Wildlife of Kerala
Overview of the wildlife in the Indian state of Kerala From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Most of Kerala's native habitat, which consists of wet evergreen rainforests at lower elevations and highland deciduous and semi-evergreen forests in the east, has a humid tropical climate. However, significant variations in terrain and elevation lead to high biodiversity. But Alappuzha district has no forests.[1]
Wikiquote has quotations related to Wildlife of Kerala.




Evergreen forests
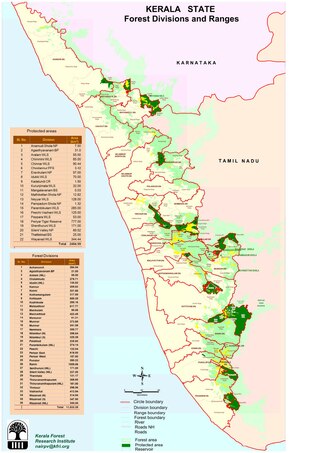
Most of Kerala's significantly biodiverse tracts of wilderness lie in the evergreen forests of its easternmost districts;[2] coastal Kerala (along with portions of the east) mostly lies under cultivation and is home to comparatively little wildlife. Despite this, Kerala contains 9,400 km2 of natural forests. Out of the approximately 7,500 km2 of non-plantation forest cover, there are wild regions of tropical wet evergreen and semi-evergreen forests (lower and middle elevations — 3,470 km2), tropical moist and dry deciduous forests (mid-elevations — 4,100 km2 and 100 km2, respectively), and montane subtropical and temperate (shola) forests (highest elevations — 100 km2). Such forests together cover 24% of Kerala's landmass.[3] Kerala also hosts four of the world's Ramsar Convention-listed wetlands: Ashtamudi Lake, Lake Sasthamkotta, Thrissur-Ponnani Kole Wetlands, and the Vembanad-Kol wetlands are noted as being wetlands of international importance.[4] There are also numerous protected conservation areas, including 1455.4 km2 of the vast Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve and 1828 km2 of the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve.[5] Parambikulam forest in Palakkad district is one of the jungle regions in Kerala.

Flora

Eastern Kerala's windward mountains shelter tropical moist forests and tropical dry forests which are generally characteristic of the wider Western Ghats: crowns of giant sonokeling (binomial nomenclature: Dalbergia latifolia — Indian rosewood), anjili (Artocarpus hirsuta), mullumurikku (Erythrina), Cassia, and other trees dominate the canopies of large tracts of virgin forest. Overall, Kerala's forests are home to more than 1,000 species of trees. Smaller flora include bamboo, wild black pepper (Piper nigrum), wild cardamom, the calamus rattan palm (Calamus rotang — a type of giant grass), and aromatic vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides).[3] The world's oldest teak plantation, Conolly's Plot, is in Nilambur.[6]
Fauna
Summarize
Perspective
In turn, the forests play host to such major fauna as the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus), Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris tigris), leopard (Panthera pardus), Nilgiri tahr (Nilgiritragus hylocrius), and grizzled giant squirrel (Ratufa macroura).[3] More remote preserves, including Silent Valley National Park in the Kundali Hills, harbour endangered species such as the Lion-tailed macaque (Macaca silenus), Indian sloth bear (Melursus (Ursus) ursinus ursinus), and gaur (the so-called "Indian bison" — Bos gaurus). More common species include the Indian porcupine (Hystrix indica), chital (Axis axis), sambar (Cervus unicolor), gray langur, flying squirrel, swamp lynx (Felis chaus kutas), boar (Sus scrofa), a variety of catarrhine Old World monkey species, the dhole, and the Asian palm civet (Paradoxurus hermaphroditus).[7]

Many reptiles, such as the tree snake, green snake, king cobra, viper, python, and various turtles and crocodiles are to be found in Kerala — again, disproportionately in the east. Kerala has about 453 species of birds such as the Sri Lanka frogmouth (Batrachostomus moniliger), leaf picking bird, Oriental bay owl, large frugivores like the great hornbill (Buceros bicornis) and Indian grey hornbill, as well as the more widespread birds such as peafowl, Indian cormorant, jungle and hill mynas, the Oriental darter, black-hooded oriole, greater racket-tailed and black drongoes, bulbul (Pycnonotidae), species of kingfisher and woodpecker, jungle fowl, Alexandrine parakeets, and assorted ducks and migratory birds. Additionally, freshwater fish such as kadu (stinging catfish)[8] and brackishwater species such as choottachi (orange chromide — Etroplus maculatus; valued as an aquarium specimen) are native to Kerala's lakes and waterways.[9]


Parks, reserves and sanctuaries
| National park | Area (km2) | Year started |
|---|---|---|
| Eravikulam National Park | 97 | 1978[5] |
| Silent Valley National Park | 237. 52 | 1984[5] |
| Anamudi Shola National Park | 7.5 | 2003[5] |
| Mathikettan Shola National Park | 12.817 | 2003[5] |
| Pambadum Shola National Park | 1.318 | 2003[5] |
| Biosphere reserve | Area (km2) | Year started |
|---|---|---|
| Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | 1455.4 | 1986[5] |
| Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve | 1828 | 2001[5] |
| Wildlife sanctuary | Area (km2) | Year started |
|---|---|---|
| Periyar Wildlife Sanctuary | 925 | 1950[5] |
| Neyyar Wildlife Sanctuary | 128 | 1958[5] |
| Peechi-Vazhani Wildlife Sanctuary | 125 | 1958[5] |
| Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary | 344.44 | 1973[5] |
| Parambikulam Wildlife Sanctuary | 286 | 1973[5] |
| Idukki Wildlife Sanctuary | 70 | 1976[5] |
| Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary | 53 | 1983[5] |
| Chimmini Wildlife Sanctuary | 85 | 1984[5] |
| Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary | 90.44 | 1984[5] |
| Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary | 171 | 1984[5] |
| Aralam Wildlife Sanctuary | 55 | 1984[5] |
| Kurinjimala Sanctuary | 32 | 2006[5] |
| Malabar Wildlife Sanctuary | 74.21 | 2009[5] |
| Kottiyoor Wildlife Sanctuary | 30.38 | 2011[5] |
| Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary | 227.97 | 2020[10] |
| Bird sanctuary | Area (km2) | Year started |
|---|---|---|
| Thattekad Bird Sanctuary | 25 | 1983[5] |
| Mangalavanam Bird Sanctuary | 0.0274 | 2004[5] |
| Chulanur Bird Sanctuary | 3.42 | 2007[5] |
| Kumarakom Bird Sanctuary | 0.0566 | [11] |
| Tiger reserve | Area (km2) | Year started |
|---|---|---|
| Periyar Tiger Reserve | 925 | 1978 |
| Parambikulam Tiger Reserve | 648.50 | 1973 |
| Community reserve | Area (km2) | Year started |
|---|---|---|
| Kadalundi Bird Sanctuary | 1.5 | 2007[5][12] |
See also
Notes
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.