Outlaw motorcycle club
Motorcycle subculture From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
An outlaw motorcycle club, known colloquially as a biker club or bikie club (in Australia), is a motorcycle subculture generally centered on the use of cruiser motorcycles, particularly Harley-Davidsons and choppers, and a set of ideals that purport to celebrate freedom, nonconformity to mainstream culture, and loyalty to the biker group. The subculture emerged in the United States in the late 1940s and has since spread globally.

In the United States, such motorcycle clubs (MCs) are considered "outlaw" not necessarily because they engage in criminal activity but because they are not sanctioned by the American Motorcyclist Association (AMA) and do not adhere to the AMA's rules. Instead, the clubs have bylaws reflecting the outlaw biker culture.[1][2][3][4][5]
The U.S. Department of Justice defines "outlaw motorcycle gangs" (OMG) as "organizations whose members use their motorcycle clubs as conduits for criminal enterprises".[6]
Organization and leadership
Summarize
Perspective

While organizations may vary, the typical internal organization of a motorcycle club consists of a president, vice president, treasurer, secretary, road captain, and sergeant-at-arms (sometimes known as enforcer).[7] In some clubs, localized groups of a single, prominent MC are called charters or chapters, and the first chapter established for an MC is referred to as the mother chapter. The mother chapter serves as the ruling body of the club.[8] Sometimes, the president of the mother chapter serves as the president of the entire MC, and sets club policy on a variety of issues, whereas other clubs either elect or appoint a National President for this role.
Larger motorcycle clubs often acquire real estate for use as a clubhouse or private compound. Clubhouses, which are frequently fortified and equipped with a sophisticated security system, serve as a meeting place for a club or chapter.[9] To meet the expenditures of running an outlaw motorcycle club, namely the renting, purchase or furnishing of a clubhouse, groups raise funds primarily through membership dues and club fines, the sale of various items to members, the brokerage of club shares, sponsoring parties and organizing motorcycle trips. Some clubs also maintain a fund for the legal defense of its members.[10]
Membership
Summarize
Perspective
Some "biker" clubs employ a process whereby members must pass several stages, such as "friend of the club", "hang-around", and "prospect", on their way to becoming full-patch (see the explanation of 'patching' below) members.[11] The actual stages and membership process can and often do vary widely from club to club. Usually, an individual must pass a membership vote and swear some level of allegiance to the club.[11] Some clubs have a unique club patch (cut or top rocker)[12] adorned with the term MC that are worn on the rider's vest, known as a kutte.
In these clubs, some amount of hazing may occur during the early stages (i.e., hang-around, prospecting) ranging from the mandatory performance of menial labor tasks for full patch members to sophomoric pranks and, in rare cases with some outlaw motorcycle clubs, acts of violence.[13] During this time, the prospect may wear the club name on the back of their vest but not the entire logo, though this practice may vary from club to club. To become a full member, the prospect or probate must be voted on by the rest of the full club members. Successful admission usually requires more than a simple majority, and some clubs may reject a prospect or a probate for a single dissenting vote. A formal induction follows, in which the new member affirms his loyalty to the club and its members. The final logo patch is then awarded. Full members are often referred to as "full patch members" or "patchholders" and the step of attaining full membership can be referred to as "being patched".[14]
Outlaw biker culture
Summarize
Perspective
The majority of members of outlaw motorcycle clubs have no serious criminal record and express their outlaw status on a social level, equating the word "outlaw" with disregard for the law of groups like the American Motorcyclist Association, not the laws of government.[1][2][3][4][5] Outlaw bikers view themselves as a fraternity of men who reject societal norms, and their sense of brotherhood is reflected in tattoos, the wearing of the club "colors", and earning ranks and titles within a club or chapter.[15] However, there is also a subculture of outlaw biker activity which revolves around performing outrageous acts, the denigration of women, maintaining a macho image, and the heavy use of drugs and alcohol.[8]
Many non-outlaw motorcycle clubs adopt similar insignia, colors, organizational structures, and trappings to outlaw clubs, making it difficult for outsiders (including police) to tell the groups apart.[16] Much of the mystique and many of the unwritten rules, values, and ideals of non-outlaw clubs are believed to come from outlaw clubs.[17]
Charity events
Outlaw clubs are often prominent at charity events, such as toy runs. Charitable giving is frequently cited as evidence that these clubs do not deserve their negative media image. Outlaw clubs have been accused of using charity rides to mask their criminal nature.[18][19][20] The American Motorcyclist Association has frequently complained of the bad publicity for motorcycling in general caused by outlaw clubs, and they have said that the presence of outlaw clubs at charity events has harmed people in need by driving down public participation and reducing donations.[21] Events such as a 2005 shootout between rival outlaw clubs amid a charity toy drive in California have raised fears about the participation of outlaw biker clubs in charity events.[22][23] Authorities have attempted to ban outlaw clubs from charity events or to restrict the wearing of colors at events to avert the sort of inter-club violence that has happened at previous charity runs.[24][25] In 2002, the Warlocks MC of Pennsylvania sued over their exclusion from a charity event.[26]
Identification
Summarize
Perspective

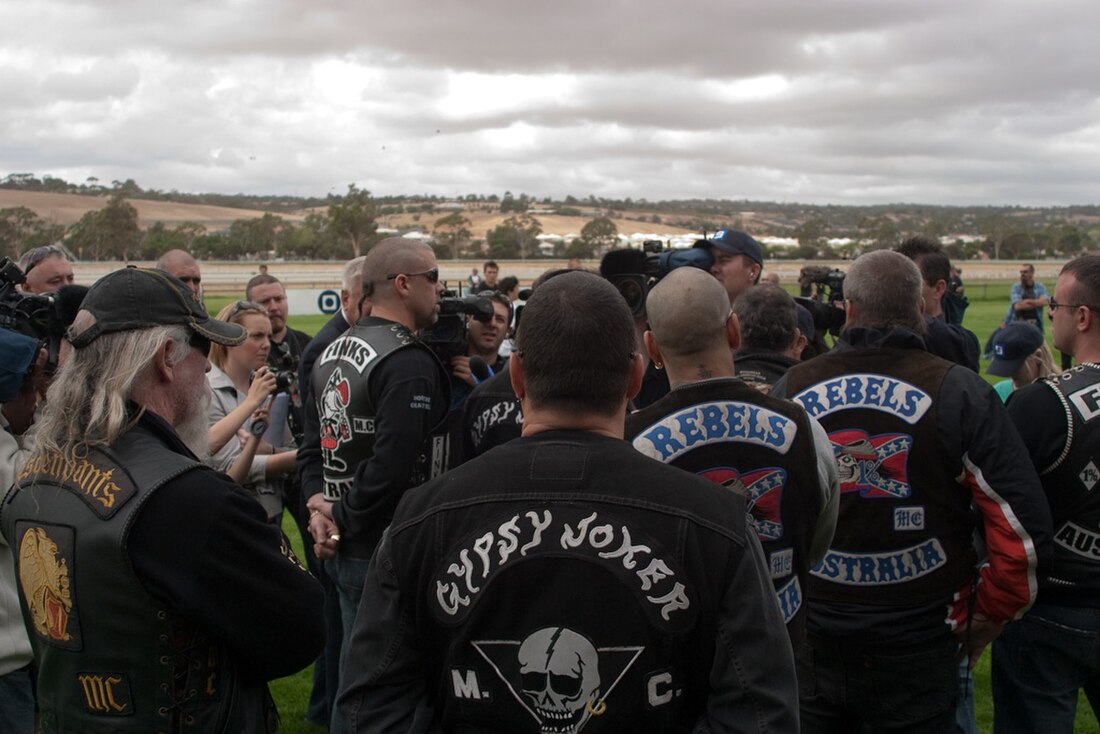
The primary visual identification of an outlaw motorcycle club member is the vest adorned with a large club-specific patch or patches predominantly located in the middle of the back. The patches will contain a club logo, the club's name, the letters MC, and a possible state, province, or other chapter identification. This garment and the patches themselves are referred to as the colors or cut (a term taken from the early practice of cutting the collars or sleeves from a denim or leather jacket). Many non-outlaw motorcycle riding clubs such as the Harley Owners Group also wear patches on the back of their vests, without including the letters MC.
The club patches always remain the property of the club itself, not the members, and only members are allowed to wear the club's patches. Hang-arounds or support club members wear support patches with the club's colors. A member must closely guard their colors, for allowing one's colors to fall into the hands of an outsider is an act of disgrace and may result in loss of membership in a club or some other punishment.[citation needed]
One-, two-, and three-piece patches
The colors worn by members of some motorcycle clubs will sometimes follow a convention of using either a one-piece patch for nonconformist[further explanation needed] social clubs, a two-piece patch for clubs paying dues[further explanation needed], a three-piece patch for outlaw clubs or side patches. The three-piece patch consists of the club logo and the top and bottom patches, usually crescent-shaped, which are referred to as rockers. The number and arrangement of patches somewhat indicate the club's nature. Since many motorcycle clubs wear the three-piece patch arrangement, this does not necessarily suggest that a club is an outlaw motorcycle club.
Law enforcement agencies have confiscated colors and other club paraphernalia of these clubs when they raid a clubhouse or the home of a MC member, and they often display these items at press conferences.[27] These items are then used at trial to support prosecution assertions that MC members perform criminal acts on behalf of their club. Courts have found that the probative value of such items is far outweighed by their unfairly prejudicial effects on the defense.[28]
One percenter
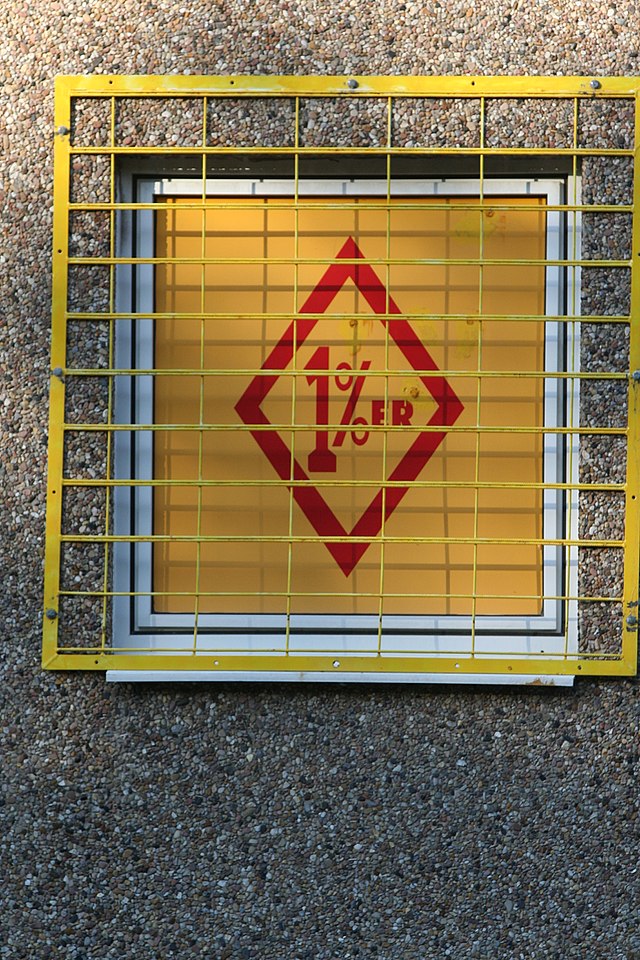
Some outlaw motorcycle clubs can be distinguished by a "1%" or "Diamond" shape patch worn on the colors. This is said to refer to a comment made in 1960 by William Berry, a former president of the American Motorcyclist Association (AMA), that 99% of motorcyclists were law-abiding citizens, implying the last one percent were outlaws.[29][30]
The alleged AMA comment, supposedly about the Hollister riot of 1947,[31][32][30] is denied by the AMA, which claims to have no record of such a statement to the press and that the story is a misquote.[29][note 1] Whether the original quote is true or not, the "1%" patch is worn only by clubs characterized by criminality.[33][34][35][36]
Outlaw clubs began wearing the "1%" patch after Hells Angels president Sonny Barger convened a meeting of the leaders of various Hells Angels chapters and other California clubs in 1960 in which the multiple clubs parleyed over the mutual problem of police harassment. The clubs voted to ally under the patch.[37] In 1963, the Outlaws became the first club east of the Mississippi River to begin wearing the "1%" emblem.[38]
Other patches
Other patches may be worn by members, including phrases and symbols. The style or meaning of these other patches can vary between clubs. Some, such as a skull and crossbones patch, or the motto "Respect Few, Fear None", are worn in some clubs by members who commit murder or other acts of violence on behalf of the club.[39][40][41][42]
There are also wings or biker's wings, which are earned similarly to jump wings or pilot's wings, but with various color-coded meanings, e.g., in some clubs, it is said that a member who has had sex with a woman with venereal disease can wear green wings.[42][43][44] It has also been suggested that these definitions are a hoax, intended to make fools of those outside the outlaw biker world and also to serve the purpose of provoking outrage among the conservative public and authorities.[45]
Frequently, additional patches may involve symbols, such as the use of the Iron Cross, Nazi swastikas, the Sig Rune insignia of the Schutzstaffel or the Totenkopf. These may not indicate Nazi sympathies but serve to express the outlaw biker's total rejection of social constraints and desire for the shock value among those who fail to understand the biker way.[46][47]
Gender and race
Summarize
Perspective

Most outlaw motorcycle clubs do not allow women to become full-patch members.[48] Rather, in some 1%er clubs, women have in the past been portrayed as submissive or victims to the men,[49] treated as property, forced into prostitution or street-level drug trafficking, and often physically and sexually abused,[50] their roles as being those of obedient followers and their status as objects. These women are claimed to pass over any pay they receive to their partners or sometimes to the entire club.[51] This appears to make these groups extremely gender segregated.[52] This has not always been the case, as during the 1950s and 1960s, some Hells Angels chapters had female members.[53]
Academic research has criticized the methodology of such previous studies as being "vague and hazy" and lacking in participant demography.[54] Such reports may have made clear statements and authoritative analyses about the role of women associated with outlaw motorcycle clubs, but few state how they have come to such conclusions; one admitting that, "[his] interviews with biker women were limited lest [his] intentions were misinterpreted" by their male companions[55] and that such views of women are mythic and "sexist research" in itself, using deeply flawed methodologies and serve two highly political purposes of maintaining a dominance myth of women by men and amplifying the deviance of the male club members.[54]
These myths about the women are: that they are subservient working-class women, used as objects for club sexual rites[clarification needed]; are hard-bitten, unattractive, and politically conservative; and that they are 'money makers' for the biker men and clubs, i.e., prostitutes, topless barmaids or strippers who are forced to hand over their money to the club.[56] A 1990 paper noted the changing role of women within outlaw motorcycle clubs,[57] and a 2000 paper stated that they now have agency and political savvy, reframing the narratives of their lives. "We did it. We showed them we are real women dealing with real men. I'd much prefer to be living with an OMC member than some dork who is a pawn in the system", said one woman who felt she and her peers had "set the record straight".[58] One woman in 2001 described the previous work done by men about women in the outlaw motorcycle club world by saying "the men that wrote that must be meatheads".[54] They [women] are part of the scene because they want to be and enjoy it. These women have broken from society's stereotypically defined roles and found freedom in the biker world.[59]
High-profile outlaw bikers have historically been white, and their clubs are typically exclusively racially homogeneous.[60] Other sources state outright that "With few exceptions, blacks are excluded from membership or riding with one-percenter biker clubs."[61] The average age for a club studied was 34.[62]
There are black clubs, white clubs, and Mexican and other Spanish-speaking clubs. Bikers in American prisons, as prisoners generally do, band together along racial lines.[63][64][65] It is claimed that racial discrimination within clubs has led to creation of rival clubs in the past, such as the Mongols Motorcycle Club after members were rejected by the local Hells Angels chapter.[66] Some clubs or individual chapters are now multi-racial, but the number of "white supremacist biker clubs are growing nationwide", according to the ADL.[67][68]
Outlaw motorcycle clubs and crime
Summarize
Perspective
Many members of outlaw motorcycle clubs engage in criminal activities and organized crime and "pose a serious domestic threat".[69] Law enforcement agencies perceive such individuals and motorcycle clubs as being unique among criminal groups because they maintain websites and businesses, identify themselves through patches and tattoos, write and obey constitutions and bylaws, trademark their club names and logos, and even hold publicity campaigns aimed at improving their public image.[18][60] The term "outlaw motorcycle gang" was coined by the journalist Hunter S. Thompson in 1966 and was subsequently adopted by federal and local law enforcement agencies in the United States and elsewhere.[70]
Outlaw motorcycle clubs as criminal enterprises
The U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and Criminal Intelligence Service Canada have designated four MCs as "outlaw motorcycle gangs": the Hells Angels, the Pagans, the Outlaws, and the Bandidos,[71][72] known as the "Big Four".[73] These four have a large enough national impact to be prosecuted under the U.S. Federal Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) statute.[74] The California Attorney General also lists the Mongols and the Vagos as outlaw motorcycle gangs.[75][65]
The FBI asserts that outlaw motorcycle gangs (OMGs) support themselves primarily through drug dealing, trafficking in stolen goods, and extortion and that they fight over territory and the illegal drug trade[76] and collect $1 billion in illegal income annually.[77][78][79][80][81][37] Motorcycle gangs frequently begin mutually beneficial partnerships with independent criminals and maintain an extensive network of associates by doing so.[8][82] Crimes are typically carried out by associates rather than "full patch" members to protect the club from implication by law enforcement.[83] In 1985[37] a three-year, eleven-state FBI operation named Roughrider culminated in the largest OMG bust in history, with the confiscation of $2 million worth of illegal drugs, as well as an illegal arsenal of weapons, ranging from Uzi submachine guns to antitank weapons.[84] In October 2008, the FBI announced the end of a six-month undercover operation by agents into the narcotics trafficking by the Mongols Motorcycle Club. The bust went down with 160 search warrants and 110 arrest warrants[85]
Canada, especially, has in the late 20th century experienced a significant upsurge in crime involving outlaw motorcycle clubs, most notably in what has been dubbed the Quebec Biker War, which has involved more than 150 murders[86] (plus a young bystander killed by an exploding car bomb), 84 bombings, and 130 cases of arson.[87] The increased violence in Canada has been attributed to turf wars over the illegal drug trafficking business, specifically relating to access to the Port of Montreal,[88] but also as the Hells Angels have sought to obtain control of the street level trade from other rival or independent gangs in various regions of Canada.[89] The Royal Canadian Mounted Police Gazette, quoting from the Provincial Court of Manitoba, defines these groups as: "Any group of motorcycle enthusiasts who have voluntarily made a commitment to band together and abide by their organizations' rigorous rules enforced by violence, who engage in activities that bring them and their club into serious conflict with society and the law".[87]
The Hells Angels sponsors charitable events for Toys for Tots in an attempt to legitimize themselves with public opinion.[90]
Contrary to other criminal organizations, OMGs operate on an individual basis instead of top-down, which is how supporters can claim that only some members are committing crimes. Belonging guarantees each member the option of running criminal activity, using other members as support—the main characteristic of OMGs is "amoral individualism", in contrast to the hierarchical orders and bonds of "amoral familism" of other criminal organizations such as the Mafia.[91] U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) agent William Queen, who infiltrated the Mongols, wrote that what makes a group like them different from the Mafia is that crime and violence are not used as expedients in pursuit of profit, but that the priorities are reversed. Mayhem and lawlessness are inherent in living "The Life" and the money they obtain by illegal means is only wanted as a way to perpetuate that lifestyle.[92]
Recently, authorities have tried tactics aimed at undermining the gang identity and breaking up the membership. But in June 2011 the High Court of Australia overturned a law that outlawed crime-focused motorcycle clubs and required members to avoid contact with one another.[93] In the U.S., a Federal judge rejected a prosecutor's request to seize ownership of the Mongols Motorcycle Club logo and name, saying the government had no right to the trademarks.[94][95] Federal prosecutors had requested, as part of a larger criminal indictment, a court order giving the government ownership of the logo in order to prevent members from wearing the club's colors.[96]
Relationships between outlaw motorcycle clubs
Certain large one-percent MCs have rivalries between each other and will fight over territory and other issues. Sometimes, smaller clubs are forced into or willingly accept supportive roles for a larger one-percent club. They are sometimes required to wear a "support patch" on their vests that shows their affiliation with the dominant regional club. Smaller clubs are often allowed to form with the permission of the dominant regional club. Clubs that resist have been forcibly disbanded by being told to hand over their colors on threat of aggression.[97][98][99]
In Australia[100] and the United States, many MCs have established statewide MC coalitions.[101] These coalitions are composed of MCs who have chapters in the state and the occasional interested third party organization, and hold periodic meetings on neutral ground where representatives from each club meet in closed session to resolve disputes between clubs and discuss issues of common interest. Local coalitions or confederations of clubs have eliminated some of the inter-club rivalries, and together, they have acted to hire legal and PR representation.[101][102]
Support clubs
Larger outlaw motorcycle clubs will often establish localized smaller clubs subservient to the gang. These clubs are called support clubs, satellite clubs, or puppet clubs. They act as auxiliary groups, supporting the larger club by propelling their influence further, acting as recruitment sources, and various other ways in return for protection and bolstering their reputations.[103] Support clubs can also be used to help the principal club facilitate criminal activities.[104]
Regional scenes
Summarize
Perspective
Although the outlaw motorcycle club subculture tends to be associated with the United States, many regional scenes have emerged transcontinentally within countless nations across the globe.[105][106][107]
Europol has reported that there has been steady growth in the membership of outlaw motorcycle clubs worldwide since the year 2005.[108]
Australia
Outlaw motorcycle clubs were reported to have first appeared in Australia during the 1960s.[109] There, they are commonly referred to as "bikie gangs".[110][111][112][113]
There are many outlaw motorcycle clubs in Australia - many of which are homegrown clubs (founded within the country) and have since expanded overseas. However, a good amount of the country's groups are chapters of international one-percenter clubs that originated outside of the Commonwealth of Australia, such as the Hells Angels and the Mongols MC.[114][115]
The year 2007 saw an increase in the country's amount of OMCG chapters.[116] According to the Australian Criminal Intelligence Commission, there are (at least) 38 outlaw motorcycle gangs operating across the nation as of 2020.[117]
Belgium
Outlaw biker clubs first began to appear in Belgium in the 1970s, and the Belgian biker scene continued to be dominated by small local clubs until the 1990s. In 1992, Belgium's Blue Angels club became the first international club in the country when they merged with the Blue Angels of Scotland.[70] The Hells Angels opened its first Belgian chapter in Ghent in 1997.[118] In 1999, the Outlaws formed its first chapter in Belgium through a "patch over" of an Indigenous Outlaws club based in Mechelen.[70][119] The Belgian Federal Police has designated the Bandidos, the Blue Angels, the Hells Angels and the Outlaws as criminal motorcycle gangs.[120]
Canada
Outlaw motorcycle clubs first began to appear in Ontario and Quebec in the early 1950s.[9] In 1978, the Criminal Intelligence Service Canada launched Project Focus, an investigation into motorcycle gangs.[121] By 2002, 26 motorcycle gangs were operating in Canada, the largest and most powerful of which was the Hells Angels.[9] Canadian biker gangs are involved in money laundering, intimidation, assault, attempted murder, murder, fraud, theft, counterfeiting, loan-sharking, extortion, prostitution, escort agencies, strip clubs, and the trafficking of illegal weapons, stolen goods, contraband, and illicit alcohol and cigarettes.[9]
Some of the other major biker organizations (aside from Hells Angels) that have operated in Canada include the following:[122][123][78]
- Bandidos—Founded in the 1960s in Texas, the gang once operated chapters in many cities, including Toronto. However, they currently do not operate in Canada. According to NGIC's 2009 report, the Bandidos are the second-most powerful criminal biker gang, with over 2,000 members in 14 countries.
- Outlaws — First established in 1935 in the U.S., the Outlaws made their way into Canada in 1977 when several chapters of Satan's Choice (in Montreal, Quebec) changed allegiance and decided to set up shop as the Outlaws Motorcycle Club of Canada. The Outlaws are known to detest the Hells Angels.
- Rock Machine — Second only to Hells Angels in Quebec (not Canada). A long-running turf war with the Hells Angels has left hundreds of people dead while the two gangs fought over the territorial drug trade (as narcotics was, and still is, a lucrative black market business). The ongoing war also led to the enactment of anti-gang and anti-organized crime legislation by the federal government, consequentially leading to more severe penalties and harsher sentencing. The Rock Machine expanded into Ontario, where it established three new chapters. In 2001, the organization aligned itself with the Bandidos.
- Satan's Choice — Once one of Ontario's strongest, most cohesive motorcycle gangs, Satan's Choice became part of the Hells Angels during H-A's more significant expansion into Ontario in 2000–2001. Satan's Choice had branches in Keswick, Kitchener, Oshawa, Sudbury, Simcoe County, Thunder Bay, and Toronto, but nothing was outside the province then.
- Para Dice Riders—This group was once among Ontario's strongest biker gangs. Its membership was initially limited to Toronto, Ontario until the Hells Angels absorbed the group in 2001 when the H-A moved into Ontario.
- Last Chance — A small Ontario-based biker gang that agreed to switch over and join up with the Hells Angels when they, the world's most powerful biker gang, decided to move into the province (Ontario).
- Lobos — Originally from and concentrated around the Windsor, Ontario area, the Lobos motorcycle gang decided to take up with the Hells Angels on its offer to merge with them in 2001.
- Loners — The Loners Motorcycle Club was founded in Woodbridge, Ontario, in 1979, and it has a handful of chapters, including a now-defunct chapter in southwestern Ontario. The Loners have at least sixteen (16) chapters in Canada, ten (10) chapters in Italy, nine 9) in the United States, and several chapters in other countries across the world. The club was established by two well-known Italian-Canadian bikers, Frank Lenti and Gennaro Raso. As part of its Ontario expansion, the Hells Angels tried to persuade the St. Thomas, Ontario Loners chapter to merge with them. In Ontario, its highest media profile in recent years was in the infamous legal battle (by the Toronto chapter) involving animal rights and personal property. This 2001 legal court battle was so that the Loners could fight to keep their official mascot, Woody the Lion, on their property, which was located just north of Toronto. The Loners lost the legal battle, and their lion was removed and placed in an animal sanctuary outside of Toronto.[124][123]
- The Lion, nicknamed "Woody", was kept in a tidy 25-metre by 25-metre pen area.[124] He was a club pet from approximately three weeks old named for a biker who died in a motorcycle accident. Woody was confiscated and shipped to a compound near Barrie after the club was charged with violating a King Township bylaw against keeping exotic pets.[124][78] All on account of pre-dawn raids by the York Regional Police and the Ontario Provincial Police (OPP).[124]
- Vagabonds — An Ontario-based motorcycle gang mostly absorbed by the Hells Angels when they expanded into Ontario in 2000–2001.
- The Red Devils — Said to be the oldest motorcycle gang in Canada (the "Original Red Devils," founded in 1948), the group has a few dozen members concentrated in and around the Hamilton, Ontario, area.
Canadian West
The late 1970s and early 1980s were considered to be the "golden age" in Western Canada for independent outlaw motorcycle clubs.[125]
Quebec
Outlaw motorcycle clubs first appeared in the Canadian province of Quebec during the early 1950s.[126] By the year 1968, the province was home to at least 350 of such groups – with most of, if not all, being "home-grown" – rather than having origins outside of Canada (or even Quebec).[127][128][129] Some of the most notable outlaw biker gangs at this time were Satan's Choice Motorcycle Club, Popeye Moto Club, Devil's Disciples Motorcycle Club (unrelated to the American group of the same name), the Gitans, the Atomes, the Missiles MC, and of course, Hells Angels.[123][130][131][132][133][134] The largest, most-feared chapter of Hells Angels was formed in Montreal, Quebec in 1977, when a biker gang called the Popeyes joined up the Hells Angels.[123] After the Rock Machine emerged in 1986, they quickly became the number one rival of the Hells Angels, and a full-blown turf war between the two biker gangs erupted in the 1990s; unfortunately, claiming more than 150 individual lives, including two (2) prison guards and an innocent 11-year-old boy named Daniel Desrochers, who died several days after a planted car bomb exploded and a piece of shrapnel penetrated his head.[123][122]
Throughout the 1990s, the province of Quebec witnessed violent confrontations between rivaling outlaw biker gangs with activities that ranged from homicides to bombings.[135] Such violence and brutality was a decade-long conflict between the Hells Angels and the Rock Machine, better known as the "1994 Biker Wars."[122] The Quebec Biker Wars officially began on 13 July 1994, when three (3) masked-men shot and killed Pierre D'aoust (member of a Hells Angels-affiliated club called the Death Riders) at a motorcycle shop in Montreal.[122] This ongoing feud largely stemmed over territory and the narcotics trade in Quebec, while also being fueled further by long-standing rivalries, deep-seated hatred and animosities between major players in the Quebec criminal underworld at that time.[122] To provide a general idea of the criminal underworld involvement, it's essential to recall that the Hells Angels in Quebec at that time (i.e., 1994) were backed by Vito Rizzuto (of the Montreal Mafia), while the Rock Machine were affiliated with the criminal coalition known as the Alliance Against the Angels (otherwise known as the Dark Circle).[122] The two central figures in the 1994 conflict were the leaders of the two warring gangs (Hells Angels and the Rock Machine): Maurice "Mom" Boucher (leader of Quebec's Hells Angels); and Salvatore Cazzetta (leader of the Rock Machine).[122] The extreme levels of violence, assassinations, bombings, arson attacks, fly-by-fire attacks eventually led to the creation and passing of both Bill C-95 in 1997 and Bill C-24 in 2001 – setting forth harsher punishments and penalties for members of gangs and organized crime groups.[122]
Over the next several weeks, the violence reached a peak. In one week in September 1995, there was an assassination in a parking lot; bombings at a strip club, a bar, and the mansion of an organized crime figure; arson attacks on a pawn shop, tanning salon, and a used-car lot; and a friendly-fire incident where bikers accidentally killed three members of their club.
The Hells Angels (or "H-A" as they're often referred to) were, and continue to be, one of the more prominent biker gangs still in existence today in Quebec and other regions of Canada – having at least 34 different chapters across the country in April 2009.[123]
Germany
American military personnel stationed there established the first outlaw biker clubs in Germany, including the Bones MC, founded in 1968, and the Ghost Riders MC, formed in 1972.[70]
Indonesia
Outlaw motorcycle clubs began developing rapidly in Indonesia in the 1990s, although some of the country's homegrown groups are said to have existed as early as the 1970s.[136] The presence of biker gangs in Indonesia has received national media attention.[137]
Large international outlaw biker groups which have expanded into Indonesia include the Hells Angels Motorcycle Club, Eight Demons Motorcycle Club,Finks Motorcycle Club, Satudarah Motorcycle Club, Rebels Motorcycle Club, Rock Machine Motorcycle Club, and the Diablos Motorcycle Club.
Netherlands
Outlaw motorcycle clubs have been present in the Netherlands since the 1970s.[138] In 1978, the Hells Angels absorbed the Kreidler Ploeg Oost biker club in Amsterdam.[70]
The most prominent Dutch club is Satudarah MC. Following the group's initial foundation in Moordrecht, they've since expanded into 44 chapters nationwide and have branched internationally within at least 20 countries. Another notable one of these groups that came out of the Netherlands is No Surrender Motorcycle Club. While not as large as Saturdarah, they have managed to set up branches overseas with an approximate total of more than one thousand members in roughly 19 nations across the globe.
Due to the notable presence of biker gangs in the Netherlands, alongside their tendency to be involved in criminal activity, certain one-percenter groups have been subject to nationwide prohibition by the Judiciary of the Netherlands.[139]
New Zealand
New Zealand has a relatively large outlaw motorcycle club scene that has gained significant national and international media attention over the years.[140]
Biker gang violence is viewed as a growing problem within the country.[141]
Scandinavia
Sweden
The outlaw motorcycle club movement of Scandinavia and the Nordic countries started in Sweden after numerous groups were established throughout the country during the late 1960s and early 1970s.[142]
The American one-percenter biker scene greatly influenced Sweden's variation of the subculture.[142]
Thailand
The Kingdom of Thailand, along with many other parts of South-East Asia, have chapters of some of the most prominent international outlaw motorcycle clubs in the world including the Rebels Motorcycle Club, the Mongols Motorcycle Club, and the Outlaws Motorcycle Club.[143][144] Additionally, the Comanchero Motorcycle Club, Gremium Motorcycle Club, Satudarah Motorcycle Club, No Surrender Motorcycle Club, and the Hells Angels Motorcycle Club all have chapters in Thailand.[145][146][147]
One notable outlaw motorcycle club to have been founded in Thailand is the Diablos Motorcycle Club. They are a support club for the larger Bandidos Motorcycle Club, which also has chapters within the country.
United Kingdom
The outlaw biker scene in the U.K. began as early as the 1960s and has four main independent clubs, the Blue Angels MC, Road Rats MC, Commitatus MC, and the Satans Slaves MC (unrelated to the New Zealand-based MC of the same name).[148][149]
United States
The outlaw biker subculture emerged in the United States in the late 1940s, as disenfranchised service members returned from World War II and founded motorcycle clubs to replicate the camaraderie and psychological stimulation they had experienced in the war.[9] Early biker clubs established by World War II veterans included the Boozefighters, the Hells Angels, the Market Street Commandos and the Pissed Off Bastards of Bloomington.[150] Various other clubs, such as the Bandidos, the Sons of Silence and the Warlocks, were later formed by Vietnam veterans.[151]
According to the U.S. Department of Justice, approximately 500 motorcycle gangs were operating in the United States in 1991, with a combined membership of several thousand.[152] These gangs range in levels of criminal sophistication, from groups of thugs to well-organized criminal networks.[153] A government survey published in 1990 found that outlaw motorcycle gangs control 40% of the traffic of dangerous drugs in the U.S., including three-quarters of the methamphetamine trade. A subsequent study concluded that outlaw motorcycle gangs control or are heavily involved in the sale of meth in 38 states.[152]
East Coast
The drug trade is the primary source of income for motorcycle gangs, and the bikers on the East Coast deal primarily in cocaine. Outlaw biker clubs also control approximately 70–80% of the methamphetamine market in New York City and Albany, New York, however. Motorcycle gangs are also more heavily involved in prostitution on the East Coast than on the West; women operate the streets and out of gang-owned massage parlors and escort services. Eastern U.S. biker gangs use bodyguard services, horse ranches, vending machine companies, lawn services, and real estate to launder money.[152]
Midwest
Cocaine is the drug most commonly distributed by biker gangs in the Midwest. Motorcycle gangs in the central U.S. launder money via beauty shops, towing companies, construction companies, horse ranches, and real estate.[152]
Detroit has had an affluent presence of outlaw motorcycle clubs since the 1960s.[154][155][156][157] Some of the most notable clubs to have come out of the city of Detroit include the Forbidden Wheels Motorcycle Club, Highwaymen Motorcycle Club,[158][159] Outcast Motorcycle Club,[160] Satan's Sidekicks Motorcycle Club,[161] and Scorpions Motorcycle Club.[162]
West Coast

In post–World War II California, four motorcycle clubs—the Market Street Commandos, the Boozefighters, the Galloping Gooses, and the Pissed Off Bastards of Bloomington—became prominent. Such clubs first came to the attention of state and federal authorities following the Hollister riot of July 1947.[163] As of 2008, there are approximately 60 outlaw motorcycle gangs active in California, with a combined membership of around 2,000.[153]
Motorcycle gangs in the Western U.S. deal primarily in methamphetamine. As a result of stringent laws regarding the sale of precursor chemicals and the formation of task forces to target clandestine labs in California, many methamphetamine manufacturers from the state relocated to the Pacific Northwest, where the rugged terrain and sparse population of rural Oregon and Washington made ideal conditions for clandestine meth labs. According to a 1989 report by the Western States Information Network (SWIN), 11% of drug labs seized had outlaw motorcycle gang paraphernalia present at the site. Motorcycle gangs in the western U.S. launder money through interior decorating businesses, construction companies, locksmiths, pizza parlors, jewelry businesses, and real estate.[152]
Cultural influence
Summarize
Perspective
Outlaw motorcyclists and their clubs have been frequently portrayed and parodied in movies and the media generally, giving rise to an "outlaw biker film" genre.[164] It generally exists as a negative stereotype in the public's subconscious[165] and yet has inspired fashion trends[166][167][168] for both males and, as "biker babes", for females.[169][170][171] The appearance has even been exploited by the fashion industry, bringing it into legal conflict with some clubs[172] and simultaneously encouraging a cultural specific fetishistic look that conveys sex, danger, rebelliousness, masculinity, and working class values.[173]
The biker style has influenced the look of other sub-cultures such as punk,[173] heavy metal,[174] leather subculture[175] and cybergoth fashion,[176] and, initially an American subculture, has had an international influence.[177] Bikers, their clothing, and motorcycles have become cultural icons[178][179] of mythic status, their portrayal generally exaggerates a criminal or deviant association exploited by the media for personal financial interests.[180]
In popular culture
Literature
- Winterhalder, Edward; De Clercq, Wil (2008), The Assimilation: Rock Machine Become Bandidos – Bikers United Against the Hells Angels, ECW Press, ISBN 978-1-55022-824-3
- Winterhalder, Edward (2006), Out in Bad Standings: Inside the Bandidos Motorcycle Club - the Making of a Worldwide Dynasty, Blockhead City Press, ISBN 0-9771747-0-0
- Brigands M.C. (2009), the eleventh novel in the teenage spy series CHERUB by Robert Muchamore, sees the protagonists attempt to take down the eponymous biker club.
- The outlaw biker film genre took off in the mid-1960s, after the Hells Angels club became prominent in the media,[181] in particular, after Hunter S. Thompson's book Hell's Angels: The Strange and Terrible Saga of the Outlaw Motorcycle Gangs (1966) was published.
Television
- The mini-series The Last Chapter (2002) was set in Toronto and Montreal and portrayed a fictional feud reminiscent of the Quebec Biker War in which The Triple Sixers MC attempted to establish a chapter in the province of Ontario.[182] This show predated Sons of Anarchy by six years.
- Sons of Anarchy portrays a fictional outlaw motorcycle club, founded mainly by Vietnam War veterans, which is involved in various criminal activity and associated with underworld gangs. The show's creator thought it was too obvious to have them be methamphetamine dealers, and so instead, they traffic illegal guns.[183][184]
- True Detective season one portrays an antagonistic outlaw biker club located in Galveston, Texas called the Iron Crusaders. Homicide Detective Rust Cohle infiltrates the club as his former undercover alias "Crash" and joins some of its members on a failed home invasion to elicit information on their methamphetamine cook who is believed to have ties to serial murders in Louisiana.[185]
- Bikie Wars: Brothers in Arms: The six-episode series dramatises the story of the Milperra massacre, when the Bandidos and the Comanchero motorcycle clubs went to war on Father's Day, Sunday 2 September 1984. The massacre had its beginnings after a group of Comancheros broke away and formed the first Bandidos Motorcycle Club chapter in Australia. This resulted in intense rivalry between the two chapters. At a public swap meet at the Viking Tavern at Milperra, New South Wales, a brief but violent battle ensued with seven people shot dead, including a 14-year-old innocent female bystander. A further 28 people were wounded, with 20 requiring hospitalisation.[27] Each episode starts with a quote stated by Justice Adrian Roden when the clubs went before the New South Wales Supreme Court; "As patriotism can lead to jingoism and mateship can lead to cronyism, so bikie club loyalty can lead to bikie club war."
- Gangland Undercover is an American dramatized series inspired by the true story of police informant Charles Falco, who infiltrated several bike clubs in the United States in the early 2000s.
- Mayans M.C. is a spin-off of Sons of Anarchy centered around the Sons' rivals turned allies, the predominantly Mexican Mayans Motorcycle Club.
- The plot of the Danish-language miniseries Warrior revolves around a fictional biker gang in Copenhagen known as the Wolves MC.[186][187]
- The German-language TV show, Dogs of Berlin, features a fictional Muslim outlaw motorcycle club known as the Death Daggers MC.[188][189][190]
- The TV series Bad Blood features a fictional French-Canadian biker gang known as the Devil's Kings MC as a participant in Montreal's drug trade.[191][192]
- In Season 11, Episode 9 of Law & Order: Special Victims Unit features a New York-based outlaw motorcycle gang known as the Death Knights who reputably engage in contract killing as well as prostitution. The plot of the episode is centered around the murder of one of the club's members.[193][194]
- Several TV series set in the Marvel Cinematic Universe feature a fictional outlaw motorcycle gang called the Dogs of Hell, who engage in various criminal activities, including theft, drug trafficking, and murder. In the episode "Yes Men" of Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D., members of the gang are enthralled by the Asgardian Lorelai as her army. In the Marvel/Netflix series Daredevil and The Punisher, the Hell's Kitchen, New York chapter of the gang is targeted for extermination by Frank Castle during his vigilante campaign against his family's killers, and are fought by both Castle and Matt Murdock/Daredevil.
Video games
- The 2008 action-adventure game Grand Theft Auto IV and its episodic content feature two warring outlaw motorcycle clubs: the Lost and the Angels of Death. The former serve as the main focus of the first story expansion, Grand Theft Auto IV: The Lost and Damned, which follows the efforts of the club's vice-president (later president), Johnny Klebitz, to keep the gang afloat when they are faced with various problems, such as the war with the Angels and a conflict with the Mafia. The Lost return as minor antagonists in Grand Theft Auto V, where they become caught in a war with one of the protagonists, Trevor Philips, which ends with heavy losses for the gang. The club is also featured as antagonists in Grand Theft Auto Online, where many missions involve the player stealing the Lost's product or killing their members. An outlaw biker-themed update for the game, entitled GTA Online: Bikers, was released on 4 October 2016 and introduced various biker-themed weapons, clothing, and vehicles, as well as the ability for players to join or start motorcycle clubs and run illicit businesses, such as counterfeit cash factories and cocaine lockups.[195]
- The critically panned 2013 videogame Ride to Hell: Retribution tells the story of a one-percenter who seeks revenge for his brother's death, caused by the bosses of rival gangs.[196]
- Days Gone is a 2019 post-apocalyptic survival game set in Oregon where the protagonist, Deacon St. John, and his friend William "Boozer" Gray, are former members of an outlaw motorcycle club known as the Mongrels. They still wear their club's colors.[197]
See also
Notes
- In March 1972 (p. 3), Chas Deane, the editor of Motorcycle Mechanics, wrote: "Motorcycling is a way of life, almost a religion to some and the next best thing to breathing for others. There is no such thing as a 'typical motorcyclist'; on the one hand we're outcasts and 'one percenters', while on the other hand we are the 'in' people."
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
