Loading AI tools
Collection of compromised internet-connected devices controlled by a third party From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A botnet is a group of Internet-connected devices, each of which runs one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, steal data,[1] send spam, and allow the attacker to access the device and its connection. The owner can control the botnet using command and control (C&C) software.[2] The word "botnet" is a portmanteau of the words "robot" and "network". The term is usually used with a negative or malicious connotation.
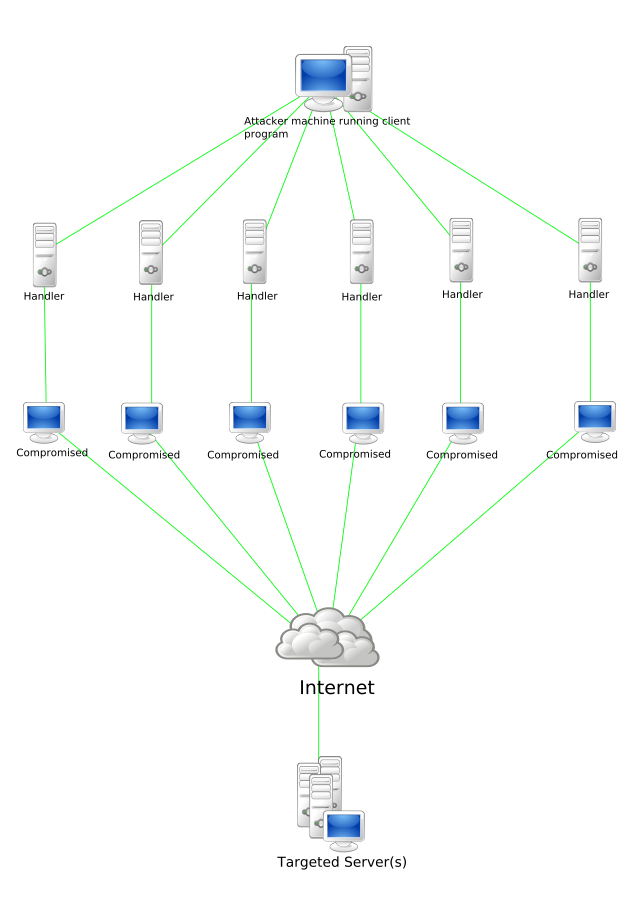
A botnet is a logical collection of Internet-connected devices, such as computers, smartphones or Internet of things (IoT) devices whose security have been breached and control ceded to a third party. Each compromised device, known as a "bot," is created when a device is penetrated by software from a malware (malicious software) distribution. The controller of a botnet is able to direct the activities of these compromised computers through communication channels formed by standards-based network protocols, such as IRC and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).[3][4]
Botnets are increasingly rented out by cyber criminals as commodities for a variety of purposes,[5] including as booter/stresser services.
Botnet architecture has evolved over time in an effort to evade detection and disruption. Traditionally, bot programs are constructed as clients which communicate via existing servers. This allows the bot herder (the controller of the botnet) to perform all control from a remote location, which obfuscates the traffic.[6] Many recent botnets now rely on existing peer-to-peer networks to communicate. These P2P bot programs perform the same actions as the client–server model, but they do not require a central server to communicate.

The first botnets on the Internet used a client–server model to accomplish their tasks.[7] Typically, these botnets operate through Internet Relay Chat networks, domains, or websites. Infected clients access a predetermined location and await incoming commands from the server. The bot herder sends commands to the server, which relays them to the clients. Clients execute the commands and report their results back to the bot herder.
In the case of IRC botnets, infected clients connect to an infected IRC server and join a channel pre-designated for C&C by the bot herder. The bot herder sends commands to the channel via the IRC server. Each client retrieves the commands and executes them. Clients send messages back to the IRC channel with the results of their actions.[6]

In response to efforts to detect and decapitate IRC botnets, bot herders have begun deploying malware on peer-to-peer networks. These bots may use digital signatures so that only someone with access to the private key can control the botnet,[8] such as in Gameover ZeuS and the ZeroAccess botnet.
Newer botnets fully operate over P2P networks. Rather than communicate with a centralized server, P2P bots perform as both a command distribution server and a client which receives commands.[9] This avoids having any single point of failure, which is an issue for centralized botnets.
In order to find other infected machines, P2P bots discreetly probe random IP addresses until they identify another infected machine. The contacted bot replies with information such as its software version and list of known bots. If one of the bots' version is lower than the other, they will initiate a file transfer to update.[8] This way, each bot grows its list of infected machines and updates itself by periodically communicating to all known bots.
A botnet's originator (known as a "bot herder" or "bot master") controls the botnet remotely. This is known as the command-and-control (C&C). The program for the operation must communicate via a covert channel to the client on the victim's machine (zombie computer).
IRC is a historically favored means of C&C because of its communication protocol. A bot herder creates an IRC channel for infected clients to join. Messages sent to the channel are broadcast to all channel members. The bot herder may set the channel's topic to command the botnet. For example, the message :herder!herder@example.com TOPIC #channel DDoS www.victim.com from the bot herder alerts all infected clients belonging to #channel to begin a DDoS attack on the website www.victim.com. An example response :bot1!bot1@compromised.net PRIVMSG #channel I am DDoSing www.victim.com by a bot client alerts the bot herder that it has begun the attack.[8]
Some botnets implement custom versions of well-known protocols. The implementation differences can be used for detection of botnets. For example, Mega-D features a slightly modified Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) implementation for testing spam capability. Bringing down the Mega-D's SMTP server disables the entire pool of bots that rely upon the same SMTP server.[10]
In computer science, a zombie computer is a computer connected to the Internet that has been compromised by a hacker, computer virus or trojan horse and can be used to perform malicious tasks under remote direction. Botnets of zombie computers are often used to spread e-mail spam and launch denial-of-service attacks (DDoS). Most owners of zombie computers are unaware that their system is being used in this way. Because the owner tends to be unaware, these computers are metaphorically compared to zombies. A coordinated DDoS attack by multiple botnet machines also resembles a zombie horde attack.[11]
The process of stealing computing resources as a result of a system being joined to a "botnet" is sometimes referred to as "scrumping".[12]
Global law enforcement agencies, with the DOJ and FBI, dismantled the 911 S5 botnet, responsible for $5.9 billion in theft and various cybercrimes. Chinese national YunHe Wang, charged with operating the botnet, faces up to 65 years in prison. Authorities seized $60 million in assets, including luxury items and properties.[13]
Botnet command and control (C&C) protocols have been implemented in a number of ways, from traditional IRC approaches to more sophisticated versions.
Telnet botnets use a simple C&C botnet protocol in which bots connect to the main command server to host the botnet. Bots are added to the botnet by using a scanning script, which runs on an external server and scans IP ranges for telnet and SSH server default logins. Once a login is found, the scanning server can infect it through SSH with malware, which pings the control server.
IRC networks use simple, low bandwidth communication methods, making them widely used to host botnets. They tend to be relatively simple in construction and have been used with moderate success for coordinating DDoS attacks and spam campaigns while being able to continually switch channels to avoid being taken down. However, in some cases, merely blocking of certain keywords has proven effective in stopping IRC-based botnets. The RFC 1459 (IRC) standard is popular with botnets. The first known popular botnet controller script, "MaXiTE Bot" was using IRC XDCC protocol for private control commands.
One problem with using IRC is that each bot client must know the IRC server, port, and channel to be of any use to the botnet. Anti-malware organizations can detect and shut down these servers and channels, effectively halting the botnet attack. If this happens, clients are still infected, but they typically lie dormant since they have no way of receiving instructions.[8] To mitigate this problem, a botnet can consist of several servers or channels. If one of the servers or channels becomes disabled, the botnet simply switches to another. It is still possible to detect and disrupt additional botnet servers or channels by sniffing IRC traffic. A botnet adversary can even potentially gain knowledge of the control scheme and imitate the bot herder by issuing commands correctly.[14]
Since most botnets using IRC networks and domains can be taken down with time, hackers have moved to P2P botnets with C&C to make the botnet more resilient and resistant to termination.
Some have also used encryption as a way to secure or lock down the botnet from others, most of the time when they use encryption it is public-key cryptography and has presented challenges in both implementing it and breaking it.
Many large botnets tend to use domains rather than IRC in their construction (see Rustock botnet and Srizbi botnet). They are usually hosted with bulletproof hosting services. This is one of the earliest types of C&C. A zombie computer accesses a specially-designed webpage or domain(s) which serves the list of controlling commands. The advantages of using web pages or domains as C&C is that a large botnet can be effectively controlled and maintained with very simple code that can be readily updated.
Disadvantages of using this method are that it uses a considerable amount of bandwidth at large scale, and domains can be quickly seized by government agencies with little effort. If the domains controlling the botnets are not seized, they are also easy targets to compromise with denial-of-service attacks.
Fast-flux DNS can be used to make it difficult to track down the control servers, which may change from day to day. Control servers may also hop from DNS domain to DNS domain, with domain generation algorithms being used to create new DNS names for controller servers.
Some botnets use free DNS hosting services such as DynDns.org, No-IP.com, and Afraid.org to point a subdomain towards an IRC server that harbors the bots. While these free DNS services do not themselves host attacks, they provide reference points (often hard-coded into the botnet executable). Removing such services can cripple an entire botnet.
Calling back to popular sites[15] such as GitHub,[16] Twitter,[17][18] Reddit,[19] Instagram,[20] the XMPP open source instant message protocol[21] and Tor hidden services[22] are popular ways of avoiding egress filtering to communicate with a C&C server.[23]
This example illustrates how a botnet is created and used for malicious gain.
Newer bots can automatically scan their environment and propagate themselves using vulnerabilities and weak passwords. Generally, the more vulnerabilities a bot can scan and propagate through, the more valuable it becomes to a botnet controller community.[24]
Computers can be co-opted into a botnet when they execute malicious software. This can be accomplished by luring users into making a drive-by download, exploiting web browser vulnerabilities, or by tricking the user into running a Trojan horse program, which may come from an email attachment. This malware will typically install modules that allow the computer to be commanded and controlled by the botnet's operator. After the software is downloaded, it will call home (send a reconnection packet) to the host computer. When the re-connection is made, depending on how it is written, a Trojan may then delete itself or may remain present to update and maintain the modules.
In some cases, a botnet may be temporarily created by volunteer hacktivists, such as with implementations of the Low Orbit Ion Cannon as used by 4chan members during Project Chanology in 2010.[25]
China's Great Cannon of China allows the modification of legitimate web browsing traffic at internet backbones into China to create a large ephemeral botnet to attack large targets such as GitHub in 2015.[26]
The botnet controller community constantly competes over who has the most bots, the highest overall bandwidth, and the most "high-quality" infected machines, like university, corporate, and even government machines.[34]
While botnets are often named after the malware that created them, multiple botnets typically use the same malware but are operated by different entities.[35]
Botnets can be used for many electronic scams. These botnets can be used to distribute malware such as viruses to take control of a regular users computer/software[36] By taking control of someone's personal computer they have unlimited access to their personal information, including passwords and login information to accounts. This is called phishing. Phishing is the acquiring of login information to the "victim's" accounts with a link the "victim" clicks on that is sent through an email or text.[37] A survey by Verizon found that around two-thirds of electronic "espionage" cases come from phishing.[38]
The geographic dispersal of botnets means that each recruit must be individually identified/corralled/repaired and limits the benefits of filtering.
Computer security experts have succeeded in destroying or subverting malware command and control networks, by, among other means, seizing servers or getting them cut off from the Internet, denying access to domains that were due to be used by malware to contact its C&C infrastructure, and, in some cases, breaking into the C&C network itself.[39][40][41] In response to this, C&C operators have resorted to using techniques such as overlaying their C&C networks on other existing benign infrastructure such as IRC or Tor, using peer-to-peer networking systems that are not dependent on any fixed servers, and using public key encryption to defeat attempts to break into or spoof the network.[42]
Norton AntiBot was aimed at consumers, but most target enterprises and/or ISPs. Host-based techniques use heuristics to identify bot behavior that has bypassed conventional anti-virus software. Network-based approaches tend to use the techniques described above; shutting down C&C servers, null-routing DNS entries, or completely shutting down IRC servers. BotHunter is software, developed with support from the U.S. Army Research Office, that detects botnet activity within a network by analyzing network traffic and comparing it to patterns characteristic of malicious processes.
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories are analyzing botnets' behavior by simultaneously running one million Linux kernels—a similar scale to a botnet—as virtual machines on a 4,480-node high-performance computer cluster to emulate a very large network, allowing them to watch how botnets work and experiment with ways to stop them.[43]
Detecting automated bot attacks is becoming more difficult each day as newer and more sophisticated generations of bots are getting launched by attackers. For example, an automated attack can deploy a large bot army and apply brute-force methods with highly accurate username and password lists to hack into accounts. The idea is to overwhelm sites with tens of thousands of requests from different IPs all over the world, but with each bot only submitting a single request every 10 minutes or so, which can result in more than 5 million attempts per day.[44] In these cases, many tools try to leverage volumetric detection, but automated bot attacks now have ways of circumventing triggers of volumetric detection.
One of the techniques for detecting these bot attacks is what's known as "signature-based systems" in which the software will attempt to detect patterns in the request packet. However, attacks are constantly evolving, so this may not be a viable option when patterns cannot be discerned from thousands of requests. There is also the behavioral approach to thwarting bots, which ultimately tries to distinguish bots from humans. By identifying non-human behavior and recognizing known bot behavior, this process can be applied at the user, browser, and network levels.
The most capable method of using software to combat against a virus has been to utilize honeypot software in order to convince the malware that a system is vulnerable. The malicious files are then analyzed using forensic software.
On 15 July 2014, the Subcommittee on Crime and Terrorism of the Committee[45] on the Judiciary, United States Senate, held a hearing on the threats posed by botnets and the public and private efforts to disrupt and dismantle them.[46]
The rise in vulnerable IoT devices has led to an increase in IoT-based botnet attacks. To address this, a novel network-based anomaly detection method for IoT called N-BaIoT was introduced. It captures network behavior snapshots and employs deep autoencoders to identify abnormal traffic from compromised IoT devices. The method was tested by infecting nine IoT devices with Mirai and BASHLITE botnets, showing its ability to accurately and promptly detect attacks originating from compromised IoT devices within a botnet.[47]
Additionally, comparing different ways of detecting botnets is really useful for researchers. It helps them see how well each method works compared to others. This kind of comparison is good because it lets researchers evaluate the methods fairly and find ways to make them better.[48]
The first botnet was first acknowledged and exposed by EarthLink during a lawsuit with notorious spammer Khan C. Smith[49] in 2001. The botnet was constructed for the purpose of bulk spam, and accounted for nearly 25% of all spam at the time.[50]
Around 2006, to thwart detection, some botnets were scaling back in size.[51]
| Date created | Date dismantled | Name | Estimated no. of bots | Spam capacity (bn/day) | Aliases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | MaXiTE | 500-1000 servers | 0 | MaXiTE XDCC Bot, MaXiTE IRC TCL Script, MaxServ | |
| 2004 (Early) | Bagle | 230,000[52] | 5.7 | Beagle, Mitglieder, Lodeight | |
| Marina Botnet | 6,215,000[52] | 92 | Damon Briant, BOB.dc, Cotmonger, Hacktool.Spammer, Kraken | ||
| Torpig | 180,000[53] | Sinowal, Anserin | |||
| Storm | 160,000[54] | 3 | Nuwar, Peacomm, Zhelatin | ||
| 2006 (around) | 2011 (March) | Rustock | 150,000[55] | 30 | RKRustok, Costrat |
| Donbot | 125,000[56] | 0.8 | Buzus, Bachsoy | ||
| 2007 (around) | Cutwail | 1,500,000[57] | 74 | Pandex, Mutant (related to: Wigon, Pushdo) | |
| 2007 | Akbot | 1,300,000[58] | |||
| 2007 (March) | 2008 (November) | Srizbi | 450,000[59] | 60 | Cbeplay, Exchanger |
| Lethic | 260,000[52] | 2 | none | ||
| Xarvester | 10,000[52] | 0.15 | Rlsloup, Pixoliz | ||
| 2008 (around) | Sality | 1,000,000[60] | Sector, Kuku | ||
| 2008 (around) | 2009-Dec | Mariposa | 12,000,000[61] | ||
| 2008 (around) | Kraken | 495,000[62] | 9 | Kracken | |
| 2008 (November) | Conficker | 10,500,000+[63] | 10 | DownUp, DownAndUp, DownAdUp, Kido | |
| 2008 (November) | 2010 (March) | Waledac | 80,000[64] | 1.5 | Waled, Waledpak |
| Maazben | 50,000[52] | 0.5 | None | ||
| Onewordsub | 40,000[65] | 1.8 | |||
| Gheg | 30,000[52] | 0.24 | Tofsee, Mondera | ||
| Nucrypt | 20,000[65] | 5 | Loosky, Locksky | ||
| Wopla | 20,000[65] | 0.6 | Pokier, Slogger, Cryptic | ||
| 2008 (around) | Asprox | 15,000[66] | Danmec, Hydraflux | ||
| Spamthru | 12,000[65] | 0.35 | Spam-DComServ, Covesmer, Xmiler | ||
| 2008 (around) | Gumblar | ||||
| 2009 (May) | November 2010 (not complete) | BredoLab | 30,000,000[67] | 3.6 | Oficla |
| 2009 (Around) | 2012-07-19 | Grum | 560,000[68] | 39.9 | Tedroo |
| Mega-D | 509,000[69] | 10 | Ozdok | ||
| 2009 (August) | Festi | 250,000[70] | 2.25 | Spamnost | |
| 2010 (March) | Vulcanbot | ||||
| 2010 (January) | LowSec | 11,000+[52] | 0.5 | LowSecurity, FreeMoney, Ring0.Tools | |
| 2010 (around) | TDL4 | 4,500,000[71] | TDSS, Alureon | ||
| Zeus | 3,600,000 (US only)[72] | Zbot, PRG, Wsnpoem, Gorhax, Kneber | |||
| 2010 | (Several: 2011, 2012) | Kelihos | 300,000+ | 4 | Hlux |
| 2011 or earlier | 2015-02 | Ramnit | 3,000,000[73] | ||
| 2012 (Around) | Chameleon | 120,000[74] | None | ||
| 2014 | Necurs | 6,000,000 | |||
| 2016 (August) | Mirai | 380,000 | None | ||
| 2022 | Mantis[75] | 5000 |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.