Cuyuní River
River in Venezuela and Guyana From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
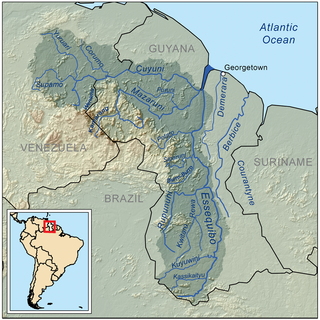
The Cuyuni River is a South American river and a tributary of the Essequibo River. It rises in the Guiana Highlands of Venezuela, where it descends northward to El Dorado, and turns eastward to meander through the tropical rain forests of the Cuyuni-Mazaruni Region of Guyana. It finally turns southeastward, flowing to its confluence with the Mazaruni River.
| Cuyuni River | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Venezuela and Guyana |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Guiana Highlands, Venezuela |
| • coordinates | 6°2′5.0316″N 61°36′34.1388″W |
| • elevation | 399 m (1,309 ft) |
| Mouth | Essequibo |
• location | Bartica, Guyana |
• coordinates | 6°24′28″N 58°37′18″W |
• elevation | 1 m (3 ft 3 in) |
| Length | 618 km (384 mi) |
| Basin size | 85,635 km2 (33,064 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Bartica, Guyana (near mouth) |
| • average | 85.808 km3/a (2,719.1 m3/s)[2] (Period: 1971–2000)2,674.2 m3/s (94,440 cu ft/s)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Kamaria Falls (Basin size: 53,354 km2 (20,600 sq mi) |
| • average | 1,360 m3/s (48,000 cu ft/s)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Anacoco |
| • average | 719.5 m3/s (25,410 cu ft/s)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | El Dorado, Venezuela |
| • average | (Period: 1971–2000)503.8 m3/s (17,790 cu ft/s)[3] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Essequibo → Atlantic Ocean |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Yuruarí, Corumpo |
| • right | Wenamu, Mazaruni |
The Cuyuni River marks a border in the Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute for approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi).
Makarapan Mountain is a sandstone range by the Cuyuni.[5]
History
In 1681, an island in the mouth of the Cuyuni River was cleared and planted with cassava for the use of the Dutch garrison. By 1694, a new plantation on the Cuyuni River above the fort was established. By 1703 a post was established on the Pariacot Savannah, in the upper Cuyuni.
On January 2, 1895, the "Incident of the Cuyuni river", so named by the general Domingo Antonio Sifontes, was an armed confrontation between Venezuelans and British in the region of the river over the territorial dispute between Venezuela and British Guyana, which under Sifontes the Venezuelans left winners.

At dawn, British policemen led by an Inspector Barnes of England took an unoccupied military station of Venezuelan nationality, located on the left bank of the river. Barnes’ men hoisted the British flag during the day.
Captain Andrés Avelino Domínguez, second in command of Sifontes, was sent to recover the settlement. The result was the withdrawal of the British and the capture of Barnes and his men, who were taken to the General Police Station, which increased tensions between the two countries amid an internal crisis in Venezuela. [6]
Settlement
The river is a source of alluvial gold and attracts mining in the form of dredging. Illegal mining also occurs on the river banks,[7] and mining also has exacerbated the border issue between Guyana and Venezuela.[8]
Large-scale mining operation Aurora gold mine is on the Cuyuni River.[9]
Development of a hydroelectric power site is under consideration at Kamaria on the Cuyuni River.[10]
Venezuela
El Dorado is a Venezuelan settlement on the Cuyuni River.[11]
Guyana
Some of the Kali'na people live in the Cuyuni River valley, part of which is in Guyana.
Eteringbang is a border settlement[12] with an airstrip.[13] Saint Martin and Ankoko Island have been the subject of further disputes between Venezuela and Guyana. In 2015, GDF forces continued observation from Eteringbang and Kaikan and other points along the river.[14]
The town of Bartica is close to the mouth of the Cuyuni where it meets with the confluence of Essequibo and Mazaruni rivers.[15]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.