Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Eukaryotic ribosome
Large molecular machine for synthesizing proteins from messenger RNA From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Ribosomes are a large and complex molecular machine that catalyzes the synthesis of proteins, referred to as translation. The ribosome selects aminoacylated transfer RNAs (tRNAs) based on the sequence of a protein-encoding messenger RNA (mRNA) and covalently links the amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes from all organisms share a highly conserved catalytic center. However, the ribosomes of eukaryotes (animals, plants, fungi, and large number unicellular organisms all with a nucleus) are much larger than prokaryotic (bacterial and archaeal) ribosomes and subject to more complex regulation and biogenesis pathways.[1][2] Eukaryotic ribosomes are also known as 80S ribosomes, referring to their sedimentation coefficients in Svedberg units, because they sediment faster than the prokaryotic (70S) ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes have two unequal subunits, designated small subunit (40S) and large subunit (60S) according to their sedimentation coefficients. Both subunits contain dozens of ribosomal proteins arranged on a scaffold composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The small subunit monitors the complementarity between tRNA anticodon and mRNA, while the large subunit catalyzes peptide bond formation.
Remove ads
Composition
Compared to their prokaryotic homologs, many of the eukaryotic ribosomal proteins are enlarged by insertions or extensions to the conserved core. Furthermore, several additional proteins are found in the small and large subunits of eukaryotic ribosomes, which do not have prokaryotic homologs. The 40S subunit contains a 18S ribosomal RNA (abbreviated 18S rRNA), which is homologous to the prokaryotic 16S rRNA. The 60S subunit contains a 28S rRNA that is homologous to the prokaryotic 23S ribosomal RNA. In addition, it contains a 5.8S rRNA that corresponds to the 5' end of the 23S rRNA, and a short 5S rRNA. Both 18S and 28S have multiple insertions to the core rRNA fold of their prokaryotic counterparts, which are called expansion segments. For a detailed list of proteins, including archaeal and bacterial homologs please refer to the separate articles on the 40S and 60S subunits. Recent research suggests heterogeneity in the ribosomal composition, i.e., that the stoichiometry among core ribosomal proteins in wild-type yeast cells and embryonic stem cells depends both on the growth conditions and on the number of ribosomes bound per mRNA.[3]
Remove ads
Structure determination
Summarize
Perspective
Initial structures of eukaryotic ribosomes were determined by electron microscopy. First 3D structures were obtained at 30–40 Å resolution for yeast[5] and mammalian ribosomes.[6][7] Higher resolution structures of the yeast ribosome by cryo-electron microscopy allowed the identification of protein and RNA structural elements.[8]
Then structures at sub-nanometer resolution were obtained for complexes of ribosomes and factors involved in translation.[9][10][11] After the determination of the first bacterial[12][13][14] and archaeal[15] ribosome structures at atomic resolution in the 1990s, it took another decade until in 2011, high resolution structures of eukaryotic ribosome were obtained by X-ray crystallography, mainly because of the difficulties in obtaining crystals of sufficient quality.[16][17][18] The complete structure of a eukaryotic 40S ribosomal structure in Tetrahymena thermophila was published and described, as well as much about the 40S subunit's interaction with eIF1 during translation initiation.[16] The eukaryotic 60S subunit structure was also determined from T. thermophila in complex with eIF6.[17] The complete structure of the eukaryotic 80S ribosome from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was obtained by crystallography at 3.0 A resolution.[18] These structures reveal the precise architecture of eukaryote-specific elements, their interaction with the universally conserved core, and all eukaryote-specific bridges between the two ribosomal subunits.
Atomic coordinates (PDB files) and structure factors of the eukaryotic ribosome have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) under the following accession codes:
Remove ads
Architecture
Summarize
Perspective
General features
Some general architectural features of the ribosome are conserved across kingdoms:[20] The structure of the small subunit can be sub-divided into two large segments, the head and the body. Characteristic features of the body include the left and right feet, the shoulder and the platform. The head features a pointed protrusion reminiscent of a bird's beak. In the characteristic "crown view" of the large subunit, structural landmarks include the central protuberance, the L1-stalk and the P-stalk.[21][22] The majority of the eukaryote-specific RNA and protein elements are found on the solvent-exposed sides of the 40S [16] and 60S[17] subunits. The subunit interface, as well as important functional regions such as the peptidyl transferase center and the decoding site are mostly conserved, with some differences observed in the surrounding regions. In stark contrast to prokaryotic ribosomal proteins, which interact primarily with RNA, the eukaryote-specific protein segments engage in a multitude of protein-protein interactions. Long-distance interactions are mediated by eukaryote-specific helical extensions of ribosomal proteins, and several eukaryotic ribosomal proteins jointly to form inter-protein beta-sheets.
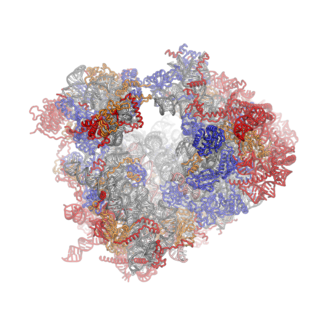
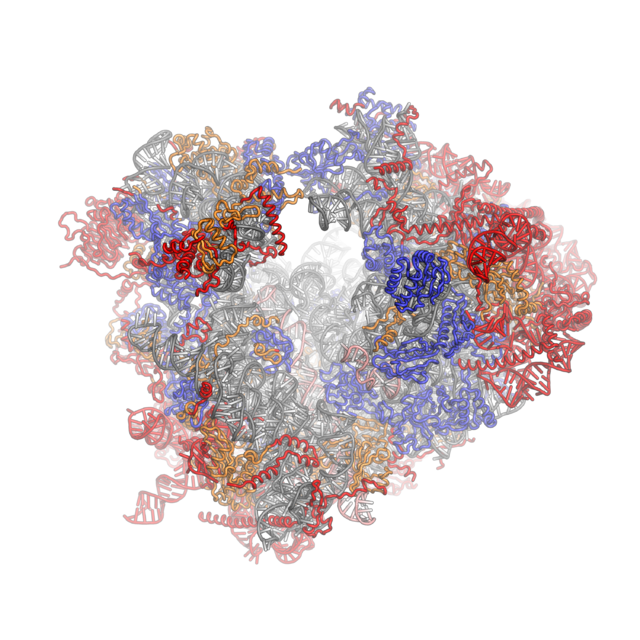
Crystal structures of the eukaryotic ribosomal subunits from T. thermophila
The ribosomal RNA core is represented as a grey tube, expansion segments are shown in red. Universally conserved proteins are shown in blue. These proteins have homologs in eukaryotes, archaea and bacteria. Proteins Shared only between eukaryotes and archaea are shown in orange, and proteins specific to eukaryotes are shown in red.
Co-evolution of rRNA and proteins
The structure of the 40S subunit revealed that the eukaryote-specific proteins (rpS7, rpS10, rpS12 and RACK1), as well as numerous eukaryote-specific extensions of proteins, are located on the solvent-exposed side of the small subunit.[16] Here, they participate in the stabilization of rRNA expansion segments. Moreover, the beak of the 40S subunit is remodeled, as rRNA has been replaced by proteins rpS10 and rpS12.[16] As observed for the 40S subunit, all eukaryote-specific proteins of the 60S subunit (RPL6, RPL22, RPL27, RPL28, RPL29 and RPL36) and many extensions are located at the solvent-exposed side, forming an intricate network of interactions with eukaryotic-specific RNA expansion segments. RPL6, RPL27 and RPL29 mediate contacts between the ES sets ES7–ES39, ES31–ES20–ES26 and ES9–ES12, respectively and RPL28 stabilized expansion segment ES7A.[17]
Ubiquitin fusion proteins
In eukaryotes, the small subunit protein RPS27A (or eS31) and the large subunit protein RPL40 (or eL40) are processed polypeptides, which are translated as fusion proteins carrying N-terminal ubiquitin domains. Both proteins are located next to important functional centers of the ribosome: the uncleaved ubiquitin domains of eS31) and eL40 would be positioned in the decoding site and near the translation factor binding site, respectively. These positions suggest that proteolytic cleavage is an essential step in the production of functional ribosomes.[16][17] Indeed, mutations of the linker between the core of eS31 and the ubiquitin domain are lethal in yeast.[23]
Active site
Comparisons between bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic ribosome structures reveal a very high degree of conservation in the active site region — the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). None of the eukaryote-specific protein elements is close enough to directly participate in catalysis.[17] However, RPL29 projects to within 18Å of the active site in T. thermophila, and eukaryote-specific extensions interlink several proteins in the vicinity of the PTC of the 60S subunit,[17][21] while the corresponding 50S proteins are singular entities.[15]
Intersubunit bridges
Contacts across the two ribosomal subunits are known as intersubunit bridges. In the eukaryotic ribosome, additional contacts are made by 60S expansion segments and proteins.[24] Specifically, the C-terminal extension of the 60S protein RPL19 interacts with ES6E of the 40S rRNA, and the C-terminal extension of the 60S protein RPL24 interacts with 40S rpS6 and rRNA helix h10. Moreover, the 60S expansion segments ES31 and ES41 interact with rpS3A(S1) and rpS8 of the 40S subunit, respectively, and the basic 25-amino-acid peptide RPL41 is positioned at the subunit interface in the 80S ribosome, interacting with rRNA elements of both subunits.[21][24]
Ribosomal proteins with roles in signaling
Two 40S ribosomal proteins (RACK1 and RPS6 (or eS6)) have been implicated in cellular signaling: RACK1, first described as the receptor of activated protein kinase C (PKC), is an integral component of the eukaryotic ribosome and is located at the back of the head.[16] It may link signal-transduction pathways directly to the ribosome though it also has a role in multiple translational processes that appear unrelated (reviewed in [25]). Ribosomal protein eS6 is located at the right foot of the 40S subunit [16] and is phosphorylated in response to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling.[26]
Remove ads
Functional aspects
Summarize
Perspective
Translation initiation
Protein synthesis is primarily regulated at the stage of translation initiation. In eukaryotes, the canonical initiation pathway requires at least 12 protein initiation factors, some of which are themselves large complexes.[27] The structures of the 40S:eIF1 [16] and 60S:eIF6 [17] complexes provide first detailed insights into the atomic interactions between the eukaryotic ribosome and regulatory factors. eIF1 is involved in start codon selection, and eIF6 sterically precludes the joining of subunits. However, structural information on the eukaryotic initiation factors and their interactions with the ribosome is limited and largely derived from homology models or low-resolution analyses.[28] Elucidation of the interactions between the eukaryotic ribosome and initiation factors at an atomic level is essential for a mechanistic understanding of the regulatory processes, but represents a significant technical challenge, because of the inherent dynamics and flexibility of the initiation complexes. The first structure of the mammalian pre initiation complex was done by cryo-electron microscopy.[29] Other structures of initiation complexes followed soon, driven by cryo-EM technical improvements.[30][31] Those structures will help better understand the process of translation initiation in eukaryotes.
Regulatory roles of ribosomal proteins
Recent genetic evidence has been interpreted to suggest that individual proteins of the eukaryotic ribosome directly contribute to the regulation of translation.[32][33][34] However, this interpretation is controversial and some researchers have proposed that genetic changes to ribosomal protein genes indirectly affect overall ribosome numbers or ribosome biogenesis processes.[35][36]
Protein translocation and targeting
To exert their functions in the cell newly synthesized proteins must be targeted to the appropriate location in the cell, which is achieved by protein targeting and translocation systems.[37] The growing polypeptide leaves the ribosome through a narrow tunnel in the large subunit. The region around the exit tunnel of the 60S subunit is very similar to the bacterial and archaeal 50S subunits. Additional elements are restricted to the second tier of proteins around the tunnel exit, possibly by conserved interactions with components of the translocation machinery.[17] The targeting and translocation machinery is much more complex in eukaryotes.[38]
Ribosomal diseases and cancer
Ribosomopathies are congenital human disorders resulting from defects in ribosomal protein or rRNA genes, or other genes whose products are implicated in ribosome biogenesis.[39] Examples include X-linked Dyskeratosis congenita (X-DC),[40] Diamond–Blackfan anemia,[41] Treacher Collins syndrome (TCS)[41][42] and Shwachman–Bodian–Diamond syndrome (SBDS).[39] SBDS is caused by mutations in the SBDS protein that affects its ability to couple GTP hydrolysis by the GTPase EFL1 to the release of eIF6 from the 60S subunit.[43]
Therapeutic opportunities
The ribosome is a prominent drug target for antibacterials, which interfere with translation at different stages of the elongation cycle [44] Most clinically relevant translation compounds are inhibitors of bacterial translation, but inhibitors of eukaryotic translation may also hold therapeutic potential for application in cancer or antifungal chemotherapy.[45] Elongation inhibitors show antitumor activity 'in vivo' and 'in vitro'.[46][47][48] One toxic inhibitor of eukaryotic translation elongation is the glutarimide antibiotic cycloheximide (CHX), which has been co-crystallized with the eukaryotic 60S subunit [17] and binds in the ribosomal E site. The structural characterization of the eukaryotic ribosome [16][17][24] may enable the use of structure-based methods for the design of novel antibacterials, wherein differences between the eukaryotic and bacterial ribosomes can be exploited to improve the selectivity of drugs and therefore reduce adverse effects.
Remove ads
Formation mechanism
Eukaryote ribosomes are produced and assembled in the nucleolus. Ribosomal proteins enter the nucleolus and combine with the four rRNA strands to create the two ribosomal subunits (one small and one large) that will make up the completed ribosome. The ribosome units leave the nucleus through the nuclear pores and unite once in the cytoplasm for the purpose of protein synthesis.
References
Notes
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads