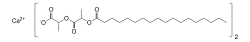
Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate (calcium stearoyl lactylate or CSL) or E482 is a versatile, FDA approved food additive. It is one type of a commercially available lactylate. CSL is non-toxic,[3][4] biodegradable,[5] and typically manufactured using biorenewable feedstocks.[6][7] Because CSL is a safe and highly effective food additive, it is used in a wide variety of products from baked goods and desserts to packaging.[2][8][9][10]
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Calcium bis(2-{[2-(octadecanoyloxy)propanoyl]oxy}propanoate) | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.851 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E482 (thickeners, ...) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C48H86CaO12 | |
| Molar mass | 895.282 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | a cream-colored nonhygroscopic powder with a caramel odor[1][2] |
| Melting point | 45 °C (113 °F; 318 K)[2] |
| sparingly soluble[2] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
As described by the Food Chemicals Codex 7th edition, CSL is a cream-colored powder.[1] CSL is currently manufactured by the esterification of stearic acid and lactic acid with partial neutralization using food-grade hydrated lime (calcium hydroxide). Commercial grade CSL is a mixture of calcium salts of stearoyl lactic acid, with minor proportions of other salts of related acids. The HLB for CSL is 5.1. It is slightly soluble in hot water. The pH of a 2% aqueous suspension is approximately 4.7.[2]
Food labeling requirements
To be labeled as CSL for sale within the United States, the product must conform to the specifications detailed in 21 CFR 172.844.[8] In the EU, the product must conform to the specifications detailed in Regulation (EC) No 96/77.[11] Tests for these specifications can be found in the Food Chemical Codex.[1] Acceptance criteria for these two regions are as follows:
| Specific Test | Acceptance Criterion (FCC) | Acceptance Criterion (EU) |
|---|---|---|
| Acid Value | 50 - 86 | 50 - 130 |
| Calcium Content | 4.2% - 5.2% | 1% - 5.2% |
| Ester Value | 125 - 164 | 125 - 190 |
| Total Recoverable Lactic Acid | 32.0% - 38.0% | 15% - 40% |
To be labeled as CSL for sale in other regions, the product must conform to the specifications detailed in that region's codex.
Food applications and maximum use levels
Summarize
Perspective
CSL finds widespread application in baked goods, cereals, pastas, instant rice, desserts, icings, fillings, puddings, toppings, sugar confectionaries, powdered beverage mixes, creamers, cream liqueurs, dehydrated potatoes, snack dips, sauces, gravies, chewing gum, dietetic foods, minced and diced canned meats, and mostarda di frutta.[9][12] In the United States, approved uses and use levels are described in 21 CFR 172.844,[8] 21 CFR 176.170[13] and 21 CFR 177.120.[10] while the corresponding regulations in the EU are listed in Regulation (EC) No 95/2.[9]
| United States | European Union | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Maximum use level | Application | Maximum use level | Application | Maximum use level | Application | Maximum use level |
| Yeast-leavened bakery products | 0.5% of flour | Fine baked goods | 5 g/kg | Bread | 3 g/kg | Breakfast cereals | 5 g/kg |
| Liquid and frozen egg whites | 0.05% | Fat emulsions | 10 g/kg | Desserts | 5 g/kg | Sugar confectionery | 5 g/kg |
| Dried egg whites | 0.5% | Beverage whiteners | 3 g/kg | Hot powder beverage mixes | 2 g/l | Dietetic foods | 2 g/l |
| Whipped vegetable oil topping | 0.3% | Quick-cook rice | 4 g/kg | Minced and diced canned meats | 4 g/kg | Mostarda di frutta | 2 g/kg |
| Dehydrated potatoes | 0.5% | Cereal-based snacks | 2 g/kg | Cereal- and potato-based snacks | 5 g/kg | Chewing gum | 2 g/kg |
| Paper and paperboard packaging component | Not limited | Emulsified liqueur | 8 g/l | Spirits <15% alcohol | 8 g/l | ||
| Cellophane | 0.5% weight of cellophane | ||||||
The largest application of CSL is in yeast leavened bakery products. Although CSL was introduced to the market first, most applications use SSL. The main reason for the preference of SSL over CSL is that CSL has less crumb softening effects than SSL. However, CSL is still preferred in some applications, such as lean hearth bread-type formulations. In these applications, CSL is preferred because CSL performs better than SSL as a dough strengthener, while the finished product does not require a soft crumb or a perfectly symmetrical loaf shape.[14]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.