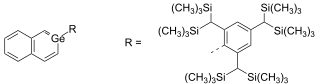Germabenzene
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Germabenzene (C5H6Ge) is the parent representative of a group of chemical compounds containing in their molecular structure a benzene ring with a carbon atom replaced by a germanium atom. Germabenzene itself has been studied theoretically,[1] and synthesized with a bulky 2,4,6-tris[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl or Tbt group.[2] Also, stable naphthalene derivatives do exist in the laboratory such as the 2-germanaphthalene-containing substance represented below.[3] The germanium to carbon bond in this compound is shielded from potential reactants by a Tbt group. This compound is aromatic just as the other carbon group representatives silabenzene and stannabenzene.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Germine | |||
| Other names
Germanabenzene; Germin; Germanin | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H6Ge | |||
| Molar mass | 138.733 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
See also
- 6-membered aromatic rings with one carbon replaced by another group: borabenzene, silabenzene, germabenzene, stannabenzene, pyridine, phosphorine, arsabenzene, bismabenzene, pyrylium, thiopyrylium, selenopyrylium, telluropyrylium
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.