Cumulative distribution function
Probability that random variable X is less than or equal to x From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Probability that random variable X is less than or equal to x From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable , or just distribution function of , evaluated at , is the probability that will take a value less than or equal to .[1]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2010) |

Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by a right-continuous monotone increasing function (a càdlàg function) satisfying and .
In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from negative infinity to . Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables.
The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable is the function given by[2]: p. 77
| (Eq.1) |
where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable takes on a value less than or equal to .
The probability that lies in the semi-closed interval , where , is therefore[2]: p. 84
| (Eq.2) |
In the definition above, the "less than or equal to" sign, "≤", is a convention, not a universally used one (e.g. Hungarian literature uses "<"), but the distinction is important for discrete distributions. The proper use of tables of the binomial and Poisson distributions depends upon this convention. Moreover, important formulas like Paul Lévy's inversion formula for the characteristic function also rely on the "less than or equal" formulation.
If treating several random variables etc. the corresponding letters are used as subscripts while, if treating only one, the subscript is usually omitted. It is conventional to use a capital for a cumulative distribution function, in contrast to the lower-case used for probability density functions and probability mass functions. This applies when discussing general distributions: some specific distributions have their own conventional notation, for example the normal distribution uses and instead of and , respectively.
The probability density function of a continuous random variable can be determined from the cumulative distribution function by differentiating[3] using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus; i.e. given , as long as the derivative exists.
The CDF of a continuous random variable can be expressed as the integral of its probability density function as follows:[2]: p. 86
In the case of a random variable which has distribution having a discrete component at a value ,
If is continuous at , this equals zero and there is no discrete component at .


Every cumulative distribution function is non-decreasing[2]: p. 78 and right-continuous,[2]: p. 79 which makes it a càdlàg function. Furthermore,
Every function with these three properties is a CDF, i.e., for every such function, a random variable can be defined such that the function is the cumulative distribution function of that random variable.
If is a purely discrete random variable, then it attains values with probability , and the CDF of will be discontinuous at the points :
If the CDF of a real valued random variable is continuous, then is a continuous random variable; if furthermore is absolutely continuous, then there exists a Lebesgue-integrable function such that for all real numbers and . The function is equal to the derivative of almost everywhere, and it is called the probability density function of the distribution of .
If has finite L1-norm, that is, the expectation of is finite, then the expectation is given by the Riemann–Stieltjes integral

and for any , as well as as shown in the diagram (consider the areas of the two red rectangles and their extensions to the right or left up to the graph of ). In particular, we have In addition, the (finite) expected value of the real-valued random variable can be defined on the graph of its cumulative distribution function as illustrated by the drawing in the definition of expected value for arbitrary real-valued random variables.
As an example, suppose is uniformly distributed on the unit interval .
Then the CDF of is given by
Suppose instead that takes only the discrete values 0 and 1, with equal probability.
Then the CDF of is given by
Suppose is exponential distributed. Then the CDF of is given by
Here λ > 0 is the parameter of the distribution, often called the rate parameter.
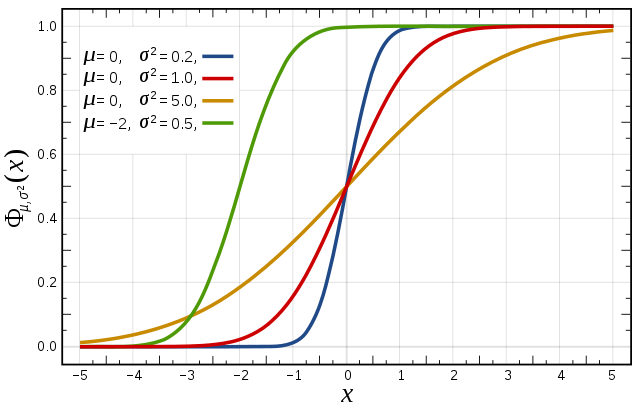
Suppose is normal distributed. Then the CDF of is given by
Here the parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution; and is its standard deviation.
A table of the CDF of the standard normal distribution is often used in statistical applications, where it is named the standard normal table, the unit normal table, or the Z table.
Suppose is binomial distributed. Then the CDF of is given by
Here is the probability of success and the function denotes the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments, and is the "floor" under , i.e. the greatest integer less than or equal to .
Sometimes, it is useful to study the opposite question and ask how often the random variable is above a particular level. This is called the complementary cumulative distribution function (ccdf) or simply the tail distribution or exceedance, and is defined as
This has applications in statistical hypothesis testing, for example, because the one-sided p-value is the probability of observing a test statistic at least as extreme as the one observed. Thus, provided that the test statistic, T, has a continuous distribution, the one-sided p-value is simply given by the ccdf: for an observed value of the test statistic
In survival analysis, is called the survival function and denoted , while the term reliability function is common in engineering.

While the plot of a cumulative distribution often has an S-like shape, an alternative illustration is the folded cumulative distribution or mountain plot, which folds the top half of the graph over,[5][6] that is
where denotes the indicator function and the second summand is the survivor function, thus using two scales, one for the upslope and another for the downslope. This form of illustration emphasises the median, dispersion (specifically, the mean absolute deviation from the median[7]) and skewness of the distribution or of the empirical results.
If the CDF F is strictly increasing and continuous then is the unique real number such that . This defines the inverse distribution function or quantile function.
Some distributions do not have a unique inverse (for example if for all , causing to be constant). In this case, one may use the generalized inverse distribution function, which is defined as
Some useful properties of the inverse cdf (which are also preserved in the definition of the generalized inverse distribution function) are:
The inverse of the cdf can be used to translate results obtained for the uniform distribution to other distributions.
The empirical distribution function is an estimate of the cumulative distribution function that generated the points in the sample. It converges with probability 1 to that underlying distribution. A number of results exist to quantify the rate of convergence of the empirical distribution function to the underlying cumulative distribution function.[9]
When dealing simultaneously with more than one random variable the joint cumulative distribution function can also be defined. For example, for a pair of random variables , the joint CDF is given by[2]: p. 89
| (Eq.3) |
where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable takes on a value less than or equal to and that takes on a value less than or equal to .
Example of joint cumulative distribution function:
For two continuous variables X and Y:
For two discrete random variables, it is beneficial to generate a table of probabilities and address the cumulative probability for each potential range of X and Y, and here is the example:[10]
given the joint probability mass function in tabular form, determine the joint cumulative distribution function.
| Y = 2 | Y = 4 | Y = 6 | Y = 8 | |
| X = 1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 |
| X = 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 |
| X = 5 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 |
| X = 7 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 0 |
Solution: using the given table of probabilities for each potential range of X and Y, the joint cumulative distribution function may be constructed in tabular form:
| Y < 2 | Y ≤ 2 | Y ≤ 4 | Y ≤ 6 | Y ≤ 8 | |
| X < 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| X ≤ 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| X ≤ 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| X ≤ 5 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.85 |
| X ≤ 7 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.75 | 1 |
For random variables , the joint CDF is given by
| (Eq.4) |
Interpreting the random variables as a random vector yields a shorter notation:
Every multivariate CDF is:
Not every function satisfying the above four properties is a multivariate CDF, unlike in the single dimension case. For example, let for or or and let otherwise. It is easy to see that the above conditions are met, and yet is not a CDF since if it was, then as explained below.
The probability that a point belongs to a hyperrectangle is analogous to the 1-dimensional case:[11]
The generalization of the cumulative distribution function from real to complex random variables is not obvious because expressions of the form make no sense. However expressions of the form make sense. Therefore, we define the cumulative distribution of a complex random variables via the joint distribution of their real and imaginary parts:
Generalization of Eq.4 yields as definition for the CDS of a complex random vector .
The concept of the cumulative distribution function makes an explicit appearance in statistical analysis in two (similar) ways. Cumulative frequency analysis is the analysis of the frequency of occurrence of values of a phenomenon less than a reference value. The empirical distribution function is a formal direct estimate of the cumulative distribution function for which simple statistical properties can be derived and which can form the basis of various statistical hypothesis tests. Such tests can assess whether there is evidence against a sample of data having arisen from a given distribution, or evidence against two samples of data having arisen from the same (unknown) population distribution.
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test is based on cumulative distribution functions and can be used to test to see whether two empirical distributions are different or whether an empirical distribution is different from an ideal distribution. The closely related Kuiper's test is useful if the domain of the distribution is cyclic as in day of the week. For instance Kuiper's test might be used to see if the number of tornadoes varies during the year or if sales of a product vary by day of the week or day of the month.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.