Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
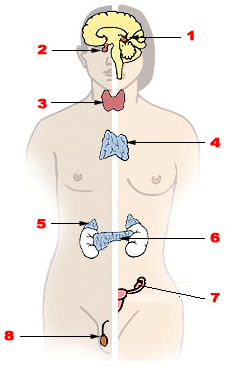
Endocrine disease
Disorders of the endocrine system From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Types of disease
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:[1]
- Endocrine gland hypofunction/hyposecretion (leading to hormone deficiency)
- Endocrine gland hyperfunction/hypersecretion (leading to hormone excess)
- Tumours (benign or malignant) of endocrine glands
Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of hyperthyroidism are associated with an excess of thyroid hormone and a low level of thyroid stimulating hormone.[2]
Remove ads
List of diseases
Glucose homeostasis disorders
Thyroid disorders
Calcium homeostasis disorders and Metabolic bone disease
- Parathyroid gland disorders
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroid myopathy[6]
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Hypoparathyroid myopathy[6]
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoporosis
- Osteitis deformans (Paget's disease of bone)
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
Pituitary gland disorders
Posterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary
Adrenal gland disorders
Sex hormone disorders
- Disorders of sex development or intersex disorders
- Hypogonadism (Gonadotropin deficiency)
- Inherited (genetic and chromosomal) disorders
- Acquired disorders
- Ovarian failure (also known as Premature Menopause)
- Testicular failure
- Disorders of Puberty
- Menstrual function or fertility disorders
Tumours of the endocrine glands not mentioned elsewhere

See also separate organs
- Autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes
- Incidentaloma - an unexpected finding on diagnostic imaging, often of endocrine glands
Remove ads
Endocrine emergencies
In endocrinology, medical emergencies include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, hypoglycemic coma, acute adrenocortical insufficiency, phaeochromocytoma crisis, hypercalcemic crisis, thyroid storm, myxoedema coma and pituitary apoplexy.[7]
Emergencies arising from decompensated pheochromocytomas or parathyroid adenomas are sometimes referred for emergency resection when aggressive medical therapies fail to control the patient's state, however the surgical risks are significant, especially blood pressure lability and the possibility of cardiovascular collapse after resection (due to a brutal drop in respectively catecholamines and calcium, which must be compensated with gradual normalization).[8][9] It remains debated when emergency surgery is appropriate as opposed to urgent or elective surgery after continued attempts to stabilize the patient, notably in view of newer and more efficient medications and protocols.[10][11][12]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads