Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the GDNF gene.[5] GDNF is a small protein that potently promotes the survival of many types of neurons.[6] It signals through GFRα receptors, particularly GFRα1. It is also responsible for the determination of spermatogonia into primary spermatocytes, i.e. it is received by RET proto-oncogene (RET) and by forming gradient with SCF it divides the spermatogonia into two cells. As the result there is retention of spermatogonia and formation of spermatocyte.[7][full citation needed]
GDNF family of ligands (GFL)
GDNF was discovered in 1991,[8] and is the first member of the GDNF family of ligands (GFL) found.
Function
GDNF is highly distributed throughout both the peripheral and central nervous system. It can be secreted by astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, motor neurons, and skeletal muscle during the development and growth of neurons and other peripheral cells.[9]
The GDNF gene encodes a highly conserved neurotrophic factor. The recombinant form of this protein was shown to promote the survival and differentiation of dopaminergic neurons in culture, and was able to prevent apoptosis of motor neurons induced by axotomy. GDNF is synthesized as a 211 amino acid-long protein precursor, pro-GDNF.[9] The pre-sequence leads the protein to the endoplasmic reticulum for secretion. While secretion takes place, the protein precursor folds via a sulfide-sulfide bond and dimerizes. The protein then is modified by N-linked glycosylation during packaging and preparation in the Golgi apparatus. Finally, the protein precursor undergoes proteolysis due to a proteolytic consensus sequence in its C-terminus end and is cleaved to 134 amino acids.[9] Proteases that play a role in the proteolysis of pro-GDNF into mature GDNF include furin, PACE4, PC5A, PC5B, and PC7. Because multiple proteases can cleave the protein precursor, four different mature forms of GDNF can be produced.[9] The proteolytic processing of GDNF requires SorLA, a protein sorting receptor. SorLA does not bind to any other GFLs.[10] The mature form of the protein is a ligand for the product of the RET (rearranged during transfection) protooncogene. In addition to the transcript encoding GDNF, two additional alternative transcripts encoding distinct proteins, referred to as astrocyte-derived trophic factors, have also been described. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Hirschsprung's disease.[6]
GDNF has the ability to activate the ERK-1 and ERK-2 isoforms of MAP kinase in sympathetic neurons as well as P13K/AKT pathways via activation of its receptor tyrosine kinases.[11][12] It can also activate Src-family kinases through its GFRα1 receptor.[13]
The most prominent feature of GDNF is its ability to support the survival of dopaminergic[14] and motor neurons.[citation needed] It prevents apoptosis in motor neurons during development, decreases the overall loss of neurons during development, rescues cells from axotomy-induced death, and prevents chronic degeneration.[9]
These neuronal populations die in the course of Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). GDNF also regulates kidney development and spermatogenesis, and has a powerful and rapid negative (ameliorating) effect on alcohol consumption.[15] GDNF also promotes hair follicle formation and cutaneous wound healing by targeting resident hair follicle stem cells (BSCs) in the bulge compartment.[16]
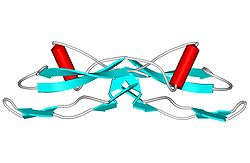
Structure
GDNF has a structure that is similar to TGF beta 2.[11] GDNF has two finger-like structures that interact with the GFRα1 receptor. N-linked glycosylation, which occurs during the secretion of pro-GDNF, takes place at the tip of one of the finger-like structures. The C-terminal of mature GDNF plays an important role in binding with both Ret and the GFRα1 receptor. The C-terminus forms a loop out of the interactions between cysteines Cys131, Cy133, Cys68, and Cys 72.[9]
Interactions
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor has been shown to interact with GFRA1[9][17] and GDNF family receptor alpha 1. The activity of GDNF, as well as other GFLs, is mediated by RET receptor tyrosine kinase. In order for the receptor to modulate GDNF activity, GDNF must also be bound to GFRα1.[11] The intensity and duration of RET signaling can likewise be monitored by the GPI-anchor of GFRα1 by interacting with compartments of the cell membrane, such as lipid rafts or cleavage by phospholipases.[12] In cells that lack RET, some GDNF family ligand members also have the ability to be activated through the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM). GDNF can associate with NCAM through its GFRα1 GPI-anchor. The association between GDNF and NCAM results in the activation of cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases Fyn and FAK.[18]
Potential as therapeutics
GDNF has been investigated as a treatment for Parkinson's disease, though early research has not shown a significant effect.[8][19] Vitamin D potently induces GDNF expression.[20]
In 2012, the University of Bristol began a five-year clinical trial on Parkinson's sufferers, in which surgeons introduced a port into the skull of each of the 41 participants through which the drug could be delivered, in order to enable it to reach the damaged cells directly.[21] The results of the double-blind trial, where half the participants were randomly assigned to receive regular infusions of GDNF and the other half placebo infusions, did not show a statistically significant difference between the active treatment group and those who received placebo, but did confirm the effects on damaged brain cells.[22]
The study was funded by Parkinson’s UK (Grant J-1102), with support from The Cure Parkinson’s Trust (whose founder, Tom Isaacs, was one of the participants[23]) and was sponsored by North Bristol NHS Trust. Study drug, additional project resources and supplementary funding was provided by MedGenesis Therapeutix Inc., who in turn received program funding support from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. Renishaw plc manufactured the CED device on behalf of North Bristol NHS Trust and provided additional technical and analytical support. The Gatsby Foundation provided a 3T MRI scanner.[24]
Neuropsychopharmacology
Administration of the African hallucinogen ibogaine potently increases GDNF expression in the ventral tegmental area, which is the mechanism behind the alkaloid's anti-addictive effect.[25] Rodent models for a non-psychedelic analogue of this compound show promise in promoting GDNF expression without the hallucinogenic or cardiotoxic effects well documented for ibogaine.[26]
There is evidence, that Gdnf is an alcohol-responsive gene upregulated during short-term alcohol intake but downregulated during withdrawal from excessive alcohol intake.[27] Specifically, one study showed that alcohol withdrawal alters the expression of Gdnf in addiction related brain areas like the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the Nucleus Accumbens as well as DNA methylation of the Gdnf gene in rats.[28]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.