2013 season.[90][91]
Remove ads
Season effects
Summarize
Perspective
This is a table of all of the storms that formed in the 2007 Atlantic hurricane season. It includes their name, duration, peak classification and intensities, areas affected, damage, and death totals. Deaths in parentheses are additional and indirect (an example of an indirect death would be a traffic accident), but were still related to that storm. Damage and deaths include totals while the storm was extratropical, a wave, or a low, and all of the damage figures are in 2007 USD.
| Saffir–Simpson scale | ||||||
| TD | TS | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
Remove ads
See also
- Tropical cyclones in 2007
- 2007 Pacific hurricane season
- 2007 Pacific typhoon season
- 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2006–07, 2007–08
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2006–07, 2007–08
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2006–07, 2007–08
Notes
- The cumulative damage figures were obtained by summing the damage figures on the individual Tropical Cyclone Reports referenced throughout the article, with the exception of Hurricane Dean. Dean's damage figures were obtained by adding the per-country totals referenced in the Impact section of this article.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads