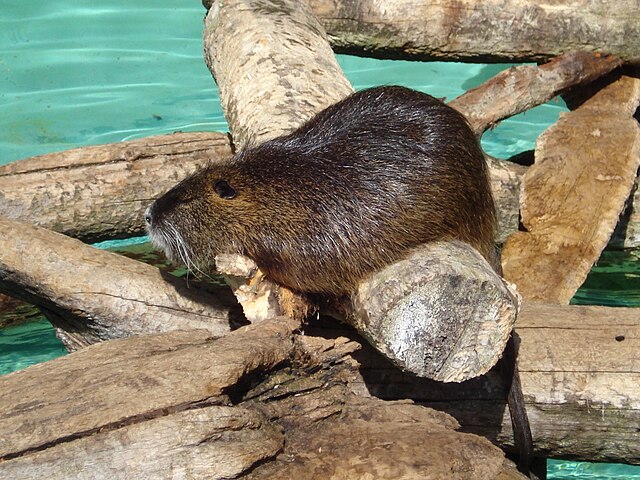
Nutria
Semi-aquatic rodent from South America From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The nutria (/ˈnjuːtriə/) or coypu (/ˈkɔɪpuː/) (Myocastor coypus)[1][2] is a herbivorous,[3] semiaquatic rodent from South America. Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae,[4] Myocastor has since been included within Echimyidae, the family of the spiny rats.[5][6][7] The nutria lives in burrows alongside stretches of water and feeds on river plant stems.[8]
| Nutria Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Echimyidae |
| Subfamily: | Echimyinae |
| Tribe: | Myocastorini |
| Genus: | Myocastor |
| Species: | M. coypus |
| Binomial name | |
| Myocastor coypus (Molina, 1782) | |
 | |
| The range of the Nutria Regions Extant (resident) Extant & Introduced (resident) Countries Extant & Introduced (resident) Extant (resident) Extant & Introduced | |
Originally native to subtropical and temperate South America, it was introduced to North America, Europe and Asia, primarily by fur farmers.[9] Although it is still hunted and trapped for its fur in some regions, its destructive burrowing and feeding habits often bring it into conflict with humans, and it is considered an invasive species in the United States.[10] Nutria also transmit various diseases to humans and animals, mainly through water contamination.[11]
Etymology
The genus name Myocastor derives from the two Ancient Greek words μῦς (mûs) 'rat, mouse', and κάστωρ (kástōr) 'beaver'.[12][13][14] Therefore, the name Myocastor literally means 'mouse beaver'.
Two names are commonly used in English for Myocastor coypus. The name nutria (from the Spanish word nutria 'otter') is generally used in North America, Asia, and throughout countries of the former Soviet Union; however, in most Spanish-speaking countries, the word nutria refers primarily to the otter. To avoid this ambiguity, the name coypu or coipo (derived from Mapudungun) is used in South America, Britain and other parts of Europe.[15] In France, the nutria is known as a ragondin. In Dutch, it is known as beverrat 'beaver rat'. In German, it is known as Nutria, Biberratte 'beaver rat', or Sumpfbiber 'swamp beaver'. In Italy, instead, the popular name is, as in North America and Asia, nutria, but it is also called castorino 'little beaver', by which its fur is known in Italy. In Swedish, the animal is known as sumpbäver 'marsh/swamp beaver'. In Brazil, the animal is known as ratão-do-banhado 'big swamp rat', nútria, or caxingui (the last from Tupi).
Taxonomy

The nutria was first described by Juan Ignacio Molina in 1782 as Mus coypus, a member of the mouse genus.[16] The genus Myocastor was assigned in 1792 by Robert Kerr.[17] Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, independently of Kerr, named the species Myopotamus coypus,[18] and it is occasionally referred to by this name.
Four subspecies are generally recognized:[16]
- M. c. bonariensis: northern Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay, Uruguay, southern Brazil (RS, SC, PR, and SP)
- M. c. coypus: central Chile, Bolivia
- M. c. melanops: Chiloé Island
- M. c. santacruzae: Patagonia
M. c. bonariensis, the subspecies present in the northernmost (subtropical) part of the nutria's range, is believed to be the type of nutria most commonly introduced to other continents.[15]
Phylogeny
Comparison of DNA and protein sequences showed that the genus Myocastor is the sister group to the genus Callistomys (painted tree-rats).[19][7] In turn, these two taxa share evolutionary affinities with other Myocastorini genera: Proechimys and Hoplomys (armored rats) on the one hand, and Thrichomys on the other hand.
| Genus-level cladogram of the Myocastorini. |
| The cladogram has been reconstructed from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA characters.[5][6][20][19][21][22][7] |
Appearance
Summarize
Perspective

The nutria somewhat resembles a very large rat, or a beaver with a small, long and skinny hairless tail. Adults are typically 4–9 kg (9–20 lb) in weight, and 40–60 cm (16–24 in) in body length, with a 30 to 45 cm (12 to 18 in) tail. It is possible for nutria to weigh up to 16 to 17 kg (35 to 37 lb), although adults usually average 4.5 to 7 kg (10 to 15 lb).[23][24][25] Nutria have three sets of fur. The guard hairs on the outer coat are three inches long.[26] They have coarse, darkish brown midlayer fur with soft dense grey under fur, also called the nutria. Three distinguishing features are a white patch on the muzzle, webbed hind feet, and large, bright orange-yellow incisors.[27] They have approximately 20 teeth with four large incisors that grow during the entirety of their lives.[28] The orange discoloration is due to pigment staining from the mineral iron in the tooth enamel. Nutria have prominent four inch long whiskers on each side of their muzzle or cheek area. The mammary glands and teats of female nutria are high on her flanks, to allow their young to feed while the female is in the water. There is no visible distinction between male and female nutria. Both are similar in coloring and weight.
A nutria is often mistaken for a muskrat (Ondatra zibethicus), another widely dispersed, semiaquatic rodent that occupies the same wetland habitats. The muskrat, however, is smaller and more tolerant of cold climates, and has a laterally flattened tail it uses to assist in swimming, whereas the tail of a nutria is round. It can also be mistaken for a small beaver, as beavers and nutria have very similar anatomies and habitats. However, beavers' tails are flat and paddle-like, as opposed to the round tails of nutria.[29]
Life history
Summarize
Perspective
view in Full HD
Nutria can live up to six years in captivity, but individuals rarely live past three years old in the wild. According to one study, 80% of nutrias die within the first year, and less than 15% of a wild population is over three years old.[30] A nutria is considered to have reached old age at four years old. Male nutria reach sexual maturity as early as four months, and females as early as three months; however, both can have a prolonged adolescence, up to the age of nine months. Once a female is pregnant, gestation lasts 130 days, and she may give birth to as few as one or as many as 13 offspring. The average nutria reproduction is four offspring. Female nutria will mate within two days after offspring are born. The years of reproduction cycle by litter size. Year one might be large, year two litter size will be smaller and year three the litter size will be another larger size. Females can only produce six litters in her life, rarely seven litters.[26] A female on average will have two litters a year.
Nutria generally line nursery nests with grasses and soft reeds. Baby nutria are precocial, born fully furred and with open eyes; they can eat vegetation and swim with their parents within hours of birth. A female nutria can become pregnant again the day after she gives birth to her young. If timed properly, a female can become pregnant three times within a year. Newborn nutria nurse for seven to eight weeks, after which they leave their mothers.[31] Nutria have been known to be territorial and aggressive when caught or cornered. They will bite and attack humans and dogs when threatened.[32] Nutria are mainly crepuscular or nocturnal, with most activity occurring around dusk and sunset with highest activity around midnight. When food is scarce, nutria will forage during the day. When food is plentiful, nutria will rest and groom during the day.[33]
Distribution
Summarize
Perspective

Native to subtropical and temperate South America, its range includes Chile, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay and the southern parts of Brazil and Bolivia. It has been introduced to North America, Europe and Asia, primarily by fur ranchers. The distribution of nutrias outside South America tends to contract or expand with successive cold or mild winters. During cold winters, nutria often suffer frostbite on their tails, leading to infection or death. As a result, populations of nutria often contract and even become locally or regionally extinct as in the Scandinavian countries and such U.S. states as Idaho, Montana, and Nebraska during the 1980s.[35] During mild winters, their ranges tend to expand northward. For example, in recent years, range expansions have been noted in Washington and Oregon,[36] as well as Delaware.[37]
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, nutria were first introduced to the United States in California, in 1899 by William Franklin Frakes. As of 2024[update], they had spread to the San Francisco Bay Area, where their digging threatened storm levees, and the California Department of Fish and Wildlife had an active eradication program.[38][39]
They were first brought to Louisiana in the early 1930s for the fur industry, and the population was kept in check, or at a small population size, because of trapping pressure from the fur traders.[15] The earliest account of nutria spreading freely into Louisiana wetlands from their enclosures was in the early 1940s; a hurricane hit the Louisiana coast for which many people were unprepared, and the storm destroyed the enclosures, enabling the nutria to escape into the wild.[15] According to the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries, nutria were also transplanted from Port Arthur, Texas, to the Mississippi River in 1941 and then spread due to a hurricane later that year.[40]
Habitat and feeding
Summarize
Perspective
Besides breeding quickly, each nutria consumes large amounts of aquatic vegetation.[41] An individual consumes about 25% of its body weight daily, and feeds year-round.[31][42] Being one of the world's larger extant rodents, a mature, healthy nutria averages 5.4 kg (11 lb 14 oz) in weight, but they can reach as much as 10 kg (22 lb).[43][44] They eat the base of the above-ground stems of plants, and often dig through soil for roots and rhizomes to eat.[45] Nutria eat parts and whole plants, and go after roots, rhizomes, tubers and black willow tree bark in the winter. Their creation of "eat-outs", areas where a majority of the above- and below-ground biomass has been removed, produces patches in the environment, which in turn disrupts the habitat for other animals and humans dependent on wetlands and marshes.[46] Nutria eat the following plant varieties: cattail, rushes, reeds, arrowheads, flatsedges, and cordgrasses. Commercial crops that nutria also eat are lawn grasses, alfalfa, corn, rice, and sugarcane.[26]
Nutria are found most commonly in freshwater marshes and wetlands, but also inhabit brackish marshes and rarely salt marshes.[47][48] They either construct their own burrows, or occupy burrows abandoned by beaver, muskrats, or other animals.[10] They are also capable of constructing floating rafts out of vegetation.[10] Nutria live in partially underwater dens. The main chamber is not submerged underground. Nutria are considered to be a species that lives in colonies. One male will share a den with three or four females and their offspring. Nutria use "feeding platforms" which are constructed in the water from cut pieces of vegetation supported by a structure like a log or branches. Muskrat dens and beaver lodges are also often used as feeding platforms.[26]
Commercial use and issues
Summarize
Perspective

Farming and the fur trade
Local extinction in their native range due to overharvesting led to the development of nutria fur farms in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The first farms were in Argentina and then later in Europe, North America, and Asia. These farms have generally not been successful long-term investments, and farmed nutria often are released or escape as operations become unprofitable. The first attempt at nutria farming was in France in the early 1880s, but it was not much of a success.[49] The first efficient and extensive nutria farms were located in South America in the 1920s.[49] The South American farms were very successful, and led to the growth of similar farms in North America and Europe. Nutrias from these farms often escaped, or were deliberately released into the wild to provide a game animal or to remove aquatic vegetation.[50]
Nutria were introduced to the Louisiana ecosystem in the 1930s, when they escaped from fur farms that had imported them from South America. Nutria were released into the wild by at least one Louisiana nutria farmer in 1933 and these releases were followed by E. A. McIlhenny who released his entire stock in 1945 on Avery Island.[51] In 1940, some of the nutria escaped during a hurricane and quickly populated coastal marshes, inland swamps, and other wetland areas.[52] From Louisiana, nutria have spread across the Southern United States, wreaking havoc on marshlands.
Following a decline in demand for nutria fur, nutria have since become pests in many areas, destroying aquatic vegetation, marshes, and irrigation systems, and chewing through man-made items such as tires and wooden house panelling in Louisiana, eroding river banks, and displacing native animals. Damage in Louisiana has been sufficiently severe since the 1950s to warrant legislative attention; in 1958, the first bounty was placed on nutria, though this effort was not funded.[53]: 3 By the early 2000s, the Coastwide Nutria Control Program was established, which began paying bounties for nutria killed in 2002.[53]: 19–20 In the Chesapeake Bay region in Maryland, where they were introduced in the 1940s, nutria are believed to have destroyed 2,800 to 3,200 hectares (7,000 to 8,000 acres) of marshland in the Blackwater National Wildlife Refuge. In response, by 2003, a multimillion-dollar eradication program was underway.[54]
In the United Kingdom, nutria were introduced to East Anglia, for fur, in 1929; many escaped and damaged the drainage works, and a concerted programme by MAFF eradicated them by 1989.[55]
Food products
A small number of game meat websites on the internet sell nutria meat for consumption. As of 2016, at least one Moscow restaurant serves nutria meat dishes.[56] In 1997 and 1998, Louisiana attempted to encourage the public to consume nutria meat. Nutria meat is leaner with a lower fat content and lower in cholesterol compared to ground beef.[57] In an effort to encourage Louisianians to eat nutria, several recipes were distributed to locals and published on the internet.[58] People in poor and rural Louisiana have trapped and consumed nutria meat for decades.
Marsh Dog, a US company based in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, received a grant from the Barataria-Terrebonne National Estuary Program to establish a company that uses nutria meat for dog food products.[59] In 2012, the Louisiana Wildlife Federation recognized Marsh Dog with "Business Conservationist of the Year" award for finding a use for this eco-sustainable protein.[60] A claimed environmentally sound solution is the use of nutria meat to make dog food treats.[61]
In Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, nutria (Russian and local languages Нутрия) are farmed on private plots and sold in local markets as a poor man's meat.[56] As of 2016, however, the meat is used successfully in Moscow restaurant Krasnodar Bistro, as part of the growing Russian localvore movement and as a 'foodie' craze.[56] It appears on the menu as a burger, hotdog, dumplings, or wrapped in cabbage leaves, with the flavour being somewhere between turkey and pork.[62]
Ecological impacts
Summarize
Perspective
Herbivory and habitat degradation

Nutria herbivory "severely reduces overall wetland biomass and can lead to the conversion of wetland to open water."[42] Unlike other common disturbances in marshlands, such as fire and tropical storms, which are a once- or few-times-a-year occurrence, nutria feed year round, so their effects on the marsh are constant. Also, nutria are typically more destructive in the winter than in the growing season, due largely to the scarcity of above-ground vegetation; as nutria search for food, they dig up root networks and rhizomes for food.[45]
While nutria are the most common herbivores in Louisiana marshes, they are not the only ones. Feral hogs, also known as wild boars (Sus scrofa), swamp rabbits (Sylvilagus aquaticus), and muskrats (Ondatra zibethicus) are less common, but feral hogs are increasing in number in Louisiana wetlands. On plots open to nutria herbivory, 40% less vegetation was found than in plots guarded against nutria by fences. This number may seem insignificant, and indeed herbivory alone is not a serious cause of land loss, but when herbivory was combined with an additional disturbance, such as fire, single vegetation removal, or double vegetation removal to simulate a tropical storm, the effect of the disturbances on the vegetation were greatly amplified.[42]
As different factors were added together, they resulted in less overall vegetation. Adding fertilizer to open plots did not promote plant growth; instead, nutria fed more in the fertilized areas. Increasing fertilizer inputs in marshes only increases nutria biomass instead of the intended vegetation, therefore increasing nutrient input is not recommended.[42] The problem became so serious that Sheriff Harry Lee of Jefferson Parish used SWAT sharpshooters against the animals.[63]
Wetlands in general are a valuable resource both economically and environmentally. For instance, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service determined wetlands covered only 5% of the land surface of the contiguous 48 United States, but they support 31% of the nation's plant species.[64] These very biodiverse systems provide resources, shelter, nesting sites, and resting sites (particularly Louisiana's coastal wetlands such as Grand Isle for migratory birds) to a wide array of wildlife. Human users also receive many benefits from wetlands, such as cleaner water, storm surge protection, oil and gas resources (especially on the Gulf Coast), reduced flooding, and chemical and biological waste reduction, to name a few.[64] In Louisiana, rapid wetland loss occurs due to a variety of reasons; this state loses an estimated area about the size of a football field every hour.[65]
In 1998, the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries (LDWF) conducted the first Louisiana coast-wide survey, which was funded by the Coastal Wetlands Planning, Protection, and Restoration Act and titled the Nutria Harvest and Wetland Demonstration Program, to evaluate the condition of the marshlands.[66] The survey revealed through aerial surveys of transects that herbivory damage to wetlands totaled roughly 36,000 hectares (90,000 acres). The next year, LDWF performed the same survey and found the area damaged by herbivory increased to about 42,000 hectares (105,000 acres).[47] The LDWF has determined the wetlands affected by nutria decreased from an estimated minimum of 32,000 hectares (80,000 acres) of Louisiana wetlands in 2002–2003 season to about 2,548 hectares (6,296 acres) during the 2010–2011 season.[67] The LDWF stresses that coastal wetland restoration projects will be greatly hindered without effective, sustainable nutria population control.
Pathogenic and viral reservoirs of zoonotic diseases
In addition to direct environmental damage, nutria are the host for a roundworm nematode parasite (Strongyloides myopotami [d]) that can infect the skin of humans, causing dermatitis similar to strongyloidiasis.[68] The condition is also called "nutria itch".[69] Other parasites they can host are tapeworms, liver flukes, and blood flukes. Waterbody contamination by nutria occurs through urine and feces.[70] Nutria also host fleas, ticks and chewing louse.[71] They can carry several zoonotic diseases (diseases transmitted from animals to humans). They are reservoirs for salmonellosis, encephalomyocarditis virus, chlamydia psittaci[72] and antibiotic resistant bacteria, Aeromonas spp.[73] Other zoonotic disease of concern they are host reservoirs for are mycobacterium tuberculosis, septicemia, toxoplasmosis, and rickettsiosis.[74] According to the CDC, nutria carry two out of eight diseases of concern for the United States, rabies and salmonellosis.[75] Nutria are considered a global alien species and have potential to spread disease to livestock and humans. Nutria are found on every continent except Australia and Antarctica. Native to the southern hemisphere and spreading globally requires preventive monitoring for zoonotic disease transmission. Nutria immigration is monitored for habitat destruction of wetlands, farmlands, marshes and is measured in habitat loss in acres.[76] Increased local awareness of viral, bacterial and parasitic transmission from nutria to humans and livestock will be of greater importance as climate change progresses.
Control efforts
Summarize
Perspective
As a global alien species, nutria are monitored and managed throughout the world. Many countries have attempted eradication efforts with varying degrees of success.

Nutria are predicted to expand their range northward over the next century as global temperatures increase.[77]
European Union
This species is included since 2016 in the EU list of Invasive Alien Species of Union concern (the Union list).[78] This implies that this species cannot be imported, bred, transported, commercialized, or intentionally released into the environment in the whole of the European Union.[79]
Ireland
A nutria was first sighted in the wild in Ireland in 2010. Some nutria escaped from a pet farm in Cork City in 2015 and began breeding on the outskirts of the city. Ten were trapped on the Curraheen River in 2017, but the rodents continued to spread, reaching Dublin via the Royal Canal in 2019.[80][81][82] Animals were found along the River Mulkear in 2015. The National Biodiversity Data Centre issued a species alert in 2017, saying that nutria "[have] the potential to be a high impact invasive species in Ireland. […] This species is listed as among 100 of the worst invasive species in Europe."[83]
Great Britain
In the UK, nutria escaped from fur farms and were reported in the wild as early as 1932. There were three unsuccessful attempts to control nutria in East Anglia between 1943 and 1944. Nutria population and range increased, causing damage to agriculture in the 1950s. During the 1960s, a grant was awarded to rabbit clearance societies that included nutria.[84] This control allowed for the removal of 97,000 nutria in 1961 and 1962. From 1962 to 1965, 12 trappers were hired to eradicate as many nutria as possible confining the remaining population within the Norfolk Broads. The campaign used live traps allowing non-target species to be released while any nutria caught were shot. Combined with cold winters in 1962 to 1963, almost 40,500 nutria were removed from the population. Although nutria populations were greatly reduced after the 1962–1965 campaign ended, the population increased until another eradication campaign began in 1981. This campaign succeeded in fully eradicating nutria in Great Britain. The trapping areas were broken into eight sectors leaving no area uncontrolled. The 24 trappers were offered an incentive for early completion of the 10-year campaign. In 1989 nutria were assumed eradicated, as only three males were found between 1987 and 1989.[85]
Japan
Nutria were introduced to Japan in 1939. They were imported from France during World War II to support food shortages as well as the fur trade. After the war in 1950, many nutria were released en masse or escaped, and became one of Japan's worst invasive species, damaging river banks, rice fields and other valuable crops.[86] In 1963 an eradication program was started to remove nutria but has shown little to no success. Nutria are still present in Japan and there is a restriction on importing, transporting and obtaining nutria per the Invasive Alien Species Act established in 2004.[87]
New Zealand
Nutria are classed as a "prohibited new organism" under New Zealand's Hazardous Substances and New Organisms Act 1996, preventing it from being imported into the country.[88]
United States

Atlantic Coast
An eradication program on the Delmarva Peninsula, between Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Coast, where nutria once numbered in the tens of thousands and had destroyed thousands of hectares of marshland, had nearly succeeded by 2012.[89] In September 2022 government officials announced that nutria have been completely eradicated on the Maryland Eastern Shore.[90][91]
California
The first records of nutria invading California dates from the 1940s and 1950s, when the species was found in the agriculture-rich Central Valley and the south coast of the state, but by the 1970s the animals had been extirpated statewide.[92] They were found again in Merced County in 2017, on the edge of the San Joaquin River Delta. State officials are concerned that they will harm infrastructure that sends water to San Joaquin Valley farms and urban areas.[93] In 2019, the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) received nearly $2 million in Governor Gavin Newsom's first budget, and an additional $8.5 million via the Delta Conservancy (a state agency focused on the Delta) to be spent over the course of three years.[94] The state has adopted an eradication campaign based on the successful effort in the Chesapeake Bay, including strategies such as the "Judas nutria" (in which individualized nutria are caught, sterilized, fitted with radio collars, and released, whereupon they can be tracked by hunters as they return to their colonies) and the use of trained dogs.[94] The state has also reversed a prior "no-hunting" policy, although hunting the animals does require a license.[94] California has a restriction on importation and transportation without a permit.[11] If nutria are found or captured in the state of California, local authorities must be notified right away and the nutria cannot be released. Licensed hunters in the state of California may hunt nutria as a non-game animal. Bounty programs are not advised in California due to native species of muskrat and beaver being misidentified.[95]
Louisiana
The Louisiana Coastwide Nutria Control Program provides incentives for harvesting nutria. Starting in 2002, the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries (LDWF) performed aerial surveys just as they had done for the Nutria Harvest and Wetland Demonstration Program, except under a different program title. Under the Coastwide Nutria Control Program, which also receives funds from CWPPRA, 308,160 nutria were harvested the first year (2002–2003), revealing 33,220 hectares (82,080 acres) damage and totaling $1,232,640 in incentive payouts to those legally participating in the program.[67] Essentially, once a person receives a license to hunt or trap nutria, that person is allowed to capture an unlimited number. When a nutria is captured, the tail is cut off and turned in to a Coastal Environments Inc. (CEI) official at an approved site. As of 2019, each nutria tail is worth $6, which is an increase from $4 before the 2006–2007 season.[96] Nutria harvesting increased drastically during the 2009–2010 season, with 445,963 nutria tails turned in worth $2,229,815 in incentive payments.[67] Each CEI official keeps record of how many tails have been turned in by each individual per parish, the method used in capture of the nutria, and the location of capture. All of this information is transferred to a database to calculate the density of nutria across the Louisiana coast, and the LDWF combines these data with the results from the aerial surveys to determine the number of nutria remaining in the marshes and the amount of damage they are inflicting on the ecosystem.[67]
Another program executed by LDWF involves creating a market of nutria meat for human consumption, though it is still trying to gain public notice. Nutria is a very lean, protein-rich meat, low in fat and cholesterol with the taste, texture, and appearance of rabbit or dark turkey meat.[97] Few pathogens are associated with the meat, but proper heating when cooking should kill them. The quality of the meat and the minimal harmful microorganisms associated with it make nutria meat an "excellent food product for export markets".[48]
Several desirable control methods are ineffective for various reasons. Zinc phosphide is the only rodenticide registered to control nutria, but it is expensive, remains toxic for months, detoxifies in high humidity and rain, and requires construction of expensive floating rafts for placement of the chemical. It is not yet sure how many nontarget species are susceptible to zinc phosphide, but birds and rabbits have been known to die from ingestion.[98] Therefore, this chemical is rarely used, especially not in large-scale projects. Other potential chemical pesticides would be required by the US Environmental Protection Agency to undergo vigorous testing before being acceptable to use on nutria. The LDWF has estimated costs for new chemicals to be $300,000 for laboratory, chemistry, and field studies, and $500,000 for a mandatory Environmental Impact Statement.[98] Contraception is not a common form of control, but is preferred by some wildlife managers. It is also expensive to operate– an estimated $6 million annually to drop bait laced with birth-control chemicals. Testing of other potential contraceptives would take about five to eight years and $10 million, with no guarantee of FDA approval.[98] Also, an intensive environmental assessment would have to be completed to determine whether any non-target organisms were affected by the contraceptive chemicals. Neither of these control methods is likely to be used in the near future.[citation needed]
In Louisiana, a claimed environmentally sound solution is the killing of nutria to make dog food treats.[61]
Gallery
- Nutria heart
- Skull from various perspectives
- By the river Ljubljanica
- Feral nutria in Oise river in France
- 10-day-old baby nutria
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.