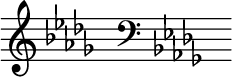Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
B-flat minor
Minor scale based on B-flat From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
B-flat minor is a minor scale based on B♭, consisting of the pitches B♭, C, D♭, E♭, F, G♭, and A♭. Its key signature has five flats. Its relative major is D-flat major and its parallel major is B-flat major. Its enharmonic equivalent, A-sharp minor, which would contain seven sharps, is not normally used.
The B-flat natural minor scale is:

Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The B-flat harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are:


Remove ads
Scale degree chords
The scale degree chords of B-flat minor are:
- Tonic – B-flat minor
- Supertonic – C diminished
- Mediant – D-flat major
- Subdominant – E-flat minor
- Dominant – F minor
- Submediant – G-flat major
- Subtonic – A-flat major
Characteristics
B-flat minor is traditionally a 'dark' key.[1]
The old valveless horn was barely capable of playing in B-flat minor: the only example found in 18th-century music is a modulation that occurs in the first minuet of Franz Krommer's Concertino in D major, Op. 80.[2]
Notable classical compositions
- Charles-Valentin Alkan
- Prelude Op. 31, No. 12 (Le temps qui n'est plus)
- Symphony for Solo Piano, 3rd movement: Menuet
- Samuel Barber
- Frédéric Chopin
- Franz Liszt
- Transcendental Étude No. 12 (Chasse-neige) from Transcendental Études
- Sergei Rachmaninoff
- Piano Sonata No. 2, Op. 36
- Dmitri Shostakovich
- Symphony No. 13, Op. 113 ("Babi Yar")
- String Quartet No. 13, Op. 138
- Richard Strauss
- An Alpine Symphony begins and ends in B-flat minor.
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
- William Walton
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads