Fladrafinil
Wakefulness-promoting drug From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
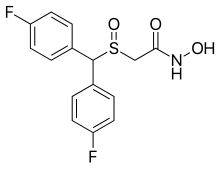
Fladrafinil (developmental code name CRL-40,941), also known as fluorafinil or as bisfluoroadrafinil, is a wakefulness-promoting agent related to modafinil that was never marketed.[1][2][3] It is sold online and used non-medically as a nootropic (cognitive enhancer).[1][2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | CRL-40,941; Fluorafinil; Bisfluoroadrafinil |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H13F2NO3S |
| Molar mass | 325.33 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Modafinil and its analogues are known to act as dopamine reuptake inhibitors and this is thought to be involved in their wakefulness-promoting effects.[1] Chemically, fladrafinil is a derivative of adrafinil (N-hydroxymodafinil) and is also known as bisfluoroadrafinil (it is the bis(4-fluoro) phenyl ring-substituted derivative of adrafinil).[1] It is closely related to flmodafinil (CRL-40,940; bisfluoromodafinil).[1][2][3]
Pharmacology
Fladrafinil has been found to produce antiaggressive effects in animals, which adrafinil does not produce.[4][failed verification] Fladrafinil is purportedly 3 to 4 times more potent than adrafinil in this action.[4]
Chemistry
Analogues of fladrafinil include modafinil, armodafinil ((R)-modafinil), esmodafinil ((S)-modafinil), adrafinil (CRL-40,028; N-hydroxymodafinil), flmodafinil (CRL-40,940; bisfluoromodafinil), and CE-123, among others.[2]
History
Fladrafinil appears to have first been patented in the 1980s.[5]
Research
The pharmacokinetics of fladrafinil are being studied.[6]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
