Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Borås
City in Västergötland, Sweden From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
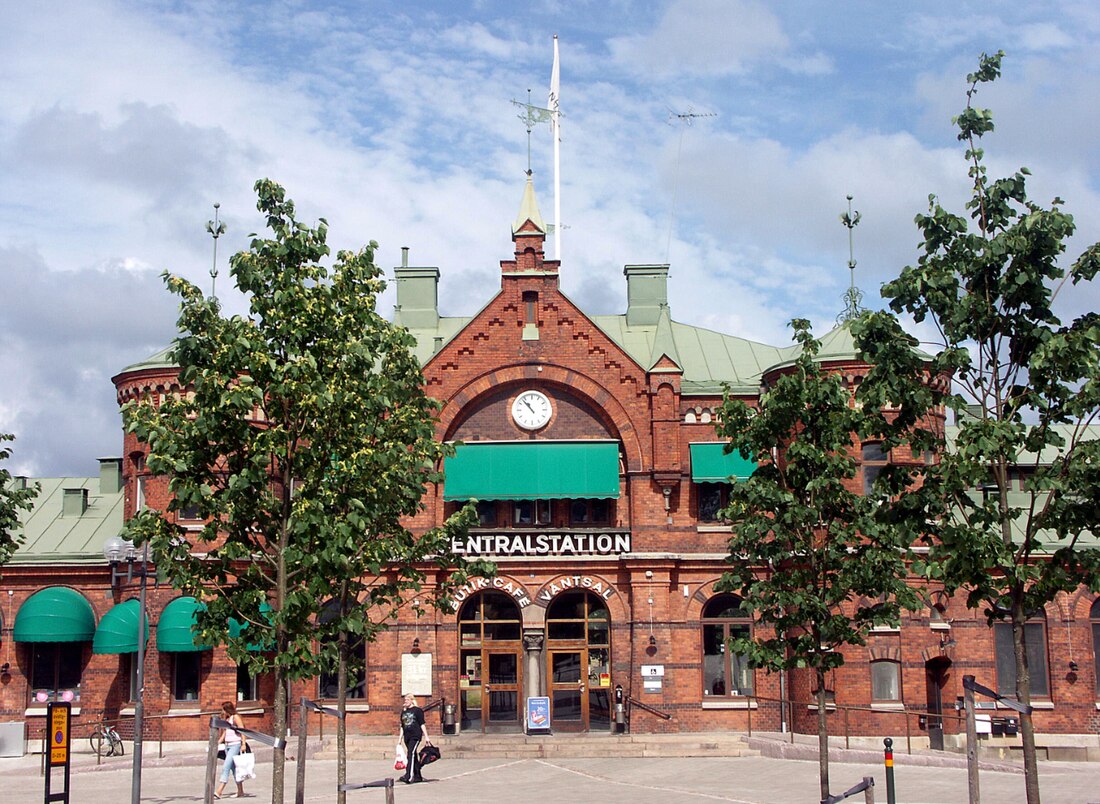
Borås (UK: /bʊˈrɔːs/ buu-RAWSS, US: /buːˈrɔːs, buːˈroʊs/ boo-RAWSS, boo-ROHSS,[3][4] Swedish: [bʊˈroːs] ⓘ) is a city (officially, a locality) and the seat of Borås Municipality, Västra Götaland County, Sweden. It had 114,556 inhabitants in 2024.[5] It is widely known for being a textile city, home to worldwide brands and companies as well as the prestigious Swedish School of Textiles, which is part of the University of Borås.
Remove ads



Remove ads
Geography
Borås is located at the point of two crossing railways, among them the railway between Gothenburg and Kalmar, and is often considered[citation needed] the Swedish city gaining the most from the nationwide railway system laid between 1870 and 1910.
History
The city of Borås received its privileges in 1621 by King Gustav II Adolf. The reason was to give local pedlars a legal place for vending their merchandise (and for the government the ability to collect taxes on this trade). The city developed soon after it was founded. After a century it had increased to over 2,000 inhabitants. Borås has been ravaged by fires four times: in 1681, 1727, 1822 and 1827. The Caroli church is the oldest of Borås's buildings, and has withstood all fires.
In its 2017 report, Police in Sweden placed the Norrby, Hässleholmen and Hulta districts in the most severe category of urban areas with high crime rates.[6]
In 2021, Borås marked its 400th anniversary.[7]
Remove ads
Industry
The city arms depicts two pairs of sheep shears, a tribute to the vast number of smiths in the town in early history. It currently holds the Swedish record in the number of established mail-order firms.
The company Swedac is based in the city, as well as Ericsson, which has a large manufacturing plant where Mini-Link microwave radios are manufactured. Worldwide clothing retailer H&M have their worldwide Online office based in the city as well.
Outside the city in the industrial park of Viared, there are many companies specializing in logistics. Industries in Borås have close collaboration with the University College of Borås as well as the SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden, the largest technical research institute of Sweden, both located in Borås. Besides being the home of the official Swedish Kilogram-weight and the atomic clock that sets the national time, SP conducts various testing and research to promote consumer safety.
Transport
Railway
Borås is a railway junction. The Coast-to-Coast Line from Gothenburg to Kalmar runs through the city centre. At the Borås Railway Station it meets the Älvsborg Line (heading north to Herrljunga and Uddevalla) and the Viskadal Line (going south to Varberg). Continuous passenger trains often run through the city along the two latter lines.
As of 2019 SJ runs 3–4 daily trains in each direction between Gothenburg and Kalmar. The regional traffic agency Västtrafik runs frequent trains between Borås and Gothenburg, Herrljunga, and Varberg. All passenger trains stop at Borås railway station. Trains on the northern line to and from Herrljunga also stop at Knalleland halt within the city.
Bus
There are several commuter buses going to both Jönköping and Gothenburg. Approximately 100.000 people commute between Borås and Gothenburg every month.[8]
Remove ads
Sports
Summarize
Perspective
The most successful sports team is the football team IF Elfsborg, six times Swedish champions (1936, 1939, 1940,1961, 2006 and 2012) and three times winner of the Swedish Cup (2001, 2003 and 2014). Elfsborg was founded in 1904, but received its current name in 1906. The team's home arena, since 2005, is Borås Arena (formerly Ryavallen Stadium) in Borås, with a capacity of 16000. Elfsborg play in yellow and black.
Other teams are Borås Hockey Club, M7 (a basketball team that worked with Magic Johnson for a short while) and Borås Rhinos which is an American football team.
The table tennis club, Mariedals IK, had three players in the Swedish youth team: Hampus Söderlund, Mattias Översjö and Jimmy Ojakangas.
Other sports that can be practiced in Borås are: archery, track and field, rowing, handball, table tennis, tennis, skiing, orienteering, sport shooting, swimming, golf, equestrian, bowling, cheerleading, floorball and various martial arts. Borås Judoclub has tried to create a national center for judo. Members from the club that have participated in the olympics include Per Kjellin and Lars Adolfsson (who competed twice).
Boråshallen is the largest indoor sports hall in Borås, where the Mariedal cup, an indoor football competition, is held annually in October or November. The competition started in 1978 in its current form.
Borås hosted the water polo events of the XIII FINA World Masters Championships 2010, from 28 July to 6 August.[9]
The city also hosted the 2019 European Athletics U20 Championships.
Other sports clubs located in Borås include:
The Rydafältet hosted the motorcycle speedway teams Saxarna in 1951 and Knallarna in 1952. The Ryavallen was the venue for the 1972 and 1973 Speedway World Pairs Championship finals.[10]
Remove ads
Culture
- Hemvärnets Musikkår Borås – a marching and sitting orchestra
- Borås kulturskola – School of the Arts (for young people).
- Borås kulturhus – theater, library, museum of art
- Borås Tidning – the local newspaper.
- Textilmuseet – a museum about textile manufacturing and clothes.
- Borås djurpark – The local zoo. They have successfully raised a number of different animals and even exported lions to other zoos.
- Åhaga – A renovated building previously used to maintain and repair locomotives. Now used for conferences and concerts.
Every summer, a number of free outdoor concerts are held on the town square on Thursday evenings.
The city has lately been recognized as a city of outdoor sculptures, such as Catafalque by Sean Henry, Carl Fredrik Reuterswärd's knotted non-violence pistol and a huge bronze version of Pinocchio called Walking to Borås by the American pop artist Jim Dine.
During the holiday All Saints' Day, there is an annual gaming convention called Borås Spelkonvent, where people, mostly youths, meet to play various board games, Warhammer 40k and Magic: The Gathering among other games.
Remove ads
Climate
Summarize
Perspective
Borås has a humid continental climate, or cold oceanic climate using the −3 °C isotherm, influenced by Atlantic trade winds travelling without major obstacles over the land, with low mean temperatures, compared to coastal areas and the more urban metropolis, Gothenburg, near to the west. Considering it being inland and quite far south, summer temperatures are rather subdued by Swedish standards, whilst winter average highs hover just above freezing. Being inland still enables severe extremes to sometimes occur, such as a 36 °C (97 °F) reading from July 1901, the warmest July temperature on record in Götaland until 2022, although not a national record (38 °C (100 °F) set on two different June dates and years on other stations). The coldest extreme was set in February 1966 with −34.1 °C (−29.4 °F), a severely cold temperature for southern Sweden.
By Swedish standards, the climate of Borås is very wet, with a precipitation average of above 1,100 millimetres (43 in). This is also due to maritime airflows coming from the Atlantic and easily being transported over lowland areas, where the precipitation eventually falls with a slight orographic lift. This renders heavy solid or wet snowfall in winter and the freeze-thaw cycle is normally dominant, with irregular snow cover.
Remove ads
Districts
Municipal subdistrict Göta
|
Municipal subdistrict Sjöbo
|
| Municipal subdistrict Brämhult |
Municipal subdistrict Norrby
|
Municipal subdistrict Centrum (city)
|
| Municipal subdistrict Sandhult |
Remove ads
Gallery
- Ramnaparken lake in winter
- City park
- Municipal court
- Winter panorama
- Water tower
- The old Pensionat Lyckebo
- Catafalque by Sean Henry in Winter.
Notable people
- Johanna Almgren, Swedish footballer [13]
- Hans Alsér, a world champion of table tennis
- Christer Björkman, singer and supervisor of Melodifestivalen
- Camilla Brodin, member of parliament
- Ingvar Carlsson, former prime minister
- Magnus Carlsson, pop singer
- Shirley Clamp, singer
- AronChupa, singer and DJ
- Evocation, Swedish Melodic Death Metal band [14]
- Peter Adolf Hall, painter
- Birger Martin Hall, Linnaean disciple, botanist and doctor
- Johan Hallgren, rower [15]
- Marcus Hansson, 1994 motocross world champion [16]
- Nils Horner, journalist
- Ingrid Janbell, actress, director and lecturer
- Jonas Jerebko, first ever Swedish NBA player [17]
- Wiktoria Johansson, pop singer
- Patrik Järbyn, former alpine ski racer
- Carolina Klüft, heptathlete
- Ivan Lapanje, professional FIFA player, better known as BorasLegend
- Martin Lorentzon, founder of Tradedoubler and Spotify.
- Daniel Norgren, singer-songwriter
- Tomas Olsson, ski mountaineer
- Helena Paparizou, Greek-Swedish singer, winner of the 2005 Eurovision Song Contest.
- Apollo Papathanasio, heavy metal vocalist of Greek descent
- Kurt Pettersén, an Olympic champion wrestler
- Hans Rosenfeldt, writer, creator of The Bridge[18]
- Christoffer Schander, biologist and active science fiction fan
- Helge Skoog, actor
- Johan Wiland, Swedish footballer
- Ola Wong, author, journalist and sinologist
- Raaban, DJ and music producer
Remove ads
Schools
High schools
- Almåsgymnasiet
- Bäckängsgymnasiet
- Sven Eriksonsgymnasiet
- Viskastrandsgymnasiet
- Tullengymnasiet
- Borås Praktiska Gymnasium
- LBS: High School of Creativity
In popular culture
- "Borås, Borås" is a song recorded by Knut Agnred. The song is a parody of Theme from New York, New York.
- "The furies from Borås" is a novel by Swedish horror author Anders Fager. It deals with a group of teenage girls who are members of a cult worshipping a Lovecraftian monstrosity.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads