Dermodactylus
Genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Late Jurassic From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dermodactylus (meaning "skin finger", from Greek derma and daktylos, in reference to pterosaur wings being skin membranes supported by the ring fingers) was a genus of pterodactyloid (general term for "short-tailed" pterosaur) pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Wyoming, United States. It is based on a single partial bone, from the hand.
| Dermodactylus Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
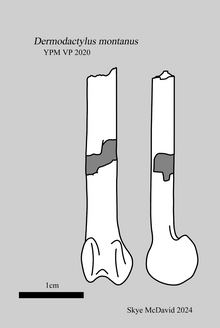 | |
| Holotype metacarpal | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Family: | †Incertae sedis |
| Genus: | †Dermodactylus Marsh, 1881 |
| Species: | †D. montanus |
| Binomial name | |
| †Dermodactylus montanus (Marsh, 1878) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
History and classification
Summarize
Perspective
Dermodactylus is based on a single distal right fourth metacarpal found by Samuel Wendell Williston at Como Bluff, Wyoming in 1878; this bone is currently housed in the collections of the Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History in New Haven, Connecticut (YPM 2020[1]). This bone constituted at the time the oldest pterosaur remains found, recognized, and described from North America.[2] Othniel Charles Marsh first named it as a species of Pterodactylus:[3] P. montanus, the specific name meaning "from the mountains" in Latin, but soon changed his mind and gave it a new generic name. At the same time he assigned another wing bone, teeth, vertebrae, and a scapulacoracoid to it,[4] but this material is probably too large to belong to the type individual.[5]
Its place within the Pterosauria is uncertain, beyond the Pterodactyloidea.[6] The material it is based on is too meager for further classification (although Carpenter et al.. [2003] note that the shape of the bone's articular end means that it did not belong to an ornithocheirid, a type of short-tailed pterosaur that often had a head crest and/or large teeth),[7] or for adding additional remains to the genus with any certainty, and so it is now regarded as a dubious pterodactyloid.[7][8][9][10] It was not even mentioned in the most recent major popular work on pterosaurs.[11]
Paleobiology
Marsh suggested it had a wingspan of 1.5–1.8 meters (4.9–5.9 feet),[4] but this is including the material excluded by Peter Wellnhofer, who estimates the wingspan of the only known individual at 1 meter (3.3 feet).[2] John Foster estimates its weight at 3.3 kilograms (7.3 pounds). It would probably have been a small aerial carnivore.[12]
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
