Gnome Lambda
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Gnome 7 Lambda was a French designed, seven-cylinder, air-cooled rotary aero engine that was produced under license in Britain and Germany. Powering several World War I-era aircraft types it was claimed to produce 80 horsepower (60 kW) from its capacity of 12 litres (730 cubic inches) although recorded figures are lower.[1]
| Lambda | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Gnome 7 Lambda as shown in a 1913 Gnome catalog | |
| Type | Rotary aero engine |
| Manufacturer | Gnome et Rhône |
| First run | c.1911 |
| Major applications | Avro 504 Bristol Boxkite Bristol Scout |
| Number built | 2,720 (French production) 979 (British production) |
Just under 1,000 units were produced in Britain, the majority (967) by the Daimler Company of Coventry. A 14-cylinder variant was known as the Gnome 14 Lambda-Lambda.
In Germany Motorenfabrik Oberursel license-built the seven-cylinder engine as the Oberursel U.0 and later copied the 14-cylinder design and designated it as the Oberursel U.III.
Variants
- Gnome 7 Lambda
- Seven-cylinder, single-row rotary engine.
- Gnome 7 Lambda (long stroke)
- Increased stroke of 145 mm (5.71 in) to raise the compression ratio to 3.87:1, and total displacement to 12.26 litres (748 cu in).
- Gnome 14 Double Lambda
- 14-cylinder, two-row rotary engine using Lambda cylinders. 160 hp (120 kW).
- Motorenfabrik Oberursel U.0
- German production of the Gnome 7 Lambda – had a 124 mm (4.88 in) cylinder bore and 140 mm (5.51 in) piston stroke for a total displacement of 11.52 litres (703 cu in), external diameter of 1.020 metres (40.16 in).[2]
- Motorenfabrik Oberursel U.III
- German production of the Gnome 14 Double Lambda
Applications
Summarize
Perspective
List from Lumsden

Gnome 7 Lambda
- Avro 504
- Blackburn Type I
- Borel hydro-monoplane[3]
- Blériot Parasol
- Blériot XI
- Bristol Boxkite
- Bristol Gordon England G.E.3
- Bristol-Coanda Monoplanes
- Bristol Coanda T.B.8
- Bristol Coanda P.B.8
- Bristol Scout
- Caudron G.III
- Deperdussin Type B
- Dunne D.8
- Farman HF.14
- Farman HF.20
- Grahame-White Type XV
- London & Provincial 4
- Lowe Marlburian
- Nieuport IVG
- Nieuport 10
- Nieuport-Macchi Parasol
- Radley-England Waterplane
- Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.3
- Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.4
- Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.8
- Royal Aircraft Factory B.S.1
- Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.2
- Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.2
- Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.4
- Short S.37
- Short S.38
- Short S.41
- Short S.60
- Short S.70
- Sikorsky S-7
- Sopwith Gordon Bennett Racer
- Sopwith Pup
- Sopwith Sociable
- Sopwith Tabloid
- Sopwith Three-Seater
- Vickers No.8 Monoplane
Gnome 14 Lambda-Lambda
- Avro 510
- Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.4
- Deperdussin Monocoque
- Farman HF.19
- Fokker D.III
- Fokker E.IV
- Paul Schmitt P.S.3
- Short S.63
- Short S.64
- Short S.70
- Short S.74
- Short S.80
- Short S.81
- Short S.82
Survivors
An original Gnome 7 Lambda engine is installed in the Sopwith Tabloid replica aircraft on display in the Grahame-White hall of the Royal Air Force Museum London.[4]
Specifications (Gnome 7 Lambda)
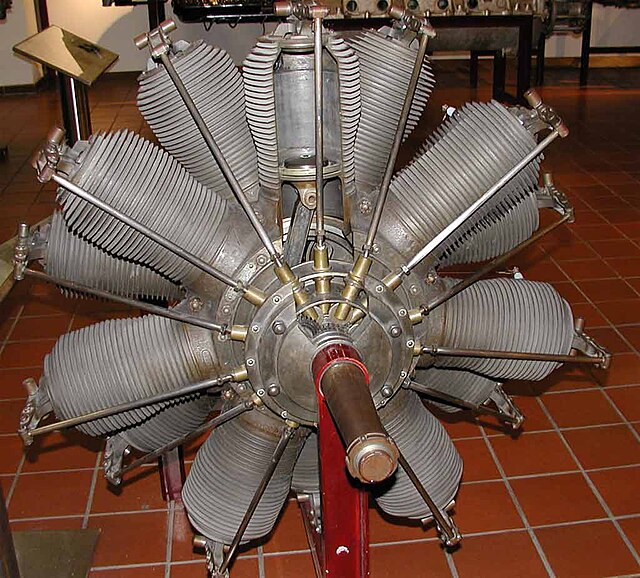
Data from Lumsden.[1]
General characteristics
- Type: 7-cylinder, single-row, rotary engine
- Bore: 124 mm (4.9 in)
- Stroke: 140 mm (5.5 in)
- Displacement: 11.8 L (720 cu in)
- Length: 112 cm (44 in)
- Diameter: 93 cm (37 in)
- Dry weight: 96 kg (212 lb)
Components
- Valvetrain: Automatic centre-piston inlet valve, overhead exhaust valve (one each per cylinder)
- Cooling system: Air-cooled
- Reduction gear: Direct drive, right-hand tractor, left-hand pusher
Performance
- Power output: 50.3 kW (67.5 hp) at 1,250 rpm (maximum power)
- Compression ratio: 3.75:1
See also
Comparable engines
Related lists
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
