Bavarian Ludwig Railway
First steam-hauled railway in Germany (commenced service 1835) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
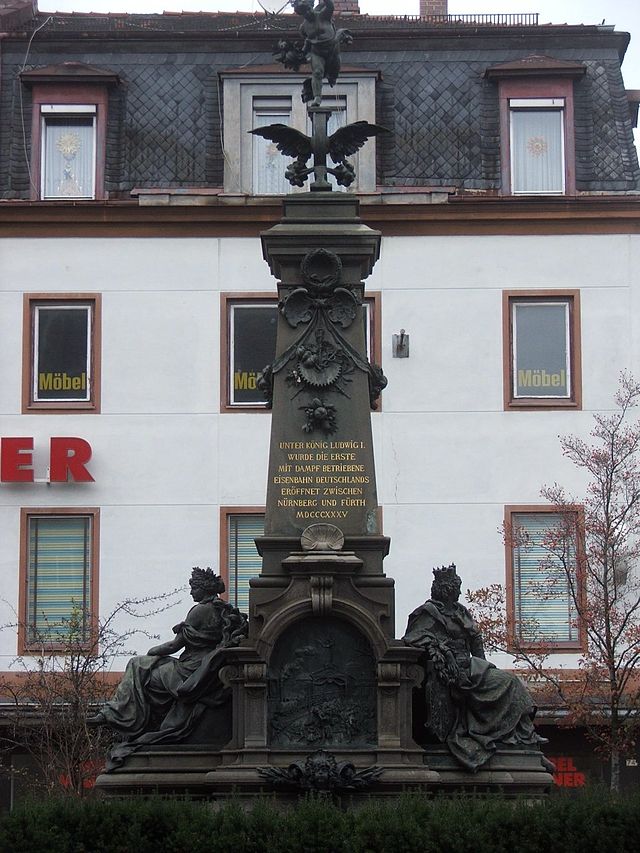
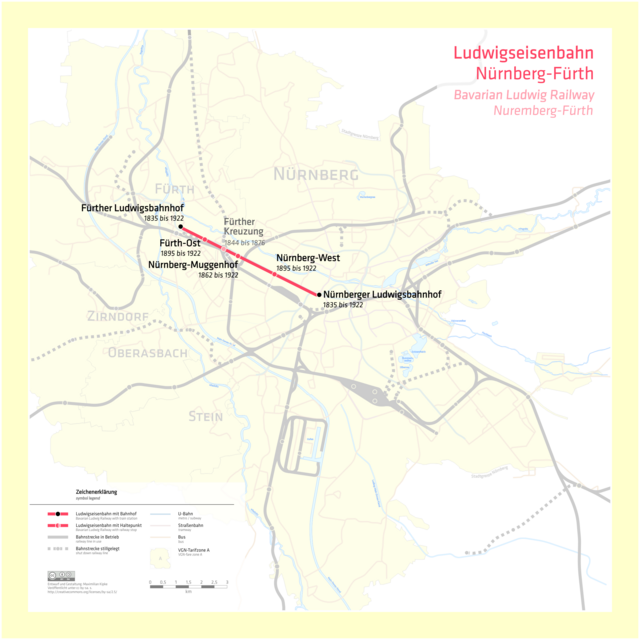
The Bavarian Ludwig Railway (Bayerische Ludwigseisenbahn or Ludwigsbahn) was the first steam-hauled railway opened in Germany. The Königlich privilegierte Ludwigs-Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft ("Royal Privileged Ludwig Railway Company", later called the Ludwigs-Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft) received a concession to build a railway from Nuremberg to Fürth (6 km) in the state of Bavaria on 19 February 1834.





Background
The first reports from England over the planning of railways attracted great attention in Germany, particularly in Bavaria, where the road between the important commercial cities of Nuremberg and Fürth was the busiest road connection in the kingdom. Bavarian interest was also stimulated by Friedrich List’s advocacy of an all-German railway system and the reports of Joseph von Baader, whom King Ludwig had sent to England to study railways. After a discussion of this topic in the Bavarian parliament in 1825, it authorised the king to build an experimental railway in the Nymphenburg Palace park. As the king’s 1828 request for Franconian merchants to begin building a railway line led to no action, he turned his attention to his favourite project, the building of the Ludwig Canal between the Danube and the Main.
Establishment
Summarize
Perspective
After railways had been operating in England for a few years, local businesspeople decided to build a railway line along the Nürnberg-Fürth road. On 14 May 1833 they founded the Gesellschaft zur Errichtung einer Eisenbahn mit Dampffahrt zwischen Nürnberg und Fürth ("company for the establishment of a steam railway between Nuremberg and Fürth") to develop the railway. Within six months the two main instigators from Nuremberg, the merchant and market chief, George Zacharias Platner, and the head of the poly-technical school, Johannes Scharrer, had successfully raised the planned share capital of 132,000 guilders. The proposed dividend of 122⁄3% was met with skepticism, although the company did, in fact, pay a dividend of 20% in 1836.
King Ludwig was an unenthusiastic supporter of railways because of his preference for building the Ludwig Canal between the Main and the Danube; this was actually built between 1836 and 1846. The canal was relatively unsuccessful because of its profusion of locks, its narrowness and early competition from railways, but it foreshadowed the more successful Rhine-Main-Danube Canal built on a similar route and completed in 1992. Ludwig allowed the railway company to use his name and authorized his government to buy a token two shares in it. Significantly for the construction of the railway, the king made available the Bavarian road builder, Paul Camille von Denis, for the railway construction. Von Denis adopted the English rail gauge of 1435 mm for the nearly dead-straight 6.04 km-long single-track line next to the Fürth-Nuremberg road.
Start of services
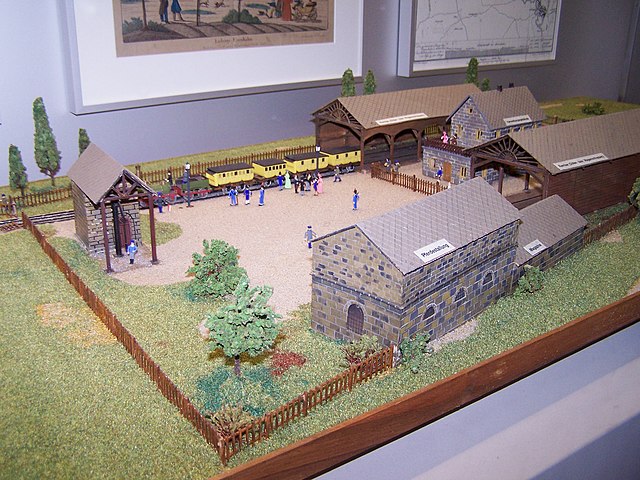
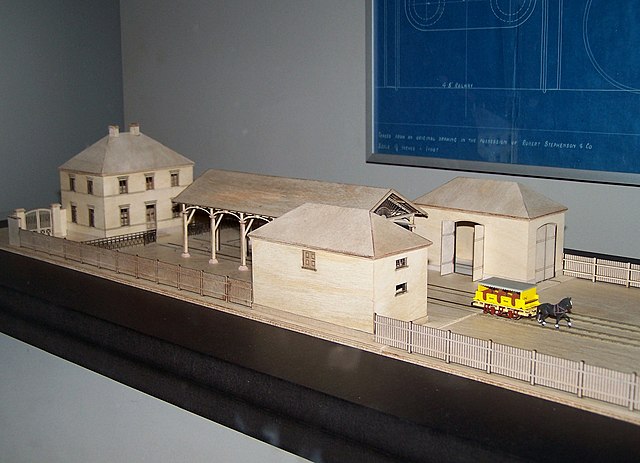
On 7 December 1835 the company opened the first German steam-powered railway line for passenger and freight traffic before a large public gathering. The steam locomotive Adler ("eagle") had been supplied with its driver by Stephenson’s company from Newcastle. The Remy & Co aus Rasselstein company of Neuwied, supplied only the 15-foot (4.6 m)-long rails of rolled wrought iron. The carriages were supplied by local wagon-builders.
On 20 September 1831 the private narrow gauge, horse-drawn Prince William Railway coal railway had opened between Hinsbeck (Ruhr) and Nierenhof, but it did not excite the public attention of a steam-hauled and passenger railway. Nevertheless, King Ludwig did not visit the railway named after him until August 1836. The cost of building the railway, which had been estimated at 132,000 guilders, actually reached 170,000 guilders as a result of lack of railway building experience and, in particular, the high price of land acquisition in the absence of a law providing for compulsory purchase.
Operations
Beginning on 8 December 1835 a horse-drawn service operated on the line from Nuremberg to Fürth once an hour. The Adler only operated at 13:00 and 14:00 daily. The high cost of importing hard coal from Saxony, which in the beginning still had to be brought by horse cart, prevented in the early years regular use of the Adler or the Pfeil ("arrow"). With the acquisition of more locomotives, only the early and late services were horse-drawn. Finally in 1863 horse operations were abandoned to reduce maintenance costs (especially the provision of horse tracks) and to raise speeds.
Goods traffic at first consisted of the carriage of newspapers and beer. General freight traffic only started in 1839 and mail traffic in 1840. The success of the line is shown by the fact that up to 1855 dividends were never less than 12%. At the time this was considered a magnificent capital return. Nevertheless, the government refused permission to extend the line to Würzburg.
Closure
Competition developed with the building of horse trams between Nuremberg and Fürth, particularly once they were electrified in 1898. From 1893, part of the line was double-tracked but this was never completed. Traffic and profits fell constantly.
The Ludwigsbahn closed on 31 October 1922. The old station building in Fürth was torn down in 1938, to make room for a Nazi Party parade ground, now a plaza called Fürther Freiheit ("Fürth Liberty"). The Nuremberg station was demolished in 1952 to allow the construction of a new multi-storey building.
After its closures, the line was leased to the Nuremberg tramways. A high-speed tram service operated on the Ludwigsbahn's right of way from 1927 until 1981. It was then replaced by the line U1 of the Nuremberg U-Bahn along the route, running partly underground and partly elevated. This was opened to Fürth station on 5 December 1985, 150 years after the opening of the original line.
The line ran from the Nuremberg station in Plärrer place, along today's Fürther Straße, past the boundary with Fürth and then followed the present Hornschuchpromenade to the Ludwig station at Fürther Freiheit, 100 metres north of Fürth station.
Locomotives and carriages
Summarize
Perspective
The Ludwigsbahn possessed many locomotives during its 87 years of operation. Some were bought second-hand, many were sold when it was closed.
| Name | Design | Manufacturer | Acquired | Disposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adler | 1A1 | Stephenson 1835 | 1835 | sold 1857 |
| Pfeil | 1A1 | Stephenson 1836 | 1836 | sold |
| Nürnberg-Fürth | 1A1 | Henschel 1852/14 | 1852 | scrapped 1889 |
| Phoenix | 1A1 | Maffei 1853/127 | 1853 | scrapped 1869 |
| Adler II | 1A1 | Maffei 1857/279 | 1857 | scrapped 1889 |
| Johannes Scharrer | 1A1 | Henschel 1865/108 | 1865 | scrapped 1887 |
| Faust | 1A1 | Maffei 1845/6 | 1872 | scrapped 1881 |
| Henlein | 1A1 | Maffei 1845/8 | 1873 | scrapped 1880 |
| Wallenstein | 1A1 | Kessler 1845/30 | 1875 | scrapped 1885 |
| Bavaria | Bn2t | Maffei 1879/1204 | 1879 | sold 1923 |
| Pegnitz | Bn2t | Maffei 1880/1224 | 1880 | sold 1923 |
| Franconia | Bn2t | Maffei 1881/1248 | 1881 | sold 1923 |
| Daniel Ley | 1Bn2t | Maffei 1886/1414 | 1886 | sold 1923 |
| Johannes Scharrer II | Bn2t | Maffei 1887/1453 | 1887 | sold 1923 |
| Nürnberg-Fürth II | Bn2t | Maffei 1889/1538 | 1889 | sold 1923 |
| Germania | 1Bn2t | Maffei 1906/2511 | 1906 | sold 1923 |
| Ludwig | 1Bn2t | Maffei 1906/2549 | 1906 | sold 1923 |
In 1935 a replica of the Adler was constructed on old plans for the 100-year anniversary of the German railways, but it was seriously damaged on 17 October 2005 together with many other preserved locomotives in the great fire at the Nuremberg shed. However it was painstakingly restored in 2007 at a cost of € 1M and made operational again. The greatest number of carriages during the line's existence was in 1893: 44 coaches, 1 luggage van and 10 wagons.
Sources
- Klee, Wolfgang, Bayerische Eisenbahngeschichte, Part 1: 1835–1875 in Bayern-Report, Fürstenfeldbruck, 1993. (in German)
- Wolff, Gerd, Deutsche Klein- und Privatbahnen, Part 6, Bayern, Gifhorn, 1978. (in German)
- Deutsche Reichsbahn, Die Deutschen Eisenbahnen in ihrer Entwicklung 1835–1935, Berlin, 1935. (in German)
- DB Museum, Geschichte der Eisenbahn in Deutschland, Volume 1: Ein Jahrhundert unter Dampf, Die Eisenbahn in Deutschland 1835 – 1919, Nürnberg, 2005 (in German)
See also
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
