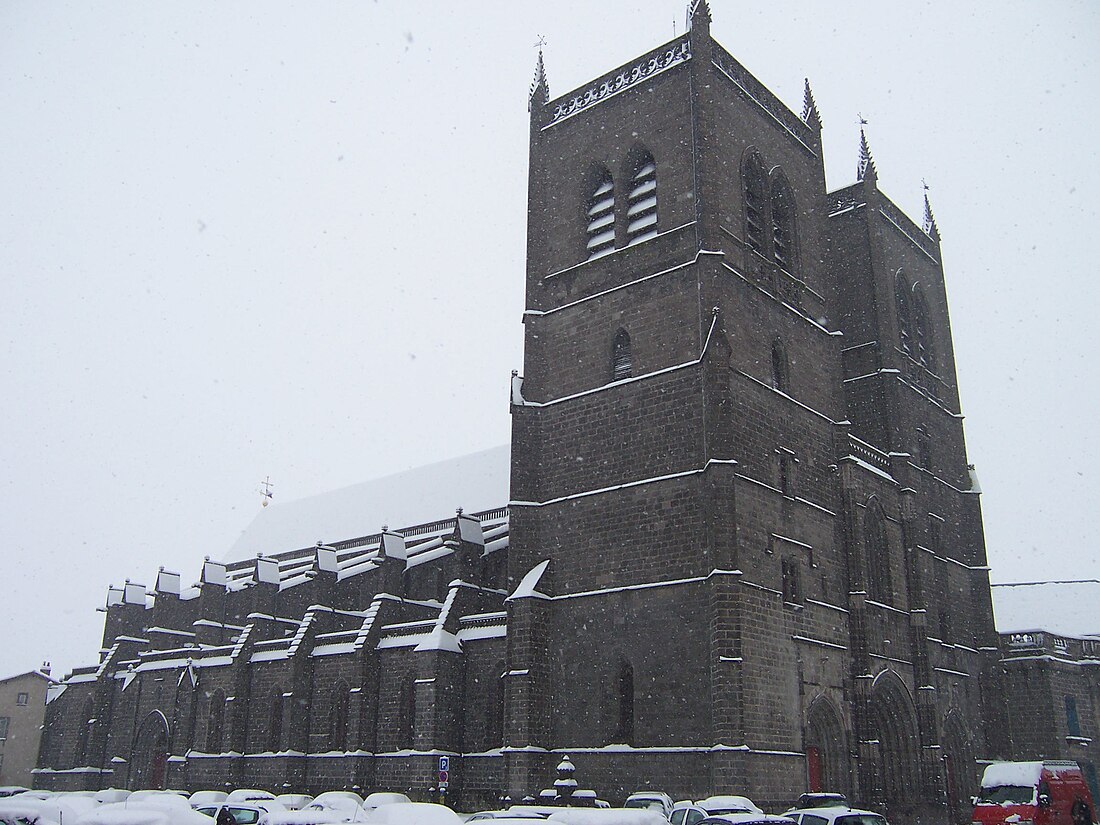
Roman Catholic Diocese of Saint-Flour
Catholic diocese in France From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Diocese of Saint-Flour (Latin: Dioecesis Sancti Flori; French: Diocèse de Saint-Flour) is a Latin diocese of the Catholic Church in France. The diocese comprises the department of Cantal. Erected in 1317, the diocese was suffragan of (subject to) the Archdiocese of Bourges until 2002. With the general reorganization of the structure of the French church by Pope John Paul II, Saint-Flour became the suffragan of the Archdiocese of Clermont. The seat of the bishop is located in Saint-Flour, Cantal.
Diocese of Saint-Flour Dioecesis Sancti Flori Diocèse de Saint-Flour | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | France |
| Ecclesiastical province | Clermont |
| Metropolitan | Archdiocese of Clermont |
| Statistics | |
| Area | 5,726 km2 (2,211 sq mi) |
Population
|
|
| Parishes | 20 |
| Information | |
| Denomination | Roman Catholic |
| Sui iuris church | Latin Church |
| Rite | Roman Rite |
| Established | 20 February 1317 |
| Cathedral | Cathedral of St Peter and St Flour in Saint-Flour, Cantal |
| Patron saint | Saint Flour of Lodeve |
| Secular priests | 44 (diocesan) 6 (Religious Orders) 9 Permanent Deacons (2020) |
| Current leadership | |
| Pope | Sede vacante |
| Bishop | Didier Noblot |
| Metropolitan Archbishop | François Kalist |
| Bishops emeritus | Bruno Grua |
| Map | |
 | |
| Website | |
| Website of the Diocese of Saint-Flour | |
The current bishop is Bruno Grua, who was appointed in March 2006 by Pope Benedict XVI. Like many French bishops, he was compelled to face the problem created by the dwindling number of priests in the Roman Catholic Church. In 1970 in Saint-Flour there were 264 priests; in 2010 there were 85.[1] The number of parishes was 161 in 2010, and half did not have a full-time priest.[2] Bishop Grua therefore reorganized the parish structure, reducing the number of parishes from 161 to 32 to ensure that every Catholic had a priest who was responsible for his/her spiritual needs. In 2014 there was one priest for every 1,914 Catholics. In 2017 there was one priest for every 2,553 Catholics.
History
Summarize
Perspective
The diocese is named after St. Florus (Flour), who is said to have been the first Bishop of Lodève and to have died at Indiciat (later Saint-Flour) while evangelizing Haute-Auvergne. These traditions have been the subject of numerous discussions. In two documents concerning the foundation of the second monastery of St-Flour, drawn up in 1013 and 1031, and in a letter written to Pope Urban IV in 1261 by Pierre de Saint-Haon, prior of Saint-Flour, St. Flour is already considered as belonging to the Apostolic times, and the Speculum sanctorale of Bernard Gui in 1329 relates at length the legend of this "disciple of Christ". Marcellin Boudet believes it more likely that St. Flour lived in the fifth century, and that it was he who attended the Council of Arles in 450 or 451.[citation needed]
At the close of the tenth century there was already a monastery at Indiciat. A local seigneur, Astorg de Brezons, surnamed "the Red Bull", gave this monastery to the abbey of Cluny, then under the direction of Odilo, Abbot of Cluny, and the donation was confirmed by Pope Gregory V (996–99).[3] Amblard de Brezons, his nephew, surnamed "le Mal Hiverné", seized the monastery and destroyed all of it except the church. Amblard and Astorg, from 1010 to 1013, gave this church and its fief to St. Peter's at Rome, together with the monastery of Sauxillanges, governed by Odilo; but later Amblard considered this donation as void, and constructed a fortress, a remnant of which is now the sacristy of the cathedral, on the site of the old monastery; afterwards Amblard, seized with remorse at Rome, between 1025 and 1031 gave back to Odilo all he possessed, and a large monastery was again founded. Pope Urban II, after the Council of Clermont (1095), consecrated the church of this new monastery. Pope Callistus II (1119–1124) passed some time there, on 1 and 2 June 1119.[4] The church collapsed in 1396, and no remains of it exist.
Creation of the diocese
In August, 1317, Pope John XXII detached Haute-Auvergne from the bishopric of Clermont and raised St-Flour to the rank of a bishopric, the first ordinary of which was his chaplain Raymond de Montuéjols. Among his successors were Pierre d'Estaing (1361–67), afterwards Archbishop of Bourges and cardinal in 1370; and Louis-Siffrein-Joseph de Salamon (1820–29), former counseiller-clerc to the Parlement of Paris, who during the French Revolution had secretly acted in France as the pope's agent, a rôle concerning which he has left very important memoirs.[citation needed]
The diocese of Saint-Flour was particularly hard hit by the Black Death of 1348–1353.[5] The mortality rate was over 50%.[6]
Revolution
During the French Revolution, the National Constituent Assembly reformed the Church in France, drawing up the Civil Constitution of the Clergy (12 July 1790).[7] All clergy were obliged to swear an oath of allegiance to the Constitution,[8] thereby effectively entering into a schism with the Papacy and the Roman Catholic Church. The Assembly ordered that the number of dioceses in France be reduced from 135 to 83, and that these surviving dioceses should be coterminous with the new 'départements' which were being created for civil administration; the new dioceses were to be grouped into new Metropolitanates. Saint-Flour was one of the dioceses to be suppressed. These revisions were contrary to the procedures of the Canon Law of the Roman Catholic Church.
In the Haut-Auvergne, the new Constitutional diocese was to be called 'Cantal', and it was assigned to the 'Metropole du Sud-Est'. The legitimate bishop of Saint-Flour, Ruffo de Bonneval, refused to take the oath to the Constitution, and therefore his seat was declared vacant. The electors of 'Cantal' were convened at Aurillac in March 1791, and nearly every village had its candidate. Half of the eligible electors refused to participate (198 out of 396), and the remaining voters took some time to sort out the candidates. On 15 March, they elected Anne-Alexandre-Marie Thibault, who had been a parish priest at Souppes in the diocese of Meaux. He was consecrated in Paris at Nôtre-Dame on 3 April 1791 by Constitutional Bishop Lamourette, his Metropolitan. Naturally he did not have his bulls of consecration from Rome, and therefore his consecration was valid, but illegitimate in Canon Law. He returned to his diocese in May to considerable hostility; he dismissed all the faculty of the seminary, since they had refused to take the oath to the Constitution, and then returned to Paris, where he was elected a member of the National Convention. He never returned, becoming a politician and successfully maneuvering the changes in government up to 1801 and the Concordat. He was forced to retire into private life, and died on 26 February 1813 without having been reconciled to the Church.[9]
Restoration
The diocese was re-established by the Holy See in accordance with canon law and the Concordat of 1801, which had been agreed by First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte and Pope Pius VII. The boundaries of the canonically re-established diocese were aligned, however, to coincide with those of the civil département of Cantal, rather than the territory of the pre-revolutionary diocese.
The Abbey of Aurillac is located in the diocesan territory.[10]
Bishops of Saint-Flour
to 1800
- Raymond de Vehens de Mostuejouls : (31 July 1317 – 1319)[11]
- Henri de Faltrédi : (19 April 1319 – 29 January 1320)[12]
- Archambaud : (6 February 1320 – 1347)[13]
- Deodatus de Canillac, O.S.B. : (25 July 1347 – 2 August 1361)[14]
- Pierre d'Estaing : (19 November 1361 – 2 April 1368)[15]
- Pierre Raussen : (2 April 1368 – 1374)[16]
- Pontius de Rochefort : (14 July 1374 – 1383)[17]
- Pierre de Vissac : (13 March 1383 – 12 July 1395)[18]
- Hugues de Manhac : (12 July 1295 – 16 January 1404)[19]
- Gerard du Puy (de Miremont) : (17 December 1404 – 4 January 1413)[20]
- Bertrand de Cadoent, O.S.B. : (15 February 1413 – 28 January 1426)[21]
- Jacques Lupi : (19 August 1426 – 1451)[22]
- Pierre de Lautoin : (7 July 1452 – 1461)[23]
- Antoine de Lautoin, O.S.B. : (30 March 1461 – 1482)[24]
- Charles de Joyeuse : (10 September 1483 – 1500)[25]
- Louis de Joyeuse : (29 January 1500 – )[26]
- Balthasar Jarente : (11 May 1543 – 9 January 1548)[27]
- Antoine de Lévis : (9 January 1548 – 1566)[28]
- Jean Paul de Selve : (23 May 1567 – 1572)[29]
- Pierre de Baume : (9 February 1573 – 1599)[30]
- Raymond de Rouchon : (10 March 1599 – September 1609)[31]
- Charles de Noailles : (28 September 1609 – 8 April 1647)[32]
- Jacques de Montrouge : (8 April 1647 – 1664)[33]
- Jérôme de la Mothe-Houdancourt : (23 June 1664 – 9 May 1693)[34]
- Joachim Joseph d'Estaing : (9 November 1693 – 13 April 1742)[35]
- Paul de Ribeyre : (9 July 1742 – 10 June 1776)[36]
- Anne Hippolyte Hay de Bontville : (16 September 1776 – 13 December 1779)[37]
- Claude Marie de Ruffo de Laric : (13 December 1779 – 1801)[38]
since 1800
- Jean-Eléonor Montanier de Belmont : (5 Jul 1802 – 1 May 1808 Died)
- Louis-Siffrein-Joseph de Salamon : (6 Mar 1820 – 11 Jun 1829 Died)
- François-Marie-Edouard de Gualy : (8 Jul 1829 – 18 Mar 1833 Appointed, Archbishop of Albi)
- Jean-Pierre-Marie Cadalen (24 Jun 1833 Appointed – 17 Apr 1836 Died)[39]
- Frédéric-Gabriel-Marie-François de Marguerye:[40] (1 Apr 1837 – 15 Oct 1851) (Appointed Bishop of Autun)
- Jean-Paul-François-Marie-Félix Lyonnet:[41] (15 Oct 1851 – 24 Jun 1857) (Appointed Bishop of Valence)
- Pierre-Antoine-Marie Lamouroux de Pompignac:[42] (24 Jun 1857 – 23 May 1877 Died)
- François-Antoine-Marie-Ambroise-Benjamin Baduel:[43] (15 Jun 1877 – 16 May 1891)
- Jean-Marie-François Lamouroux : (2 Apr 1892 – 12 Jul 1906 Died)
- Paul-Augustin Lecoeur : (13 Jul 1906 – 18 Mar 1942 Died)
- Henri-Marie-Joseph Pinson : (12 Jan 1943 – 18 Apr 1951 Died)
- Gabriel Auguste François Marty:[44] (6 Feb 1952 – 14 Dec 1959) (Appointed Coadjutor Archbishop of Reims)
- Maurice-Jean-Fernand-Alexis Pourchet (28 Mar 1960 – 6 May 1982 Retired)
- Jean Cuminal † (6 May 1982 Appointed – 25 Jul 1990 Appointed, Bishop of Blois)
- René Pierre Louis Joseph Séjourné (13 Sep 1990 Appointed – 16 Jan 2006 Retired)
- Bruno Grua[45] (31 Mar 2006 Appointed – 11 Jun 2021 Retired)
References
Books
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
