Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
European Health Insurance Card
Health insurance card in Europe From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The European Health Insurance Card (EHIC) is issued free of charge to anyone who is insured by or covered by a statutory social security scheme of the EEA countries or Switzerland and certain citizens and residents of the United Kingdom. It allows holders to receive medical treatment in another member state in the same way as residents of that state—i.e., free or at a reduced cost—if treatment becomes necessary during their visit (for example, due to illness or an accident), or if they have a chronic pre-existing condition which requires care such as kidney dialysis. The term of validity of the card varies according to the issuing country. The EEA countries and Switzerland have reciprocal healthcare arrangements with the United Kingdom, which issues a UK Global Health Insurance Card (GHIC) valid in the EEA countries and, in most cases, in Switzerland.[4]
Remove ads


The intention of the scheme is to allow people to continue their stay in a country without having to return home for medical care, and does not cover people who have visited a country for the purpose of obtaining medical care, or non-urgent care that can be delayed until the individual returns to their home country (for example, most dental care). The costs not covered by self-liability fees are paid by the issuing country, which is usually the country of residence, but may also be the country from which the patient receives the most pension.[5] The card only covers healthcare which is normally covered by a statutory health care system in the visited country; additional costs can be met by taking out travel insurance.
The format of the EHIC complies with the ID-1 format, i.e. the size of most banking cards and ID cards (53.98 mm high, 85.60 mm wide and 0.76 mm thick).[6]
Remove ads
History
The card was phased in from 1 June 2004 and throughout 2005, becoming the sole healthcare entitlement document on 1 January 2006.
It replaced the following medical forms:
- E110 – For international road hauliers
- E111 – For tourists
- E119 – For unemployed people/job seekers
- E128 – For students and workers in another member state
Territorial applicability
The card is applicable in all French overseas departments (Martinique, Guadeloupe, Réunion, and French Guiana) as they are part of the EEA, but not non-EEA dependent territories such as Aruba, or French Polynesia.[7] However, there are agreements for the use of the EHIC in the Faroe Islands and Greenland,[8] even though they are not in the EEA.
Personal eligibility
The card exists because the right to health care in the European Union is based on the country of legal residence, not the country of citizenship. Therefore, a passport is not enough to receive health care. It is however possible that a photo ID document is asked for, since the European Health Insurance Card does not contain a photo.
In some cases, even if a person is covered by the health insurance of an EU country, one is not eligible for a European Health Insurance Card. For instance, in Romania, a person who is currently insured has to have been insured for the previous five years to be eligible.[9]
Third party application processors
European Health Insurance cards are provided free to all legal residents of participating countries. There are however various businesses who act as non-official agents on behalf of individuals, arranging supply of the cards in return for payment, often offering additional services such as the checking of applications for errors and general advice or assistance.[10] This has proved extremely controversial. In 2010 the British government moved against companies that invited people to pay for the free EHIC, falsely implying that through payment the applicant could speed up the process.[11][12]
Remove ads
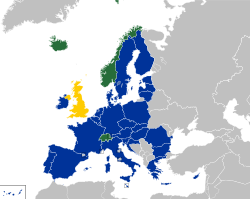
Participating member states
Summarize
Perspective
As of 2021, 31 countries in Europe participate: the 30 member states of the European Economic Area (EEA) plus Switzerland. This includes the 27 member states of the European Union (EU) and 4 member states of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).[13]
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom was a participant in the scheme as a member of the European Union until its withdrawal from the union. It continued to participate provisionally until the end of the Brexit transition period on 31 December 2020.
The EU–UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement grants continued reciprocal healthcare access between the EU and the UK. EU citizens can continue to use their EHIC within the UK,[14] while EHIC in the UK was replaced by a UK Global Health Insurance Card (GHIC).[15][16] Since 2022, some UK citizens and permanent residents are eligible for a new UK-issued EHIC valid for visits to these countries as well as to Switzerland.[17][4] Eligible persons are those who meet one of the following criteria:[18]
- those living in the European Union, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, or Liechtenstein, and have been since before 1 January 2021 with a registered S1, E121, E106 or E109 form issued by the UK
- those living in the EU, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, or Liechtenstein, since before 1 January 2021 with an A1 issued by the UK
- those who are a national of the EU, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, or Liechtenstein who have legally resided in the UK since before 1 January 2021 and are covered under the Withdrawal Agreement; one may not be covered if they also a UK national or if they were born in the UK
- those who are a family member or dependant of an entitled individual already listed
- those who fall under the court rulings Chen v Home Secretary(UK)[19] or Bashar Ibrahim and Others v Bundesrepublik Deutschland[20] or their carer
During its participation in the scheme, EHIC access covered the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. The crown dependencies of the Channel Islands and Isle of Man were not covered by the EHIC as they were never members of the EU and EEA, and their residents were not eligible for EHICs.[21]
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- The legal acquis is identified as EEA-relevant by the EU, and is incorporated into the EEA Agreement (by Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway).
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads