Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
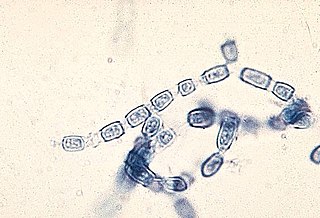
Arthroconidium
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Arthroconidia are a type of fungal spore typically produced by segmentation of pre-existing fungal hyphae.
Background
These spores are asexual and are generally not as durable and environmentally persistent as, for instance, bacterial endospores or chlamydospores. Some medically significant pathogens, such as Coccidioides immitis, and Coccidioides posadasii, both causative agents of coccidioidomycosis (also known as San Joaquin Valley fever), are transmitted through airborne arthroconidia.[1] Additionally, some pathogenic yeasts, such as Geotrichum and Trichosporon, also reproduce asexually via arthroconidia. The small size of the arthroconidia, 3 to 5 μm, allow them to lodge themselves into the terminal bronchioles of the lung. There, they develop into a thick-walled spherule filled with endospores that cause a pyogenic (pus-causing) inflammation.[2]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
