Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
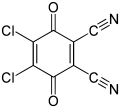
2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (or DDQ) is the chemical reagent with formula C6Cl2(CN)2O2. This oxidant is useful for the dehydrogenation of alcohols,[3] phenols,[4] and steroid ketones.[5] DDQ decomposes in water, but is stable in aqueous mineral acid.[6]
Remove ads
Remove ads
Preparation
Synthesis of DDQ involves cyanation of chloranil. J. Thiele and F. Günther first reported a 6-step preparation in 1906.[7] The substance did not receive interest until its potential as a dehydrogenation agent was discovered. A single-step chlorination from 2,3-dicyanohydroquinone was reported in 1965.[8]
Reactions
The reagent removes pairs of H atoms from organic molecules. The stoichiometry of its action is illustrated by the conversion of tetralin to naphthalene:
- 2 C6Cl2(CN)2O2 + C10H12 → 2 C6Cl2(CN)2(OH)2 + C10H8
The resulting hydroquinone is poorly soluble in typical reaction solvents (dioxane, benzene, alkanes), which facilitates workup.
Solutions of DDQ in benzene are red, due to the formation of a charge-transfer complex.[9]
Dehydrogenation
Aromatization
Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling
Remove ads
Safety
DDQ reacts with water to release highly toxic hydrogen cyanide (HCN).[6]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads