Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Sharp-tailed snake
Species of snake From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The sharp-tailed snake or sharptail snake (Contia tenuis) is a small species of nonvenomous snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to the Western United States and British Columbia.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2016) |
Remove ads
Remove ads
Common names
Additional common names for C. tenuis include brown snake, gentle brown snake, Oregon worm snake, Pacific brown snake, Pacific ground snake, and purple-tailed snake.[5]
Geographic range
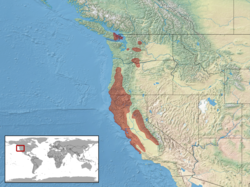
C. tenuis is distributed through the states of California, Oregon, and Washington, as well as British Columbia, Canada: Southern Vancouver Island, British Columbia around Victoria, British Columbia,[6] and a newly discovered site in Pemberton, British Columbia.[7][8]
Description
The sharp-tailed snake has an average total length (including tail) of 12–18 in (30–46 cm) as an adult. It is distinguished by its sharp tail spine, which is the protruding tip of the last tail vertebra. The spine is not toxic and cannot injure humans. Rather, the tail is used to stabilize small prey, such as slugs, for consumption. The dorsal surface ranges in color from grayish brown to brown to brick red, with bubble-gum pink and peachy-orange specimens occasionally found. The ventral surface is a striking series of black and white crossbars.[9]
Behavior
The sharp-tailed snake is a shy, secretive creature most often encountered under rocks and logs, and rarely to never found in the open.[9] It is able to persist in urban areas where appropriate cover can be found. It is known to burrow into soft soil or cracks in the clay, and may be encountered by people who are digging in the garden or removing concrete. When encountered, the sharp-tailed snake may roll into a ball and remain still. It can be mistaken for a worm by the casual observer.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Diet
The diet of C. tenuis is largely restricted to slugs and eggs of slugs. It sometimes also eats insects and earthworms.[9]
Reproduction
The adult female C. tenuis lays 4–16 eggs in the summer, underground or in a burrow. Each hatchling is 3–4 in (7.6–10.2 cm) in total length (including tail).[citation needed]
References
External links
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads