Dagnum
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
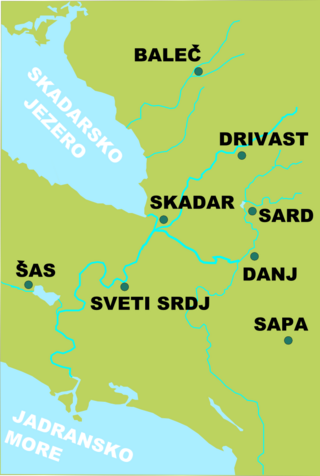
Dagnum (Albanian: Danjë or Dejë, Serbian: Danj, Italian: Dagno) was a town, bishopric and important medieval fortress located on the territory of present-day Albania, which has been under Albanian, Serbian, Venetian and Ottoman control and remains a Latin Catholic titular see. It is close to the modern day town of Vau i Dejës.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2009) |

History
Summarize
Perspective
In period 1081—1116 Dagnum belonged to the kingdom of Duklja.[1]
The Ragusan-Serbian peace treaty was signed in Danj on 25 March 1326, attended by vojvoda (Slavic count) Mladen and čelnik Đuraš Ilijić.[2]
Until 1395 Sati (whose castellan was Koja Zaharia) and Dagnum belonged to a fief of Kostadin Balšić and was part of the Lordship of Zeta under Đurađ II Balšić. In 1395 Balšić ceded Sati (with Dagnum) together with Scutari and Drivast to Venetian Republic (in order to create a buffer zone between remaining part of his Zeta and Ottoman Empire), but Zaharia refused to allow Venetians to take control over the Sati. He proclaimed himself the Lord of Sati and Dagnum ("dominus Sabatensis et Dagnensis")[3] after he captured Dagnum in 1396 which became the seat of his domain.

In 1429 Stefan Maramonte, supported by Ottomans and forces of Gojčin Crnojević and Little Tanush, plundered the region around Scutari and Ulcinj and attacked Drivast in 1429, but failed to capture it.[4] While Venetian forces were busy fighting to repel this attack, the Ottoman forces captured Dagnum and territory of Dukagjini and entrusted it to be governed by Ottoman voivode Ismail.[5]
After receiving incorrect information about the death of the Ottoman Sultan, Murad II, Gjergj Arianiti raised a large rebellion against the Ottomans in 1432. Nicholas Dukagjini, however, took advantage of this rebellion and conquered his family's former lands, accepting Venetian suzerainty. He yielded Dagnum to Venice. Venice soon learned that Sultan Murad was actually alive. Fearing that Venice would be provoking the Ottomans, they broke all relations with Dukagjini, and transferred Dagnum to Turkish hands by 1435.
Members of the Albanian League of Lezhë, Nikollë Dukagjini and Lekë Zaharia, lord of Dagnum, were in dispute over who should marry Irene Dushmani, the only child of Lekë Dushmani, prince of Zadrima. The Albanian princes were invited to the wedding of Skanderbeg's younger sister, Mamica, who was to wed Muzaka Thopia in 1445. Irene entered and hostilities soon began. Dukagjini asked Irene to marry him, but a drunken Zaharia saw this and assaulted Dukagjini. Some of the nobles attempted to end the fight, but this only led to more people being involved and resulted in many deaths until peace was established. Neither of the two antagonists had suffered any physical damage, but Dukagjini was morally humiliated. In an act of revenge, Dukagjini ambushed and killed Zaharia in 1447.
This resulted in the town's hostility towards the Albanian League. Venice quickly sent a force into Dagnum and the local population gave their support to Venice, including Zaharia's mother. Venice then set out to capture the rest of Zaharia's holdings, including Sati, Gladri and Dushmani, with Zaharia's mother's agreement. Skanderbeg had ordered the return of these towns, and Drivast, to Albanian hands, however, Venice refused. The Albanian League sent envoys to their northern neighbors, Principality of Zeta (under Stefan Crnojević) and the Despotate of Serbia (under Đurađ Branković) to aid the League against their Venetian enemies. Branković expressed his willingness to help against Venice, however, made it clear he would not aid against their common Ottoman enemies.
Skanderbeg ordered the invasion of Dagnum in 1447. The Venetians, however, saw this city as important, more important in fact than their anti-Ottoman war. Venice offered an award to anyone who could assassinate Skanderbeg. Venice even sent out envoys to the Ottomans to attack Albania once more.
Skanderbeg, however, heard that Venice sent out a force to protect Dagnum. He then left a small force to continue the siege on the city. In the meantime, Skanderbeg marched from the town to meet the Venetian army at the Drin River. What would be known as the Battle of the Drin in 1448, the League of Lezhë defeated the Venetians.
Venetian presence was reduced to small garrisons within several walled cities, including Dagnum. The Venetians opened up negotiations for peace with the Albanians in Alessio and peace was signed between the various representatives of both parties on 4 October 1448. The signatories agreed that Venice would pay 1,400 ducats a year to Skanderbeg and his male heirs and that Dagnum and all lands surrounding it would be relinquished to Venice.
Lekë Dukagjini fought the Venetians over the control of Dagnum since 1456. In 1456, Dukagjini captured the city, but Venice retook the city by August 1457.[6] Venetian forces led by Andrea Venier were supported by Skanderbeg.[7] Dukagjini finally made peace with Venice in 1459.
In 1474, the Ottoman Turks directed an attack against Crnojević Zeta and Venetian Zeta (around Lake Scutari). This war directly led to Ottoman conquest of the city from Venetian hands. The Ottomans had no intentions of retaining the city, but were content to demolish its fortifications.
Ecclesiastical history
Summarize
Perspective
Established circa 1000? as Diocese of Dagno / Dagne / Danj, without direct precursor, although the territory in the former Roman province of Dalmatia Superior was under the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Doclea.
Suppressed circa 1550. [8]
Episcopal Ordinaries
(very incomplete; all Roman Rite)
- Suffragan Bishops of Dagno
- Godefroid Greveray, Carmelite Order (O. Carm.) (1456.03.15 – ?)
- Bishop-elect Matthias Michaelis de Posegavan (consecrated 1481.09.10 – ?)
Titular see
In 1933 the diocese was nominally restored as Titular bishopric of Dagnum (Latin; Dagno in Curiate Italian).
It has had the following incumbents, so far of the fitting Episcopal (lowest) rank : [8]
- Luis Andrade Valderrama, Friars Minor (O.F.M.) (1939.03.03 – 1944.06.16) as Auxiliary Bishop of Bogotá (Colombia) (1939.03.03 – 1944.06.16), later Bishop of Antioquía (Colombia) (1944.06.16 – 1955.03.09), emeritate as Titular Bishop of Sarepta (1955.03.09 – death 1977.06.29)
- Bernhard Stein (1944.09.02 – 1967.04.13) as Auxiliary Bishop of Trier (Germany) (1944.09.02 – 1967.04.13), succeeding as Bishop of Trier ([1967.04.13] 1967.04.25 – retired 1980.09.05); died 1993
- Czesław Domin (1970.06.06 – 1992.02.01) as Auxiliary Bishop of Katowice (Poland) (1970.06.06 – 1992.02.01), next Bishop of Koszalin–Kołobrzeg (Poland) (1992.02.01 – death 1996.03.15)
- Stefan Siczek (1992.03.25 – 2012.07.31) as Auxiliary Bishop of Radom (Poland) (1992.03.25 – death 2012.07.31)
- Ángel Francisco Caraballo Fermín (2012.11.30 – 29 January 2019, as Auxiliary Bishop of Maracaibo (Venezuela)
- Américo Aguiar (1 March 2019 – 21 September 2023), auxiliary bishop of the Patriarchate of Lisbon
See also
References
Sources and external links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.