Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
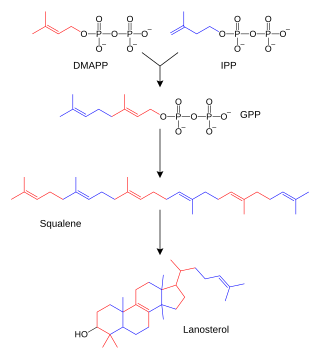
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Methyl-2-buten-1-yl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names
Dimethylallyl diphosphate; isoprenyl pyrophosphate; isoprenyl diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 3,3-dimethylallyl+pyrophosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O7P2 | |
| Molar mass | 246.092 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In the mevalonate pathway, DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway.
At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpenes and terpenoids, such as in plants, and that DMAPP is the crossover product.

Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.