Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
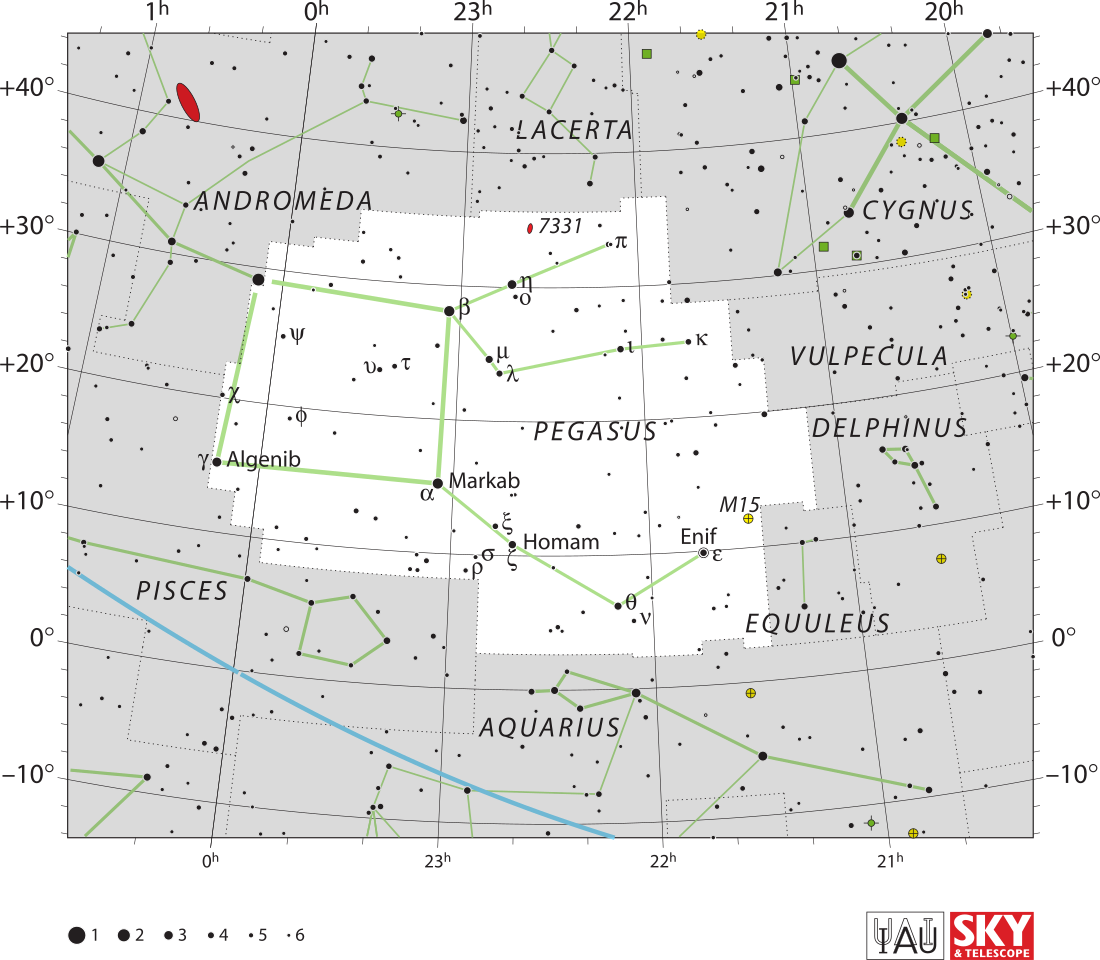
Theta Pegasi
Single star in the constellation Pegasus From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
θ Pegasi, Latinized as Theta Pegasi, is a binary star in the equatorial constellation of Pegasus, lying about 7.5 degrees southwest of Enif.[8] It has the traditional name Biham /ˈbaɪ.æm/,[9][10] and the Flamsteed designation 26 Pegasi. This object is visible to the naked eye as a white-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.52.[2] The system is located 92 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −8 km/s.[2]
This object is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A2V.[4] It is 448[6] million years old with a high rate of spin, with a projected rotational velocity of 136 km/s.[6] This star has 2.09[5] times the mass of the Sun and 2.6[11] times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 25 times the luminosity of the Sun from its outer envelope at an effective temperature of 7,951 K.[11] The star appears to display a slight infrared excess.[12]
θ Pegasi was suspected of being a binary star due to an acceleration detected by Hipparcos. In 2021, a low-mass companion star was discovered, associated with θ Pegasi.[5] It is a red dwarf with a spectral type of M4 to M5.5, and a luminosity of 0.5% that of the Sun.[5] The orbit around the primary is estimated to be moderately eccentric, at 0.54, and has a semimajor axis of 6.55 au.[5]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
θ Pegasi (Latinised to Theta Pegasi) is the star's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name Biham or Baham from the Arabic phrase s'ad al Biham "Lucky Stars of the Young Beasts".[13] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[14] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Biham for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so entered in the IAU Catalog of Star Names.[10]
In Chinese, 危宿 (Wēi Sù), meaning Rooftop, refers to an asterism consisting of Theta Pegasi, Alpha Aquarii and Epsilon Pegasi.[15] Consequently, the Chinese name for Theta Pegasi itself is 危宿二 (Wēi Sù èr, English: the Second Star of Rooftop.)[16]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads